Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy Analysis on Type III
... Although this is a well known relationship among the three parameters, its use is limited to only one circuit element -- the ideal resistor, which has the following properties [4]: It follows Ohm's Law at all current and voltage levels Its resistance value is independent of frequency AC curren ...
... Although this is a well known relationship among the three parameters, its use is limited to only one circuit element -- the ideal resistor, which has the following properties [4]: It follows Ohm's Law at all current and voltage levels Its resistance value is independent of frequency AC curren ...
Universal Voltage Conveyor and its Novel Dual-Output Fully
... shown in Figure 3. The experimental measurement results were carried out using an Agilent 4395A Network/Spectrum/Impedance Analyzer (Agilent Technologies: Penang, Malaysia). In all measurements, the passive component values of the filter were selected as C1 = C2 = 560 pF and R1 = R2 = 1 kΩ, which en ...
... shown in Figure 3. The experimental measurement results were carried out using an Agilent 4395A Network/Spectrum/Impedance Analyzer (Agilent Technologies: Penang, Malaysia). In all measurements, the passive component values of the filter were selected as C1 = C2 = 560 pF and R1 = R2 = 1 kΩ, which en ...
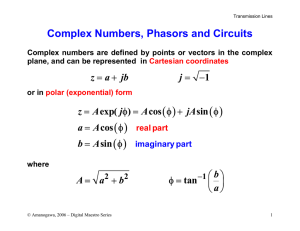
Complex Numbers
... The angles in the complex impedances are the same as the voltage phase angles observed on pages 15-17. Technically, we should express the angles in radians. However we shall be combining these impedances using complex arithmetic and you may find that a little easier to do by working in degrees. ...
... The angles in the complex impedances are the same as the voltage phase angles observed on pages 15-17. Technically, we should express the angles in radians. However we shall be combining these impedances using complex arithmetic and you may find that a little easier to do by working in degrees. ...
5.3 Power Supply Systems Word Document | GCE AS/A
... any changes that take place in the input or output circuits. In particular, the mains supply voltage, (the line voltage,) increases and decreases significantly depending on national factors such as demand (weather conditions, ‘Coronation Street’, FA Cup Final, ‘X Factor’ etc.) The output voltage of ...
... any changes that take place in the input or output circuits. In particular, the mains supply voltage, (the line voltage,) increases and decreases significantly depending on national factors such as demand (weather conditions, ‘Coronation Street’, FA Cup Final, ‘X Factor’ etc.) The output voltage of ...
Power Supply Systems
... any changes that take place in the input or output circuits. In particular, the mains supply voltage, (the line voltage,) increases and decreases significantly depending on national factors such as demand (weather conditions, ‘Coronation Street’, FA Cup Final, ‘X Factor’ etc.) The output voltage of ...
... any changes that take place in the input or output circuits. In particular, the mains supply voltage, (the line voltage,) increases and decreases significantly depending on national factors such as demand (weather conditions, ‘Coronation Street’, FA Cup Final, ‘X Factor’ etc.) The output voltage of ...
The Equivalent Circuit of a Transformer
... • A transformer is a device that changes ac electric power at one voltage level to ac electric power at another voltage level through the action of a magnetic field. • There are two or more stationary electric circuits that are coupled magnetically. • It involves interchange of electric energy betwe ...
... • A transformer is a device that changes ac electric power at one voltage level to ac electric power at another voltage level through the action of a magnetic field. • There are two or more stationary electric circuits that are coupled magnetically. • It involves interchange of electric energy betwe ...
I s
... • A transformer is a device that changes ac electric power at one voltage level to ac electric power at another voltage level through the action of a magnetic field. • There are two or more stationary electric circuits that are coupled magnetically. • It involves interchange of electric energy betwe ...
... • A transformer is a device that changes ac electric power at one voltage level to ac electric power at another voltage level through the action of a magnetic field. • There are two or more stationary electric circuits that are coupled magnetically. • It involves interchange of electric energy betwe ...
LT1886 - Dual 700MHz, 200mA Operational Amplifier
... noise compared to a current feedback amplifier, especially for higher source resistances. Layout and Passive Components With a gain bandwidth product of 700MHz the LT1886 requires attention to detail in order to extract maximum performance. Use a ground plane, short lead lengths and a combination of ...
... noise compared to a current feedback amplifier, especially for higher source resistances. Layout and Passive Components With a gain bandwidth product of 700MHz the LT1886 requires attention to detail in order to extract maximum performance. Use a ground plane, short lead lengths and a combination of ...
Behavior of HV Cable of Power Supply at Short Circuit And Related
... Then the processes in the cable can be described by conventional transmission line equations. Pattern of traveling waves developing at short-circuit conditions and overvoltages (OV) at the power supply side are shown as a function of the cable parameters. In the second case, the shield at the power ...
... Then the processes in the cable can be described by conventional transmission line equations. Pattern of traveling waves developing at short-circuit conditions and overvoltages (OV) at the power supply side are shown as a function of the cable parameters. In the second case, the shield at the power ...
DV23725732
... The voltage generated by power stations has a sinusoidal waveform with a constant frequency. Any disturbances to voltage waveform can result in problems related with the operation of electrical and electronic devices. Users need constant sine wave shape, constant frequency and symmetrical voltage wi ...
... The voltage generated by power stations has a sinusoidal waveform with a constant frequency. Any disturbances to voltage waveform can result in problems related with the operation of electrical and electronic devices. Users need constant sine wave shape, constant frequency and symmetrical voltage wi ...
Standing wave ratio

In radio engineering and telecommunications, standing wave ratio (SWR) is a measure of impedance matching of loads to the characteristic impedance of a transmission line or waveguide. Impedance mismatches result in standing waves along the transmission line, and SWR is defined as the ratio of the partial standing wave's amplitude at an antinode (maximum) to the amplitude at a node (minimum) along the line.The SWR is usually thought of in terms of the maximum and minimum AC voltages along the transmission line, thus called the voltage standing wave ratio or VSWR (sometimes pronounced ""viswar""). For example, the VSWR value 1.2:1 denotes an AC voltage due to standing waves along the transmission line reaching a peak value 1.2 times that of the minimum AC voltage along that line. The SWR can as well be defined as the ratio of the maximum amplitude to minimum amplitude of the transmission line's currents, electric field strength, or the magnetic field strength. Neglecting transmission line loss, these ratios are identical.The power standing wave ratio (PSWR) is defined as the square of the VSWR, however this terminology has no physical relation to actual powers involved in transmission.The SWR can be measured with an instrument called an SWR meter. Since SWR is defined relative to the transmission line's characteristic impedance, the SWR meter must be constructed for that impedance; in practice most transmission lines used in these applications are coaxial cables with an impedance of either 50 or 75 ohms. Checking the SWR is a standard procedure in a radio station, for instance, to verify impedance matching of the antenna to the transmission line (and transmitter). Unlike connecting an impedance analyzer (or ""impedance bridge"") directly to the antenna (or other load), the SWR does not measure the actual impedance of the load, but quantifies the magnitude of the impedance mismatch just performing a measurement on the transmitter side of the transmission line.