Doxycycline Concentration (ng/µl) Median Intensity
... We found a dose-dependent relationship between the concentration of doxycycline and gene expression from SG-TRE. In certain inducible systems there is not a dose-dependent relationship, but rather complete expression of a gene once a certain dose is introduced to the system (“on or off”). The fact ...
... We found a dose-dependent relationship between the concentration of doxycycline and gene expression from SG-TRE. In certain inducible systems there is not a dose-dependent relationship, but rather complete expression of a gene once a certain dose is introduced to the system (“on or off”). The fact ...
Purified Mouse Anti-Human HLA-A2 — 551230
... histocompatibility complex (MHC). The MHC gene locus encodes a group of highly polymorphic, cell-surface proteins that play a broad role in the immune response to protein antigens. MHC molecules function by binding and presenting small antigenic protein fragments to antigen-specific receptors expres ...
... histocompatibility complex (MHC). The MHC gene locus encodes a group of highly polymorphic, cell-surface proteins that play a broad role in the immune response to protein antigens. MHC molecules function by binding and presenting small antigenic protein fragments to antigen-specific receptors expres ...
Lecture 1: Introduction and scope of Proteomics The word
... Lecture 1: Introduction and scope of Proteomics The word “proteome” represents the complete protein pool of an organism encoded by the genome. In broader term, Proteomics, is defined as the total protein content of a cell or that of an organism. Proteomics helps in understanding of alteration in pro ...
... Lecture 1: Introduction and scope of Proteomics The word “proteome” represents the complete protein pool of an organism encoded by the genome. In broader term, Proteomics, is defined as the total protein content of a cell or that of an organism. Proteomics helps in understanding of alteration in pro ...
Mitochondrial DNA in the Sea Urchin Arbacia Zixula: Evolutionary
... Table 2 shows the T/ T’ values of the three species pairs, calculated on the basis of the second-codon positions of the protein-coding genes. We analyzed each individual gene, as well as the “supergene” obtained by linking together all the protein genes except ND3, the divergence of which has alread ...
... Table 2 shows the T/ T’ values of the three species pairs, calculated on the basis of the second-codon positions of the protein-coding genes. We analyzed each individual gene, as well as the “supergene” obtained by linking together all the protein genes except ND3, the divergence of which has alread ...
The Discovery, Structure, and Function of DNA
... of homologous chromatids called a Holliday junction. This will involve some “repairing” of mismatched base-pairs in order to make complementary copies across the new DNA molecule. 3. One of the two appropriate backbone strand pairs are then cut at the opposite ends of the crossing region, and reconn ...
... of homologous chromatids called a Holliday junction. This will involve some “repairing” of mismatched base-pairs in order to make complementary copies across the new DNA molecule. 3. One of the two appropriate backbone strand pairs are then cut at the opposite ends of the crossing region, and reconn ...
viruses
... of the brain), small pox, and AIDS. Some viruses can even cause cancer by disrupting the normal cell cycle. Usually, a cell’s DNA contains information about when the cell should stay at rest and when it should replicate. Some cancer-causing viruses are able to direct the cell to keep dividing over a ...
... of the brain), small pox, and AIDS. Some viruses can even cause cancer by disrupting the normal cell cycle. Usually, a cell’s DNA contains information about when the cell should stay at rest and when it should replicate. Some cancer-causing viruses are able to direct the cell to keep dividing over a ...
No Slide Title
... SstI restricted plaice DNA was hybridised to the probes generated from the first coding exons of the three plaice PPAR genes, or the DNA-binding region. Sizes of fragments correspond to those predicted from the gene sequences. ...
... SstI restricted plaice DNA was hybridised to the probes generated from the first coding exons of the three plaice PPAR genes, or the DNA-binding region. Sizes of fragments correspond to those predicted from the gene sequences. ...
Nucleotide Sequence of an Iron Superoxide Dismutase
... because: (a) the SAM46 cDNA is a full-length cDNA, or very close to it, suggesting that translation does not begin upstream of position 24 to 26, and (b) the N-terminus of the mature soybean FeSOD is predicted, based on N-terminal amino acid sequences of other known FeSODs, to be the lysine encoded ...
... because: (a) the SAM46 cDNA is a full-length cDNA, or very close to it, suggesting that translation does not begin upstream of position 24 to 26, and (b) the N-terminus of the mature soybean FeSOD is predicted, based on N-terminal amino acid sequences of other known FeSODs, to be the lysine encoded ...
