5.3 The Isosceles Triangle Theorems
... sides congruent. The two congruent sides are called legs and the third side is called the base. Since an equilateral triangle, by definition, is also isosceles then any two sides can be referred to as the legs and the third side the base. Look at the figure below. vertex angle ...
... sides congruent. The two congruent sides are called legs and the third side is called the base. Since an equilateral triangle, by definition, is also isosceles then any two sides can be referred to as the legs and the third side the base. Look at the figure below. vertex angle ...
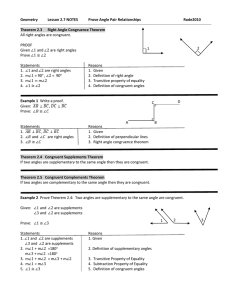
List of common Triangle Theorems you can use when proving other
... Other Common Definitions and Properties that are Useful in Writing Proofs 8. Definition of congruence – all corresponding parts are equal in size. 9. Definition of similarity – all angles are congruent, all sides are proportional. 10. Definition of bisector – Both parts are congruent. 11. Definitio ...
... Other Common Definitions and Properties that are Useful in Writing Proofs 8. Definition of congruence – all corresponding parts are equal in size. 9. Definition of similarity – all angles are congruent, all sides are proportional. 10. Definition of bisector – Both parts are congruent. 11. Definitio ...
Section 5.4
... the adjacent side depend upon the reference angle. To determine the length of a side, given one side and one acute angle, the trigonometric ratios are used. These ratios relate the reference angle with two sides of the triangle. ...
... the adjacent side depend upon the reference angle. To determine the length of a side, given one side and one acute angle, the trigonometric ratios are used. These ratios relate the reference angle with two sides of the triangle. ...