Document
... The frequency of the mains voltage is 50 Hz. The current i1 splits at the node to form the currents i2 and i3. All the current waveforms are sinusoidal; however i1 and i2 have a phase angle between them of 90 degrees. The amplitudes of the currents i1 and i2 are √3 Amps and 1 Amp respectively. ...
... The frequency of the mains voltage is 50 Hz. The current i1 splits at the node to form the currents i2 and i3. All the current waveforms are sinusoidal; however i1 and i2 have a phase angle between them of 90 degrees. The amplitudes of the currents i1 and i2 are √3 Amps and 1 Amp respectively. ...
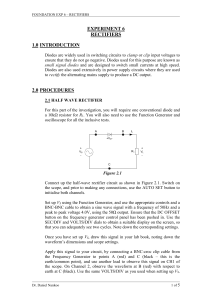
Experiment 6: Rectifiers
... Because the earth of both the oscilloscope and Function Generator are not isolated, scope measurements for the circuits of Figures 2.2 and 2.3 are not possible using the known conventional techniques. Thus, the scope has to be set up to function in differential mode. A consequence of this set up is ...
... Because the earth of both the oscilloscope and Function Generator are not isolated, scope measurements for the circuits of Figures 2.2 and 2.3 are not possible using the known conventional techniques. Thus, the scope has to be set up to function in differential mode. A consequence of this set up is ...
3J-3 Reciprocal Operation of Ultrasonic Transducers
... We have identified a number of possible error sources: • Different capacitive loading during transmission and reception, caused by the voltage dependent capacitance of the discharging transistor and the added capacitance when the receiving amplifier is connected. However, these capacitances are in t ...
... We have identified a number of possible error sources: • Different capacitive loading during transmission and reception, caused by the voltage dependent capacitance of the discharging transistor and the added capacitance when the receiving amplifier is connected. However, these capacitances are in t ...
Wireless Power Charging Coil Changing Considerations
... Figure 6: Scope captures of various test conditions By analyzing these signals it can be concluded that condition #1 is exhibiting the best performance. The criteria considered are the coil’s efficiency and the ability to support the maximum load current while maintaining as high voltage as possible ...
... Figure 6: Scope captures of various test conditions By analyzing these signals it can be concluded that condition #1 is exhibiting the best performance. The criteria considered are the coil’s efficiency and the ability to support the maximum load current while maintaining as high voltage as possible ...
0128 - Dual FET-Input, Low Distortion Operational Amplifiers
... DISTORTION MEASUREMENTS The distortion produced by the OPA2604 is below the measurement limit of virtually all commercially available equipment. A special test circuit, however, can be used to extend the measurement capabilities. ...
... DISTORTION MEASUREMENTS The distortion produced by the OPA2604 is below the measurement limit of virtually all commercially available equipment. A special test circuit, however, can be used to extend the measurement capabilities. ...
Electrical Harmonics: An Introduction and Overview of What
... systems can also overheat leading to open circuits and downtime. Another indirect problem introduced by current distortion is called resonance. Certain current harmonics may excite resonant frequencies in the system. This resonance can cause extremely high harmonic voltages, possibly damaging sensit ...
... systems can also overheat leading to open circuits and downtime. Another indirect problem introduced by current distortion is called resonance. Certain current harmonics may excite resonant frequencies in the system. This resonance can cause extremely high harmonic voltages, possibly damaging sensit ...
Three Phase Power Calculations File
... v AN 2V p cos(t ) vBN 2V p cos(t 120) vCN 2V p cos(t 120) ia 2 I p cos(t ) ib 2 I p cos(t 120) ic 2 I p cos(t 120) p pa pb pc v AN ia vBN ib vCN ic cos(t ) cos(t ) cos(t 120) cos(t 120) p 2V p I p ...
... v AN 2V p cos(t ) vBN 2V p cos(t 120) vCN 2V p cos(t 120) ia 2 I p cos(t ) ib 2 I p cos(t 120) ic 2 I p cos(t 120) p pa pb pc v AN ia vBN ib vCN ic cos(t ) cos(t ) cos(t 120) cos(t 120) p 2V p I p ...
