1326015008.
... Find the symmetric equation of the straight line passing through the point (1,2,1) and is normal to the plane 2 x 3 y z 2 . Find the point of intersection of the line in (b) above with the plane x y 2 z 9 . ...
... Find the symmetric equation of the straight line passing through the point (1,2,1) and is normal to the plane 2 x 3 y z 2 . Find the point of intersection of the line in (b) above with the plane x y 2 z 9 . ...
Framework objectives - Coombeshead Academy Frog VLE
... Use diagrams and tables to record in a systematic way all possible mutually exclusive outcomes for single events and for two successive events. ...
... Use diagrams and tables to record in a systematic way all possible mutually exclusive outcomes for single events and for two successive events. ...
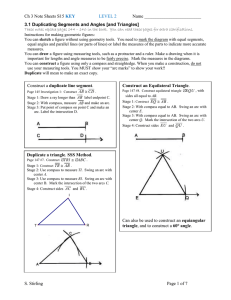
Find m JKM. Holt McDougal Geometry 1-3
... Use the diagram to find the measure of each angle. Then classify each as acute, right, or obtuse. a. BOA mBOA = 40° BOA is acute. b. DOB mDOB = 125° DOB is obtuse. c. EOC mEOC = 105° EOC is obtuse. Holt McDougal Geometry ...
... Use the diagram to find the measure of each angle. Then classify each as acute, right, or obtuse. a. BOA mBOA = 40° BOA is acute. b. DOB mDOB = 125° DOB is obtuse. c. EOC mEOC = 105° EOC is obtuse. Holt McDougal Geometry ...