Unnatural amino acids
... cell, Schultz and his colleagues have demonstrated, as a proof of principle, that it is technically possible to have mutually orthogonal systems operating at once in the same cell. This opens up the possibility of doing multiple site substitution with additional unnatural amino acids in the ...
... cell, Schultz and his colleagues have demonstrated, as a proof of principle, that it is technically possible to have mutually orthogonal systems operating at once in the same cell. This opens up the possibility of doing multiple site substitution with additional unnatural amino acids in the ...
Analyne Manzano Schroeder
... pathways are interconnected; this ensures proper distribution of fully replicated sisterchromatids, but also contributes to the complexity of cell division. The mechanism of mitotic regulation involves an ordered pattern of activation and degradation of proteins that determines the mitotic phase of ...
... pathways are interconnected; this ensures proper distribution of fully replicated sisterchromatids, but also contributes to the complexity of cell division. The mechanism of mitotic regulation involves an ordered pattern of activation and degradation of proteins that determines the mitotic phase of ...
Gene expression flash cards
... The view that nucleic acids / DNA determines protein structure is known as The Central Dogma ...
... The view that nucleic acids / DNA determines protein structure is known as The Central Dogma ...
Bennett, Eric: Utilization of primary and secondary structure elements to predict a protein's propensity to form amyloids
... meaning that 76% of all residues were correctly predicted as helix, strand, or other (26). This places prediction techniques at the level of resolution equal to the best efforts of Fouriertransform infrared (FT-IR) and circular dichroism (CD) structural techniques (27). Recent increases in the accu ...
... meaning that 76% of all residues were correctly predicted as helix, strand, or other (26). This places prediction techniques at the level of resolution equal to the best efforts of Fouriertransform infrared (FT-IR) and circular dichroism (CD) structural techniques (27). Recent increases in the accu ...
1984 BS, Seoul National University, Korea
... mediate ubiquitination, leading to selective proteolysis by the proteasome. Destabilizing residues of the N-end rule pathway include the N-terminal arginine (Arg) residue which can be post-translationally created by ATE1-encoded Arg-tRNA transferases (R-transferases) that transfer the amino acid L-A ...
... mediate ubiquitination, leading to selective proteolysis by the proteasome. Destabilizing residues of the N-end rule pathway include the N-terminal arginine (Arg) residue which can be post-translationally created by ATE1-encoded Arg-tRNA transferases (R-transferases) that transfer the amino acid L-A ...
Genes chapt15
... – Elongation – RNA nucleotides are added to the 3’ end of the new RNA – Termination – RNA polymerase stops transcription when it encounters terminators in the DNA sequence ...
... – Elongation – RNA nucleotides are added to the 3’ end of the new RNA – Termination – RNA polymerase stops transcription when it encounters terminators in the DNA sequence ...
Functional genomics: assigning functions to genome sequences
... Known subunits of E. coli complexes can be identified with high accuracy from functional linkages A protein complex suitable for structural studies has been revealed from functional linkages The procedures for identifying and producing protein complexes can be adapted for high thruput ...
... Known subunits of E. coli complexes can be identified with high accuracy from functional linkages A protein complex suitable for structural studies has been revealed from functional linkages The procedures for identifying and producing protein complexes can be adapted for high thruput ...
Principles of Protein Structure
... α Helix • If N-terminus is at bottom, then all peptide N-H bonds point “down” and all peptide C=O bonds point “up”. • N-H of residue n is H-bonded to C=O of residue n+4. • a-Helix has: ...
... α Helix • If N-terminus is at bottom, then all peptide N-H bonds point “down” and all peptide C=O bonds point “up”. • N-H of residue n is H-bonded to C=O of residue n+4. • a-Helix has: ...
MAKING RNA AND PROTEIN
... • Ribosomes are the cafeteria ladies • mRNA is the email from the principal to the cafeteria lady ...
... • Ribosomes are the cafeteria ladies • mRNA is the email from the principal to the cafeteria lady ...
Gene Section EIF3C (eukaryotic translation initiation factor 3, subunit C)
... with phosphorylated mTOR. Multiple interactions by eIF3 subsequently take place during the progression of protein translation initiation including the proper positioning of the preinitiation complex on the 40S ribosome mediated by eIF3. EIF3c has a significant role in binding to two AUG recognition ...
... with phosphorylated mTOR. Multiple interactions by eIF3 subsequently take place during the progression of protein translation initiation including the proper positioning of the preinitiation complex on the 40S ribosome mediated by eIF3. EIF3c has a significant role in binding to two AUG recognition ...
