Congruence Shortcuts GSP
... Drag the point labeled B (drag) in the broken triangle on the left so that it coincides with the other point B to form a triangle. In the broken triangle on the right, try to make the points labeled B coincide so that the triangle formed is not congruent to the triangle on the left. Change the lengt ...
... Drag the point labeled B (drag) in the broken triangle on the left so that it coincides with the other point B to form a triangle. In the broken triangle on the right, try to make the points labeled B coincide so that the triangle formed is not congruent to the triangle on the left. Change the lengt ...
1.6 Exploring the Pythagorean Theorem Notes
... The Pythagorean Theorem is true for right triangles only! To see which triangle is a right triangle, check to see if the area of the square on the longest side is equal to the sum of the areas of the squares on the other two sides. A = 225 cm2 ...
... The Pythagorean Theorem is true for right triangles only! To see which triangle is a right triangle, check to see if the area of the square on the longest side is equal to the sum of the areas of the squares on the other two sides. A = 225 cm2 ...
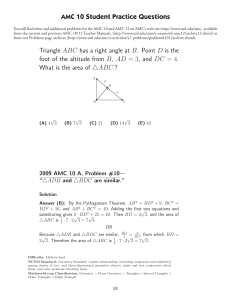
Fall Review-Geometry PAP 1) Find the values of x and y. 2) bisects
... 29) Decide whether Line 1 and Line 2 are parallel, perpendicular, or neither. Line 1 passes through (10, 7) and (13, 9) Line 2 passes through (–4, 3) and (–1, 5) ...
... 29) Decide whether Line 1 and Line 2 are parallel, perpendicular, or neither. Line 1 passes through (10, 7) and (13, 9) Line 2 passes through (–4, 3) and (–1, 5) ...