Use Square Root
... would very nearly turn a driver back in the direction from which s/he came. Hairpin turns get their name because they have interior angles similar to a real hairpin. You are traveling West (when your bearing is 270o) 90o is East, 180o is South, 360o is North. ...
... would very nearly turn a driver back in the direction from which s/he came. Hairpin turns get their name because they have interior angles similar to a real hairpin. You are traveling West (when your bearing is 270o) 90o is East, 180o is South, 360o is North. ...
northbrook primary school - Herne Junior School Kent
... Children should know that 3 x 5 has the same answer as 5 x 3. This can also be shown on the number line. ...
... Children should know that 3 x 5 has the same answer as 5 x 3. This can also be shown on the number line. ...
Lesson Plan Format
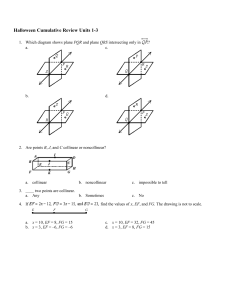
... Using the angle measures that you have just found, fill in the blanks of the following conditional statements: If two parallel lines are cut by a transversal, then the: a. corresponding angles are _______________. b. alternate interior angles are _______________. c. alternate exterior angles are ___ ...
... Using the angle measures that you have just found, fill in the blanks of the following conditional statements: If two parallel lines are cut by a transversal, then the: a. corresponding angles are _______________. b. alternate interior angles are _______________. c. alternate exterior angles are ___ ...
Name - Harmony
... alternate exterior angles are , then the lines are parallel. Thm: If two lines are cut by a transversal and two corresponding angles are , then the lines are parallel. Thm: If two lines are cut by a transversal and two interior (or exterior) angles on the same side of the transversal are supplementa ...
... alternate exterior angles are , then the lines are parallel. Thm: If two lines are cut by a transversal and two corresponding angles are , then the lines are parallel. Thm: If two lines are cut by a transversal and two interior (or exterior) angles on the same side of the transversal are supplementa ...