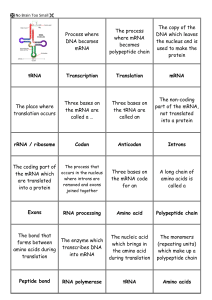
9 - Transcription and Translation
... tRNA Structure tRNA is like a “_______________” with a "nucleic acid word" (________________) on one side and a "protein word" (___________________) on the other side Specific amino acids are added to each tRNA molecule with a specific enzyme called ___________________________ _____________________ ...
... tRNA Structure tRNA is like a “_______________” with a "nucleic acid word" (________________) on one side and a "protein word" (___________________) on the other side Specific amino acids are added to each tRNA molecule with a specific enzyme called ___________________________ _____________________ ...
(GCKIII) proteins using a mechanism analogous to CCM3
... with CCM2, paxillin, and the striatin component of STRIPAK (17).7 Of note, the N-terminal region of CCM3 has also been implicated in the interaction with GCKIII proteins in cells and model organisms (5, 13, 19). Given the critical role for CCM3 and GCKIII proteins in maintaining vascular integrity, ...
... with CCM2, paxillin, and the striatin component of STRIPAK (17).7 Of note, the N-terminal region of CCM3 has also been implicated in the interaction with GCKIII proteins in cells and model organisms (5, 13, 19). Given the critical role for CCM3 and GCKIII proteins in maintaining vascular integrity, ...
Cell Nucleus and Chromatin Structure
... used in the normal life cycle of the cell. Some of the additional DNA is involved in regulation of gene expression and some contain signals for folding and condensing into chromosomes. It is possible that a large amount of the extraneous DNA is evolutionary waste which once encoded necessary informa ...
... used in the normal life cycle of the cell. Some of the additional DNA is involved in regulation of gene expression and some contain signals for folding and condensing into chromosomes. It is possible that a large amount of the extraneous DNA is evolutionary waste which once encoded necessary informa ...
Reverse Transcription - St. Michael`s Hospital
... activities: as a RNA‐dependent DNA polymerase, a DNA‐dependent DNA polymerase and ribonuclease H. Many commercially available kits, such as Super Script® III (Invitrogen/Life Technologies) have specifically engineered enzymes that possess reduced RNase H activity and provide increased thermal sta ...
... activities: as a RNA‐dependent DNA polymerase, a DNA‐dependent DNA polymerase and ribonuclease H. Many commercially available kits, such as Super Script® III (Invitrogen/Life Technologies) have specifically engineered enzymes that possess reduced RNase H activity and provide increased thermal sta ...
Microsoft Word
... is histone H3 lysine 4. (Lachner et al, 2002) Chromatin associated proteins such as HP1, Pc, Swi6 identify these specific histone tail modifications and initiate the formation and maintenance of heterochromatin. RNAi based small RNA pathways control chromatin modifications endogenously. But epigenet ...
... is histone H3 lysine 4. (Lachner et al, 2002) Chromatin associated proteins such as HP1, Pc, Swi6 identify these specific histone tail modifications and initiate the formation and maintenance of heterochromatin. RNAi based small RNA pathways control chromatin modifications endogenously. But epigenet ...
Postdoc Opening
... genome-scale regulation in bacteria. Current goals include understanding how transcriptional regulators alter RNA polymerase conformation to control RNA synthesis (Nayak et al., 2013; Hein et al., 2014; Project 1) and how nucleoprotein filaments formed on bacterial chromosomes and transcriptional pa ...
... genome-scale regulation in bacteria. Current goals include understanding how transcriptional regulators alter RNA polymerase conformation to control RNA synthesis (Nayak et al., 2013; Hein et al., 2014; Project 1) and how nucleoprotein filaments formed on bacterial chromosomes and transcriptional pa ...
Nutrition - GCO 2 - Proteins.notebook
... cell. It has the instructions for how amino acids will be linked to form the proteins in your body. ...
... cell. It has the instructions for how amino acids will be linked to form the proteins in your body. ...
Module code SC-4327 Module Title Bio
... On successful completion of this module, a student will be expected to be able to: Lower order: 50% - gain a solid knowledge of bio-organic compounds such as carbohydrates, amino acids and proteins, terpenes and alkaloids Middle order: 30% - apply theories and concepts learnt in identifyi ...
... On successful completion of this module, a student will be expected to be able to: Lower order: 50% - gain a solid knowledge of bio-organic compounds such as carbohydrates, amino acids and proteins, terpenes and alkaloids Middle order: 30% - apply theories and concepts learnt in identifyi ...