CHNOPS Lab
... polypeptide chain (protein) . The process by which the information from DNA is transferred into the language of proteins is known as translation. In this investigation, you will simulate the mechanism of protein synthesis and thereby determine the traits inherited by fictitious organisms called CHNO ...
... polypeptide chain (protein) . The process by which the information from DNA is transferred into the language of proteins is known as translation. In this investigation, you will simulate the mechanism of protein synthesis and thereby determine the traits inherited by fictitious organisms called CHNO ...
Strategies of Life
... We eat a meal (Figure 3), in so doing consuming the various components that make up the plants and animals on the table. We eat thousands of different kinds of protein -- it really doesn't matter too much which they are -- but in the end they're turned into our own. How do we do it? The trick is to ...
... We eat a meal (Figure 3), in so doing consuming the various components that make up the plants and animals on the table. We eat thousands of different kinds of protein -- it really doesn't matter too much which they are -- but in the end they're turned into our own. How do we do it? The trick is to ...
Predicting TF affinities to Promoters of tissue specific genes
... addition it is responsible for correctly positioning RNA polymerase at the TSS. Directly upstream of the TATA box lies the BRE motif with its sequence G/C-G/C-C-G-C-C (Hahn 2004, Butler et al., 2002). If present, the BRE motif is bound by the general transcription factor TFIIB. Two additional sequen ...
... addition it is responsible for correctly positioning RNA polymerase at the TSS. Directly upstream of the TATA box lies the BRE motif with its sequence G/C-G/C-C-G-C-C (Hahn 2004, Butler et al., 2002). If present, the BRE motif is bound by the general transcription factor TFIIB. Two additional sequen ...
12 Interaction of Genes
... observed in crosses of two such mutations, when each affected a different functional domain. As expected, intragenic complementation of this type is often observed with missense mutations, not with deletions, and only with special subsets of nonsense mutations. Numerous examples of intragenic comple ...
... observed in crosses of two such mutations, when each affected a different functional domain. As expected, intragenic complementation of this type is often observed with missense mutations, not with deletions, and only with special subsets of nonsense mutations. Numerous examples of intragenic comple ...
File
... • General transcription factors are essential for the transcription of all protein-coding genes • In eukaryotes, high levels of transcription of particular genes depend on control elements interacting with specific transcription factors ...
... • General transcription factors are essential for the transcription of all protein-coding genes • In eukaryotes, high levels of transcription of particular genes depend on control elements interacting with specific transcription factors ...
ppt - University of Connecticut
... • J. Duitama, et al., ReFHap: A Reliable and fast algorithm for Single Individual Haplotyping, Proc. ACM-BCB, pp. 160-169, 2010 • J. Duitama and P.K. Srivastava and I.I. Mandoiu, Towards accurate detection and genotyping of expressed variants from Whole Transcriptome Sequencing data, BMC Genomics 13 ...
... • J. Duitama, et al., ReFHap: A Reliable and fast algorithm for Single Individual Haplotyping, Proc. ACM-BCB, pp. 160-169, 2010 • J. Duitama and P.K. Srivastava and I.I. Mandoiu, Towards accurate detection and genotyping of expressed variants from Whole Transcriptome Sequencing data, BMC Genomics 13 ...
Dear Jennifer - Ms. V Biology
... 2. Why does the cell need both mRNA and tRNA in order to synthesize a protein like hemoglobin? ...
... 2. Why does the cell need both mRNA and tRNA in order to synthesize a protein like hemoglobin? ...
ORF manual_20160301 - Vigene Biosciences
... remains epichromosomal, thus the expression is transient and infection of recombinant adenovirus does not induce chromatin change in host cell. In ViGene Biosciences, we used the most common adenoviral vector, human adenovirus serotype 5, which is rendered replication defective by the deletion of ...
... remains epichromosomal, thus the expression is transient and infection of recombinant adenovirus does not induce chromatin change in host cell. In ViGene Biosciences, we used the most common adenoviral vector, human adenovirus serotype 5, which is rendered replication defective by the deletion of ...
6/16 - Utexas
... In humans: •Each cell contains ~6 billion base pairs of DNA. •This DNA is ~2 meters long and 2 nm wide. •~3% directly codes for amino acids •~10% is genes •In a single human cell only about 5-10% of genes are expressed at a time. ...
... In humans: •Each cell contains ~6 billion base pairs of DNA. •This DNA is ~2 meters long and 2 nm wide. •~3% directly codes for amino acids •~10% is genes •In a single human cell only about 5-10% of genes are expressed at a time. ...
