The Impact of Computer Technology in Molecular Biology and
... Previous versions of BLAST did not account for ...
... Previous versions of BLAST did not account for ...
Impact of Computer Technology in Molecular Biology and Genetics
... Previous versions of BLAST did not account for ...
... Previous versions of BLAST did not account for ...
Slides Gene Group Analysis
... – Conceive the data set with a Cross-Sectional Design – Question of interest: • What are the biological mechanisms that drive the differences in Estrogen Receptor status? ...
... – Conceive the data set with a Cross-Sectional Design – Question of interest: • What are the biological mechanisms that drive the differences in Estrogen Receptor status? ...
Document
... studies of material derived from thymus and from yeast cells. These two types, long known as “thymus nucleic acid” and “yeast nucleic acid,” are now known as deoxyribose nucleic acid (DNA) and ribose nucleic acid (RNA), respectively. Ascoli (1900) and Levene (1903) showed that both contain adenine, ...
... studies of material derived from thymus and from yeast cells. These two types, long known as “thymus nucleic acid” and “yeast nucleic acid,” are now known as deoxyribose nucleic acid (DNA) and ribose nucleic acid (RNA), respectively. Ascoli (1900) and Levene (1903) showed that both contain adenine, ...
Defining the role of cellulose-synthase
... domestic (Australian Permanent Residents/ Citizens) or international application as appropriate; please upload a covering letter indicating the specific project that you wish to apply for, your interests and why you are applying together with your CV. Project description: Several genes belonging to ...
... domestic (Australian Permanent Residents/ Citizens) or international application as appropriate; please upload a covering letter indicating the specific project that you wish to apply for, your interests and why you are applying together with your CV. Project description: Several genes belonging to ...
Gene Section IDO2 (indoleamine 2,3 dioxygenase 2) -
... protein has a predominantly cytoplasmic localization. Biochemical studies suggest there may be some differences in localization compared to the cytoplasmic IDO1 protein, based on the greater ease of extracting IDO1 compared to IDO2 from cells. ...
... protein has a predominantly cytoplasmic localization. Biochemical studies suggest there may be some differences in localization compared to the cytoplasmic IDO1 protein, based on the greater ease of extracting IDO1 compared to IDO2 from cells. ...
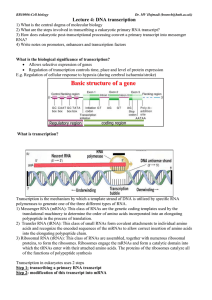
Lecture 4: DNA transcription
... Gene expression efficiency- How is transcription controlled? E.g. When to transcribe gene? How many copies to be transcribed? DNA binding proteins usually regulate transcriptional activity. These are proteins that recognise & bind to specific sequences on DNA. Recognition is determined by specific s ...
... Gene expression efficiency- How is transcription controlled? E.g. When to transcribe gene? How many copies to be transcribed? DNA binding proteins usually regulate transcriptional activity. These are proteins that recognise & bind to specific sequences on DNA. Recognition is determined by specific s ...
Sequence Alignment Introduction
... In modern taxonomic practice, scientists routinely analyze the DNA from specimens they collect to obtain a “DNA barcode,” a short DNA sequence unique to a particular species, which is used to identify the species it belongs to. For animals and many other eukaryotes, different genes have been used ...
... In modern taxonomic practice, scientists routinely analyze the DNA from specimens they collect to obtain a “DNA barcode,” a short DNA sequence unique to a particular species, which is used to identify the species it belongs to. For animals and many other eukaryotes, different genes have been used ...
103 Lecture Ch22b
... • Prokaryots have small circular pieces of DNA called plasmids in addition to the genomic DNA - plasmids contain genes for various proteins and can replicate - plasmids can be shared between bacteria • Restriction enzymes are used to cleave a gene from a foreign DNA and open DNA plasmids in bacteria ...
... • Prokaryots have small circular pieces of DNA called plasmids in addition to the genomic DNA - plasmids contain genes for various proteins and can replicate - plasmids can be shared between bacteria • Restriction enzymes are used to cleave a gene from a foreign DNA and open DNA plasmids in bacteria ...
DNA-Mediated Transformation
... pneumococcus loses its capsule after some invitro culture. Staphylococcus aureus is not able to produce golden pigment in absence of oxygen. Salmonella species loses flagella when exposing phenol on culture. Adding calcium to Bacillus anthracis culture stops converting bacteria to spore form. ...
... pneumococcus loses its capsule after some invitro culture. Staphylococcus aureus is not able to produce golden pigment in absence of oxygen. Salmonella species loses flagella when exposing phenol on culture. Adding calcium to Bacillus anthracis culture stops converting bacteria to spore form. ...
Document
... occurs in viruses. The largest known genome occurs in amoeba, about 7 · 1011 base-pairs, 200 times the length of the human genome. ...
... occurs in viruses. The largest known genome occurs in amoeba, about 7 · 1011 base-pairs, 200 times the length of the human genome. ...
T-DNA
... Must get DNA: 1. into the cells 2. integrated into the genome (unless using transient expression assays) 3. expressed (everywhere or controlled) ...
... Must get DNA: 1. into the cells 2. integrated into the genome (unless using transient expression assays) 3. expressed (everywhere or controlled) ...
Gene Section SRSF3 (serine/arginine rich splicing factor 3) -
... an RNA recognition motifs (RRM) in the N-terminus and an arginine/serine-rich domain (RS) at the C-terminus. RRM motif identifies and binds specific RNA sequences. RS domain interacts with other proteins and facilitates recruitment of the spliceosomal components. The serine residues of the RS domain ...
