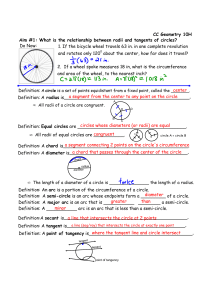
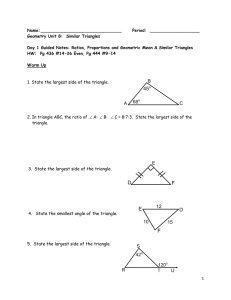
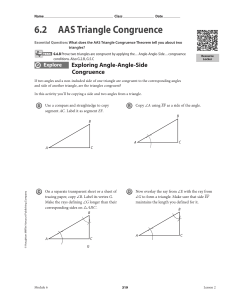
Parallel Postulate Project
... 9) m(∠C 0 AB) + m(∠CAB 0 ) + m(∠CAB) = 180◦ . (draw) 10) m(∠ABC) + m(∠BCA) + m(∠CAB) = 180◦ . (draw) QED The above is a long proof and you will notice we never really needed to show the triangles were congruent. The important steps involved the parallel lines. So why bother with triangles at all? Se ...
... 9) m(∠C 0 AB) + m(∠CAB 0 ) + m(∠CAB) = 180◦ . (draw) 10) m(∠ABC) + m(∠BCA) + m(∠CAB) = 180◦ . (draw) QED The above is a long proof and you will notice we never really needed to show the triangles were congruent. The important steps involved the parallel lines. So why bother with triangles at all? Se ...
Regular Polygons Lab Vasile
... Observation of Isosceles Triangles: Examine isosceles triangles you have created in each regular polygon. Record the following information for 4 different regular polygons. # sides: Measure of vertex angle: Measure of base angles: ...
... Observation of Isosceles Triangles: Examine isosceles triangles you have created in each regular polygon. Record the following information for 4 different regular polygons. # sides: Measure of vertex angle: Measure of base angles: ...