Oxidative Metabolism - Plant Energy Biology
... Lst8p is an integral component of Tor1 and 2 complexes Acts as a positive regulator in these complexes Details not yet clear on interaction of TOR and RTG pathway but thought to be indirect as RTG response ...
... Lst8p is an integral component of Tor1 and 2 complexes Acts as a positive regulator in these complexes Details not yet clear on interaction of TOR and RTG pathway but thought to be indirect as RTG response ...
siRNA expression vector pRNAT-H1
... This vector with attB1 and attB2 sequences flanking the gene of interest is compatible with Invitrogen Gateway Technology and can be used to move DNA sequence (any genes) into multiple vector systems for ...
... This vector with attB1 and attB2 sequences flanking the gene of interest is compatible with Invitrogen Gateway Technology and can be used to move DNA sequence (any genes) into multiple vector systems for ...
A new avenue for combating the deterioration in blood stem cells
... “When we reduce the levels of the MCM3 gene in the entire organism, we observe that replication stress especially affects the stem cells that give rise to the other blood cells and, in ...
... “When we reduce the levels of the MCM3 gene in the entire organism, we observe that replication stress especially affects the stem cells that give rise to the other blood cells and, in ...
1. What is epigenesis?
... the appearance of organisms with new structures that ancestors did not have – like amphibians with feet evolving from fish that lack feet, and birds with wings evolving from reptiles without wings. Embryologically, we see similar patterns, where complex structures are produced from simpler stages th ...
... the appearance of organisms with new structures that ancestors did not have – like amphibians with feet evolving from fish that lack feet, and birds with wings evolving from reptiles without wings. Embryologically, we see similar patterns, where complex structures are produced from simpler stages th ...
Stable Nuclear Transformation of the diatom Phaeodactylum
... transformation, a new door is open that allows diatoms to be mass produced in a laboratory making it more accessible for both researchers and commercial users. The commercial uses includes feeds in aquaculture, sources of specialty oil, and even potential sources in the pharmaceutical drug ...
... transformation, a new door is open that allows diatoms to be mass produced in a laboratory making it more accessible for both researchers and commercial users. The commercial uses includes feeds in aquaculture, sources of specialty oil, and even potential sources in the pharmaceutical drug ...
carcinogenesis: the molecular basis of cancer
... • Mutation may be acquired by the action of environmental agents, such as chemicals, radiation, or viruses, or it may be inherited in the germ line. • The genetic hypothesis of cancer implies that a tumor mass results from the clonal expansion of a single progenitor cell that has incurred genetic da ...
... • Mutation may be acquired by the action of environmental agents, such as chemicals, radiation, or viruses, or it may be inherited in the germ line. • The genetic hypothesis of cancer implies that a tumor mass results from the clonal expansion of a single progenitor cell that has incurred genetic da ...
Molecular classification of cutaneous malignant melanoma by gene
... • The similarity matrix is updated with this new node replacing the two joined elements, and the process is repeated n-1 times until only a single element remains. ...
... • The similarity matrix is updated with this new node replacing the two joined elements, and the process is repeated n-1 times until only a single element remains. ...
slides available - The National Academies of Sciences, Engineering
... associated with a guide RNA that docks the nuclease to a target gene through base complementarity. The base sequence of the guide RNA can be freely chosen, therefore the nuclease can be targeted to any target gene in the genome. ...
... associated with a guide RNA that docks the nuclease to a target gene through base complementarity. The base sequence of the guide RNA can be freely chosen, therefore the nuclease can be targeted to any target gene in the genome. ...
Virology study guide for mid
... 3. c. Direct introduction or translocation of viral genomes into the cytoplasm through channels in the plasma membrane e.g. non-enveloped viruses(Picornavirus). 4. Uncoating means:- the process where by the viral genome is released in a form suitable for transcription. Examples: 5. replication of DN ...