... an RNA recognition motifs (RRM) in the N-terminus and an arginine/serine-rich domain (RS) at the C-terminus. RRM motif identifies and binds specific RNA sequences. RS domain interacts with other proteins and facilitates recruitment of the spliceosomal components. The serine residues of the RS domain ...
BiochemLecture03
... Whereas most amino acids contain only one non-hydrogen substituent attached to their C-beta carbon, C-beta branched amino acids contain two (two carbons in Valine or Isoleucine; one carbon and one oxygen in Theronine) . This means that there is a lot more bulkiness near to the protein backbone, and ...
... Whereas most amino acids contain only one non-hydrogen substituent attached to their C-beta carbon, C-beta branched amino acids contain two (two carbons in Valine or Isoleucine; one carbon and one oxygen in Theronine) . This means that there is a lot more bulkiness near to the protein backbone, and ...
Orthology Prediction for whole Mammalian Genomes
... !!! Mouse DLG5 is: chr14:22,966,420-22,978,653 (expressed in testis: AK147699) gene identifier ...
... !!! Mouse DLG5 is: chr14:22,966,420-22,978,653 (expressed in testis: AK147699) gene identifier ...
How RNA machinery navigates our genomic obstacle
... our cells. Other researchers had suspected this but had only been able to study it in simplified, modified systems outside the cell. For example, Churchman and her team saw RNA polymerase slow down right before it reached particular obstacles called transcription factors—proteins that help RNA polym ...
... our cells. Other researchers had suspected this but had only been able to study it in simplified, modified systems outside the cell. For example, Churchman and her team saw RNA polymerase slow down right before it reached particular obstacles called transcription factors—proteins that help RNA polym ...
Chapter 3
... (polyclonal), or from a single B cell colony (monoclonal). • Every different antibody has a unique Fab region. • All antibodies isolated from the same species of animal have nearly identical Fc regions. ...
... (polyclonal), or from a single B cell colony (monoclonal). • Every different antibody has a unique Fab region. • All antibodies isolated from the same species of animal have nearly identical Fc regions. ...
TCR
... • Domains - NH ends of variable parts of heavy and light chains on B lymphocytes differs in different sequencies of aminoacids • Domains - C ends – of constant parts have limited variability in the same isotype produced by different B or plasma cells ...
... • Domains - NH ends of variable parts of heavy and light chains on B lymphocytes differs in different sequencies of aminoacids • Domains - C ends – of constant parts have limited variability in the same isotype produced by different B or plasma cells ...
Macroevolutionary Patterns
... 1. Our view of speciation was incorrect. Allopatric speciation is a GRADUAL process and can take a long time. a. This was reconciled when population biologists realized that a “rapid” change on a phylogenetic tree represents a million or more years. A million years is plenty of time for allopatric s ...
... 1. Our view of speciation was incorrect. Allopatric speciation is a GRADUAL process and can take a long time. a. This was reconciled when population biologists realized that a “rapid” change on a phylogenetic tree represents a million or more years. A million years is plenty of time for allopatric s ...
Complete genomic sequence of viral hemorrhagic septicemia virus
... Within the P gene of VSV, an additional overlapping reading frame was detected (14) encoding a deduced protein C, which is localized in cytoplasmic compartiments of virus infected cells. In the VHSV and IHNV genomes, an additional second ORF contained in the P gene is also present. The deduced hypot ...
... Within the P gene of VSV, an additional overlapping reading frame was detected (14) encoding a deduced protein C, which is localized in cytoplasmic compartiments of virus infected cells. In the VHSV and IHNV genomes, an additional second ORF contained in the P gene is also present. The deduced hypot ...
PCR amplifies any target DNA sequence. (N)
... Quantitative PCR (QPCR) defines amount of starting template. ...
... Quantitative PCR (QPCR) defines amount of starting template. ...
DNA Handout KEY - Iowa State University
... 4. What are Chargraff’s rules? If a segment of DNA is composed of 30% C, what is the % of A? A=T and C=G 20% (C=30%=G, A+G=C+T, A=T) 5. A always pairs with _T__, forming _2__ H-bonds. C always pairs with _G__, forming _3_Hbonds. 6. What is the important relationship between structure and function re ...
... 4. What are Chargraff’s rules? If a segment of DNA is composed of 30% C, what is the % of A? A=T and C=G 20% (C=30%=G, A+G=C+T, A=T) 5. A always pairs with _T__, forming _2__ H-bonds. C always pairs with _G__, forming _3_Hbonds. 6. What is the important relationship between structure and function re ...
File - The Building Blocks For Learning
... proteins for detecting light. As well as these 'specialized' proteins, almost all your cells share a common set of 'housekeeping' proteins. I know that you must be wondering……How do cells decide which proteins to make? Almost all your cells have the same set of genes (DNA). These carry instructions ...
... proteins for detecting light. As well as these 'specialized' proteins, almost all your cells share a common set of 'housekeeping' proteins. I know that you must be wondering……How do cells decide which proteins to make? Almost all your cells have the same set of genes (DNA). These carry instructions ...
Endogenous retrovirus
Endogenous retroviruses (ERVs) are endogenous viral elements in the genome that closely resemble and can be derived from retroviruses. They are abundant in the genomes of jawed vertebrates, and they comprise up to 5–8% of the human genome (lower estimates of ~1%). ERVs are a subclass of a type of gene called a transposon, which can be packaged and moved within the genome to serve a vital role in gene expression and in regulation. Researchers have suggested that retroviruses evolved from a type of transposable gene called a retrotransposon, which includes ERVs; these genes can mutate and instead of moving to another location in the genome they can become exogenous or pathogenic. This means that all ERVs may not have originated as an insertion by a retrovirus but that some may have been the source for the genetic information in the retroviruses they resemble.