UNIT 2: POWER AND ROOTS
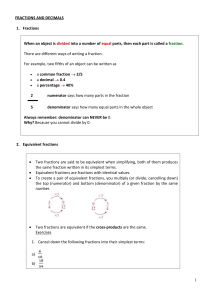
... There exists two types of recurring decimals: Pure recurring decimal: It becomes periodic just after the decimal point. Ex. 1.3535… (35 is called the period). It is usually expressed as Eventually recurring decimal: When the period is not settled just after de decimal point. Ex. 1.457777… or 1.4 ...
... There exists two types of recurring decimals: Pure recurring decimal: It becomes periodic just after the decimal point. Ex. 1.3535… (35 is called the period). It is usually expressed as Eventually recurring decimal: When the period is not settled just after de decimal point. Ex. 1.457777… or 1.4 ...
mathematics paper 1 molo
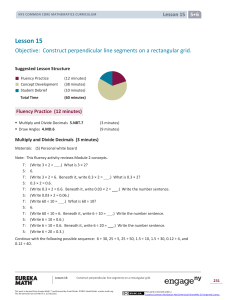
... Non- programmable silent electronic calculators and KNEC Mathematical tables may be used, except where stated otherwise. ...
... Non- programmable silent electronic calculators and KNEC Mathematical tables may be used, except where stated otherwise. ...
Slide 1
... Types of angles are Right straight obtuse (types of angles are ) Right straight acute (types of angles are ) A right angle is 90 degrees and a straight one is 180 Right straight obtuse (types of angles are ) Right straight acute (types of angles are ) Obtuse is more than 90 degrees and acute is less ...
... Types of angles are Right straight obtuse (types of angles are ) Right straight acute (types of angles are ) A right angle is 90 degrees and a straight one is 180 Right straight obtuse (types of angles are ) Right straight acute (types of angles are ) Obtuse is more than 90 degrees and acute is less ...
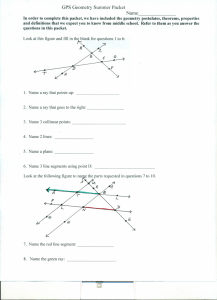
GPS Geometry Summer Packet Name
... Corresponding Angles - the angles formed when 2 lines are cut by a transversal and correspond to the same position at the points of intersection. Alternate Interior Angles - the angles formed when 2 lines are cut by a transversal and are between the lines, on opposite sides of the transversal and at ...
... Corresponding Angles - the angles formed when 2 lines are cut by a transversal and correspond to the same position at the points of intersection. Alternate Interior Angles - the angles formed when 2 lines are cut by a transversal and are between the lines, on opposite sides of the transversal and at ...
Ways to Prove that Quadrilaterals are Parallelograms
... Four theorems are presented in this lesson that can be used to show that a quadrilateral is a parallelogram. ...
... Four theorems are presented in this lesson that can be used to show that a quadrilateral is a parallelogram. ...