Slide 1
... The H4 tetramer has higher substrate affinity and also can be allosterically inhibited by pyruvate. The M4 tetramer has a lower affinity for substrate and is not allosterically regulated. The mixed tetramers exhibit properties intermediate between the the H4 and M4 tetramers- differential expression ...
... The H4 tetramer has higher substrate affinity and also can be allosterically inhibited by pyruvate. The M4 tetramer has a lower affinity for substrate and is not allosterically regulated. The mixed tetramers exhibit properties intermediate between the the H4 and M4 tetramers- differential expression ...
Ribozymes
... Peptidyl transferase activity can be enhanced by protein L27, however, even in the absence of this protein, reduced activity can still be observed ...
... Peptidyl transferase activity can be enhanced by protein L27, however, even in the absence of this protein, reduced activity can still be observed ...
Secondary structure prediction
... Beta strands that are completely buried (as is often the case in proteins containing both alpha helices and beta strands) usually contain a run of hydrophobic residues. XXXXXXXXXXXX ...
... Beta strands that are completely buried (as is often the case in proteins containing both alpha helices and beta strands) usually contain a run of hydrophobic residues. XXXXXXXXXXXX ...
The HicAB cassette, a putative novel, RNA-targeting toxin
... Table 2S shows the numbers of identified HicA and HicB proteins encoded in selected genomes. As there is little, if any, correlation between the distribution of the five HicB families and taxonomy, and representatives of different HicB families are often found in the same genome, it appears likely t ...
... Table 2S shows the numbers of identified HicA and HicB proteins encoded in selected genomes. As there is little, if any, correlation between the distribution of the five HicB families and taxonomy, and representatives of different HicB families are often found in the same genome, it appears likely t ...
Table S6: Domains present in the primary network generated from
... This uncharacterised family of proteins are principally found in cyanobacteria. This domain is found in a set of hypothetical bacterial proteins. Its exact function has not, as yet, been defined. This family of proteins are functionally uncharacterised. This family of proteins are functionally uncha ...
... This uncharacterised family of proteins are principally found in cyanobacteria. This domain is found in a set of hypothetical bacterial proteins. Its exact function has not, as yet, been defined. This family of proteins are functionally uncharacterised. This family of proteins are functionally uncha ...
Protein production: feeding the crystallographers and NMR
... Data mining. The rules governing protein expression and solubility and even protein crystallization are unknown. By assembling a database of the successes and failures of the large-scale expression and purification trials, researchers will be able to deduce correlations between protein sequence and ...
... Data mining. The rules governing protein expression and solubility and even protein crystallization are unknown. By assembling a database of the successes and failures of the large-scale expression and purification trials, researchers will be able to deduce correlations between protein sequence and ...
SR protein

SR proteins are a conserved family of proteins involved in RNA splicing. SR proteins are named because they contain a protein domain with long repeats of serine and arginine amino acid residues, whose standard abbreviations are ""S"" and ""R"" respectively. SR proteins are 50-300 amino acids in length and composed of two domains, the RNA recognition motif (RRM) region and the RS binding domain. SR proteins are more commonly found in the nucleus than the cytoplasm, but several SR proteins are known to shuttle between the nucleus and the cytoplasm.SR proteins were discovered in the 1990s in Drosophila and in amphibian oocytes, and later in humans. In general, metazoans appear to have SR proteins and unicellular organisms lack SR proteins.SR proteins are important in constitutive and alternative pre-mRNA splicing, mRNA export, genome stabilization, nonsense-mediated decay, and translation. SR proteins alternatively splice pre-mRNA by preferentially selecting different splice sites on the pre-mRNA strands to create multiple mRNA transcripts from one pre-mRNA transcript. Once splicing is complete the SR protein may or may not remain attached to help shuttle the mRNA strand out of the nucleus. As RNA Polymerase II is transcribing DNA into RNA, SR proteins attach to newly made pre-mRNA to prevent the pre-mRNA from binding to the coding DNA strand to increase genome stabilization. Topoisomerase I and SR proteins also interact to increase genome stabilization. SR proteins can control the concentrations of specific mRNA that is successfully translated into protein by selecting for nonsense-mediated decay codons during alternative splicing. SR proteins can alternatively splice NMD codons into its own mRNA transcript to auto-regulate the concentration of SR proteins. Through the mTOR pathway and interactions with polyribosomes, SR proteins can increase translation of mRNA.Ataxia telangiectasia, neurofibromatosis type 1, several cancers, HIV-1, and spinal muscular atrophy have all been linked to alternative splicing by SR proteins.