Transcription, RNA Processing, and
... Adenylate cyclase activity is lowered, so cAMP levels are low This means there is much less cAMP/CAP complex And there is decreased lac transcription ...
... Adenylate cyclase activity is lowered, so cAMP levels are low This means there is much less cAMP/CAP complex And there is decreased lac transcription ...
Test I Study Guide
... 12. Describe the process of DNA replication, during the S phase of interphase, and apply the principles of complimentary base pairing. 13. Describe the phases of mitosis. 14. Name and describe the two phases of protein synthesis and discuss the roles of DNA, mRNA, rRNA, and tRNA, in each phase. 15. ...
... 12. Describe the process of DNA replication, during the S phase of interphase, and apply the principles of complimentary base pairing. 13. Describe the phases of mitosis. 14. Name and describe the two phases of protein synthesis and discuss the roles of DNA, mRNA, rRNA, and tRNA, in each phase. 15. ...
Example of identifying a monogenic condition by positional cloning
... which occurs in the NBD segment. The R domain interacts with NBD & regulates their ATP affinity. ...
... which occurs in the NBD segment. The R domain interacts with NBD & regulates their ATP affinity. ...
Article Parallel Histories of Horizontal Gene
... Bacteria confined to intracellular environments experience extensive genome reduction. In extreme cases, insect endosymbionts have evolved genomes that are so gene-poor that they blur the distinction between bacteria and endosymbiotically derived organelles such as mitochondria and plastids. To unde ...
... Bacteria confined to intracellular environments experience extensive genome reduction. In extreme cases, insect endosymbionts have evolved genomes that are so gene-poor that they blur the distinction between bacteria and endosymbiotically derived organelles such as mitochondria and plastids. To unde ...
Gene Section E2F3 (E2F transcription factor 3) Atlas of Genetics and Cytogenetics
... E2F3 is a sequence-specific transcription factor implicated in cell cycle regulation (S-phase). It is a transcriptional activator for E2F-responsive genes. E2F proteins heterodimerize with DP proteins and are subject to inhibition by binding to the pocket domain of retinoblastoma protein (pRB). Phos ...
... E2F3 is a sequence-specific transcription factor implicated in cell cycle regulation (S-phase). It is a transcriptional activator for E2F-responsive genes. E2F proteins heterodimerize with DP proteins and are subject to inhibition by binding to the pocket domain of retinoblastoma protein (pRB). Phos ...
Milestone4
... be generated per generation? Every site at which mutations are compatible with life has been mutated an average of this number of times in just the most recent human generation (and many more times in human history). ...
... be generated per generation? Every site at which mutations are compatible with life has been mutated an average of this number of times in just the most recent human generation (and many more times in human history). ...
AtPTB-like 1 negatively regulates splicing inclusion of a plant
... representation of the Arabidopsis cell wall invertases containing a 9nt mini-exon indicated by ...
... representation of the Arabidopsis cell wall invertases containing a 9nt mini-exon indicated by ...
13059_2010_2366_MOESM1_ESM
... Many copies of ubiquitin-related genes were also up-regulated (5-18 fold). However, these were distinct from those up-regulated under mefenoxam treatment. Comparison with diatoms Plastids were likely lost multiple times in the heterokont lineage [1, 4] and Tyler et al [27] showed numerous genes of l ...
... Many copies of ubiquitin-related genes were also up-regulated (5-18 fold). However, these were distinct from those up-regulated under mefenoxam treatment. Comparison with diatoms Plastids were likely lost multiple times in the heterokont lineage [1, 4] and Tyler et al [27] showed numerous genes of l ...
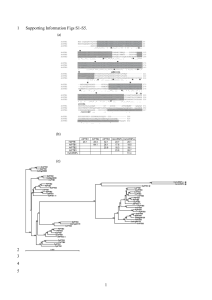
Endogenous retrovirus
Endogenous retroviruses (ERVs) are endogenous viral elements in the genome that closely resemble and can be derived from retroviruses. They are abundant in the genomes of jawed vertebrates, and they comprise up to 5–8% of the human genome (lower estimates of ~1%). ERVs are a subclass of a type of gene called a transposon, which can be packaged and moved within the genome to serve a vital role in gene expression and in regulation. Researchers have suggested that retroviruses evolved from a type of transposable gene called a retrotransposon, which includes ERVs; these genes can mutate and instead of moving to another location in the genome they can become exogenous or pathogenic. This means that all ERVs may not have originated as an insertion by a retrovirus but that some may have been the source for the genetic information in the retroviruses they resemble.