... 3. c. Direct introduction or translocation of viral genomes into the cytoplasm through channels in the plasma membrane e.g. non-enveloped viruses(Picornavirus). 4. Uncoating means:- the process where by the viral genome is released in a form suitable for transcription. Examples: 5. replication of DN ...
DNA Technology
... We all begin life from a single celled zygote with a full compliment of 46 chromosomes. Yet, through development and mitosis, cells become specialized in structure and function. Genes that code for digestive enzymes are only active in digestive cells, but that gene is still located in all of your ce ...
... We all begin life from a single celled zygote with a full compliment of 46 chromosomes. Yet, through development and mitosis, cells become specialized in structure and function. Genes that code for digestive enzymes are only active in digestive cells, but that gene is still located in all of your ce ...
rna viruses
... and directs the host cell to make viral particles. Therefore viral replication primarily depends upon DNA, RNA and protein synthesis of the host cells. Consequently, many chemicals that inhibit viral replication also inhibit some host cell function and produce toxic effects. Another problem po ...
... and directs the host cell to make viral particles. Therefore viral replication primarily depends upon DNA, RNA and protein synthesis of the host cells. Consequently, many chemicals that inhibit viral replication also inhibit some host cell function and produce toxic effects. Another problem po ...
Overview of Viruses - Food Science and Human Nutrition
... 2. Uncoating: all virions must be uncoated for gene expression to occur – Can happen before or after virus enters the cell ...
... 2. Uncoating: all virions must be uncoated for gene expression to occur – Can happen before or after virus enters the cell ...
Introduction Biotechnology Recombinant DNA Genetic Engineering
... Amino-acid sequence detection via hybridization with probes o Reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction cDNA synthesis from mRNA present at time of interest during metabolic pathway / developmental stages PRC amplification using gene specific primers Gel electrophoresis indicates prese ...
... Amino-acid sequence detection via hybridization with probes o Reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction cDNA synthesis from mRNA present at time of interest during metabolic pathway / developmental stages PRC amplification using gene specific primers Gel electrophoresis indicates prese ...
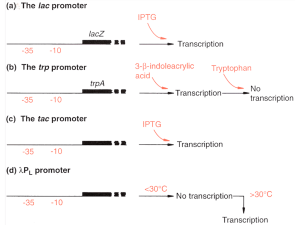
Functional Integrals for the Parallel and Eigen Models of
... Mutations during replication (Eigen model) Rate of 10-5 per base per replication for viruses Mutations without cell division (parallel model) Occurs in bacteria under stress Rate not well characterized ...
... Mutations during replication (Eigen model) Rate of 10-5 per base per replication for viruses Mutations without cell division (parallel model) Occurs in bacteria under stress Rate not well characterized ...
„Creation of a Bacterial Cell Controlled by a Chemically Synthesized
... For the final step of the assembly, µg-quantities of the 100kb intermediates were isolated by alkaline-lysis. For further purification they were treated with exonucleases and passed through an anion-exchange column. For further analysis a small amount of the total plasmid was digested with Not I. Th ...
... For the final step of the assembly, µg-quantities of the 100kb intermediates were isolated by alkaline-lysis. For further purification they were treated with exonucleases and passed through an anion-exchange column. For further analysis a small amount of the total plasmid was digested with Not I. Th ...
BTY328: Viruses
... processes (viral DNA can only be replicated in the nucleus during the S-phase of the cell cycle, when the cell replicates its own DNA). ...
... processes (viral DNA can only be replicated in the nucleus during the S-phase of the cell cycle, when the cell replicates its own DNA). ...
on February 28, 2008 Downloaded from www.sciencemag.org
... homology among ZFPJS, ttk, Br-c, PLZF, and BCL-6 also share homology with viral proteins (for example, VA55R) of the poxvirus family (23) as well as with the Drosophila kelch protein involved in nurse celloocyte interaction (24). These structural homologies suggest that BCL-6 may function as a DNA b ...