Realization of 476 MHz pulse power cavity amplifier using
... The amplifier is biased to operate in class AB 1 mode for achieving maximum power output for a given value of the max cathode current. As control grid is grounded for DC, the cathode is biased at +60V for the required control grid to cathode voltage of -60V as obtained from the simulation results. ...
... The amplifier is biased to operate in class AB 1 mode for achieving maximum power output for a given value of the max cathode current. As control grid is grounded for DC, the cathode is biased at +60V for the required control grid to cathode voltage of -60V as obtained from the simulation results. ...
Transistor Common Base Configuration Common Emitter
... collector is now common through the supply. The input signal is connected directly to the base, while the output is taken from the emitter load as shown. This type of configuration is commonly known as a Voltage Follower or Emitter Follower circuit. The emitter follower configuration is very useful ...
... collector is now common through the supply. The input signal is connected directly to the base, while the output is taken from the emitter load as shown. This type of configuration is commonly known as a Voltage Follower or Emitter Follower circuit. The emitter follower configuration is very useful ...
FC350™ Fuel Cell Monitor
... EIS measured with an FC350 can identify problems that limit a fuel cell’s efficiency, it can help optimize cell design, and it can determine anodic and cathodic process mechanisms. EIS can be useful in the selection of membranes and the study of membrane impact on performance. Clever placement of re ...
... EIS measured with an FC350 can identify problems that limit a fuel cell’s efficiency, it can help optimize cell design, and it can determine anodic and cathodic process mechanisms. EIS can be useful in the selection of membranes and the study of membrane impact on performance. Clever placement of re ...
Exp5 Full Wave Rectifier
... of the diode pairs are connected together to form the dc terminals of the rectifier set. The center terminals of the diode pairs are connected to the ac voltage source. The diodes V1, V4, resp. V2, V3 are alternatively connected in forward and reverse directions in the bridge circuit (fig. 0.9). ...
... of the diode pairs are connected together to form the dc terminals of the rectifier set. The center terminals of the diode pairs are connected to the ac voltage source. The diodes V1, V4, resp. V2, V3 are alternatively connected in forward and reverse directions in the bridge circuit (fig. 0.9). ...
Standing wave ratio

In radio engineering and telecommunications, standing wave ratio (SWR) is a measure of impedance matching of loads to the characteristic impedance of a transmission line or waveguide. Impedance mismatches result in standing waves along the transmission line, and SWR is defined as the ratio of the partial standing wave's amplitude at an antinode (maximum) to the amplitude at a node (minimum) along the line.The SWR is usually thought of in terms of the maximum and minimum AC voltages along the transmission line, thus called the voltage standing wave ratio or VSWR (sometimes pronounced ""viswar""). For example, the VSWR value 1.2:1 denotes an AC voltage due to standing waves along the transmission line reaching a peak value 1.2 times that of the minimum AC voltage along that line. The SWR can as well be defined as the ratio of the maximum amplitude to minimum amplitude of the transmission line's currents, electric field strength, or the magnetic field strength. Neglecting transmission line loss, these ratios are identical.The power standing wave ratio (PSWR) is defined as the square of the VSWR, however this terminology has no physical relation to actual powers involved in transmission.The SWR can be measured with an instrument called an SWR meter. Since SWR is defined relative to the transmission line's characteristic impedance, the SWR meter must be constructed for that impedance; in practice most transmission lines used in these applications are coaxial cables with an impedance of either 50 or 75 ohms. Checking the SWR is a standard procedure in a radio station, for instance, to verify impedance matching of the antenna to the transmission line (and transmitter). Unlike connecting an impedance analyzer (or ""impedance bridge"") directly to the antenna (or other load), the SWR does not measure the actual impedance of the load, but quantifies the magnitude of the impedance mismatch just performing a measurement on the transmitter side of the transmission line.