... homology among ZFPJS, ttk, Br-c, PLZF, and BCL-6 also share homology with viral proteins (for example, VA55R) of the poxvirus family (23) as well as with the Drosophila kelch protein involved in nurse celloocyte interaction (24). These structural homologies suggest that BCL-6 may function as a DNA b ...
Chapter 20 Notes: DNA Technology
... complementary strands of nucleic acid base pair to one another to form a duplex. If two strands of nucleic acid are not complementary, they will not hybridize to form a duplex. Gene knockouts are experiments in which a gene is deleted from the genome of an organism. Knockouts are used to gain inform ...
... complementary strands of nucleic acid base pair to one another to form a duplex. If two strands of nucleic acid are not complementary, they will not hybridize to form a duplex. Gene knockouts are experiments in which a gene is deleted from the genome of an organism. Knockouts are used to gain inform ...
Sequencing a genome - Information Services and Technology
... artificial plasmids can be inserted into bacteria to amplify DNA for sequencing ...
... artificial plasmids can be inserted into bacteria to amplify DNA for sequencing ...
Non-viral Transfection
... gene to the patient's target cells. Currently, the most common vector is a virus that has been genetically altered to carry normal human DNA. Viruses have evolved a way of encapsulating and delivering their genes to human cells in a pathogenic manner. Scientists have tried to take advantage of this ...
... gene to the patient's target cells. Currently, the most common vector is a virus that has been genetically altered to carry normal human DNA. Viruses have evolved a way of encapsulating and delivering their genes to human cells in a pathogenic manner. Scientists have tried to take advantage of this ...
DNA Oncovirus
... stimulated the erythropoietin receptor, thus inducing erythroid hyperplasia – Fr-MuLV or SFFV integration inactivates p53 ...
... stimulated the erythropoietin receptor, thus inducing erythroid hyperplasia – Fr-MuLV or SFFV integration inactivates p53 ...
IB Biology 11 HL
... About 25 of the 92 natural elements are known to be essential to life. Which four of these 25 elements make up approximately 96% of living matter? The space surrounding the nucleus of an atom contains… At what temperature is water at its densest? A substance with a pH of 6 is called… When ...
... About 25 of the 92 natural elements are known to be essential to life. Which four of these 25 elements make up approximately 96% of living matter? The space surrounding the nucleus of an atom contains… At what temperature is water at its densest? A substance with a pH of 6 is called… When ...
Gen660_Lecture12B_NetworkEvo_2014
... ChIP-seq (NFB and RNA-Pol II) and RNA-seq in 10 humans from 3 different populations Lots of variation (up to 25% variation in binding levels) ...
... ChIP-seq (NFB and RNA-Pol II) and RNA-seq in 10 humans from 3 different populations Lots of variation (up to 25% variation in binding levels) ...
Evolution & Phylogeny ppt
... Origin of large forms and thus a diversity of tissues and structures due to increased availability of Oxygen and thus more efficient metabolism. Origin of ‘hard parts” capable of preservation in the fossil record. Mass extinction of competing Ediacaran animals creating available niches for adaptive ...
... Origin of large forms and thus a diversity of tissues and structures due to increased availability of Oxygen and thus more efficient metabolism. Origin of ‘hard parts” capable of preservation in the fossil record. Mass extinction of competing Ediacaran animals creating available niches for adaptive ...
Endogenous retrovirus
Endogenous retroviruses (ERVs) are endogenous viral elements in the genome that closely resemble and can be derived from retroviruses. They are abundant in the genomes of jawed vertebrates, and they comprise up to 5–8% of the human genome (lower estimates of ~1%). ERVs are a subclass of a type of gene called a transposon, which can be packaged and moved within the genome to serve a vital role in gene expression and in regulation. Researchers have suggested that retroviruses evolved from a type of transposable gene called a retrotransposon, which includes ERVs; these genes can mutate and instead of moving to another location in the genome they can become exogenous or pathogenic. This means that all ERVs may not have originated as an insertion by a retrovirus but that some may have been the source for the genetic information in the retroviruses they resemble.