Lecture 7 - Columbus Labs
... rather than N-formylmethionine. However, as in prokaryotes, a special tRNA participates in initiation. 3. Initiation. The initiating codon in eukaryotes is always AUG. Eukaryotes, in contrast with prokaryotes, do not use a specific purine-rich sequence (RBS) on the 5′ side to distinguish initiator A ...
... rather than N-formylmethionine. However, as in prokaryotes, a special tRNA participates in initiation. 3. Initiation. The initiating codon in eukaryotes is always AUG. Eukaryotes, in contrast with prokaryotes, do not use a specific purine-rich sequence (RBS) on the 5′ side to distinguish initiator A ...
Effects of 6-Thioguanine on RNA Biosynthesis in Regenerating Rat
... cleotide not inhibit the reaction, but in contrast, it was found to partially substitute for the natural substrate. Gray and Rachmeler (6) reported that 6-TG was incorporated into Escherichia coli tRNA and that this incorporation appar ently affected the amino acid acceptor activities of some of the ...
... cleotide not inhibit the reaction, but in contrast, it was found to partially substitute for the natural substrate. Gray and Rachmeler (6) reported that 6-TG was incorporated into Escherichia coli tRNA and that this incorporation appar ently affected the amino acid acceptor activities of some of the ...
DNA to Protein Overview
... Studies that provided clues to the idea for "The Central Dogma of Biology": In 1902, Archibald Garrod, an English physician, treated an infant whose diapers had a dark reddish black stain. He recognized this stain as a rare condition named alkaptonuria. The urine of patients with this condition turn ...
... Studies that provided clues to the idea for "The Central Dogma of Biology": In 1902, Archibald Garrod, an English physician, treated an infant whose diapers had a dark reddish black stain. He recognized this stain as a rare condition named alkaptonuria. The urine of patients with this condition turn ...
Information Content in Genetics:
... groups of organisms in all eukaryote kingdoms use elongation factor-like protein (EFL) for the same purpose.] It brings the tRNA-AA complex to the large ribosome subunit Aminoacyl (A) site for the tRNA anticodon to pair with the mRNA codon. Once pairing of complementary bases occurs, the EF-1α GTPas ...
... groups of organisms in all eukaryote kingdoms use elongation factor-like protein (EFL) for the same purpose.] It brings the tRNA-AA complex to the large ribosome subunit Aminoacyl (A) site for the tRNA anticodon to pair with the mRNA codon. Once pairing of complementary bases occurs, the EF-1α GTPas ...
Gene Regulation Topic Guide
... digest lactose. If it is on, lactose can be digested. First, draw the lac operon. 14. How many genes does the lac operon have? 15. What is the function of the operon? 16. What is the function of the repressor? 17. Why is this called positive control? 18. What happens to the lac operon when lactose ...
... digest lactose. If it is on, lactose can be digested. First, draw the lac operon. 14. How many genes does the lac operon have? 15. What is the function of the operon? 16. What is the function of the repressor? 17. Why is this called positive control? 18. What happens to the lac operon when lactose ...
Descriptions of translation related genes that
... Aminophospholipid translocase protein homolog to human ATP8B1, involved in RNA processing Small cytosolic ribosomal protein, involved in translation initiation and metabolic processes Component of heteroheptameric complexes, involved in mRNA processing Ribonucleoprotein involved in regulating mRNA t ...
... Aminophospholipid translocase protein homolog to human ATP8B1, involved in RNA processing Small cytosolic ribosomal protein, involved in translation initiation and metabolic processes Component of heteroheptameric complexes, involved in mRNA processing Ribonucleoprotein involved in regulating mRNA t ...
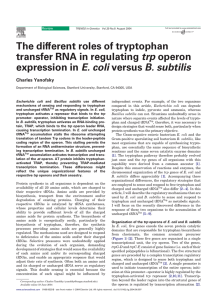
The different roles of tryptophan transfer RNA in regulating trp
... the level that is attained in the presence of excess tryptophan and charged tRNATrp. Figure 2a presents the organization and functions of the segments of the trp leader transcript that are responsible for attenuation control. Figure 2b summarizes the regulatory events that occur when cultures either ...
... the level that is attained in the presence of excess tryptophan and charged tRNATrp. Figure 2a presents the organization and functions of the segments of the trp leader transcript that are responsible for attenuation control. Figure 2b summarizes the regulatory events that occur when cultures either ...
Chapter 10
... DNA TO RNA TO PROTEIN – DNA functions as the inherited directions for a cell or organism. – An organism’s genotype is its genetic makeup, the sequence of nucleotide bases in DNA. – The phenotype is the organism’s physical traits, which arise from the actions of a wide variety of proteins. – DNA spec ...
... DNA TO RNA TO PROTEIN – DNA functions as the inherited directions for a cell or organism. – An organism’s genotype is its genetic makeup, the sequence of nucleotide bases in DNA. – The phenotype is the organism’s physical traits, which arise from the actions of a wide variety of proteins. – DNA spec ...
Document
... Chemical modification of the histones (primarily at the NH3 termini) leads to altered nucleosome-nucleosome interactions. These alterations are important forthe regulation of gene expression. ...
... Chemical modification of the histones (primarily at the NH3 termini) leads to altered nucleosome-nucleosome interactions. These alterations are important forthe regulation of gene expression. ...
A Positive Selection Function for miRNA
... miRNA, which is what would be created in the new ligated message, do appear much more frequently than once in the protein data base of known protein sequences ...
... miRNA, which is what would be created in the new ligated message, do appear much more frequently than once in the protein data base of known protein sequences ...
Mechanism of Translation
... 4. How are the termination codons different from other codons? A) They contain thymines. B) The termination codon always codes for methionine. C) They are not recognized by any tRNA molecules. D) Their conformations do not allow them to fit properly in the A site of the ribosome. ...
... 4. How are the termination codons different from other codons? A) They contain thymines. B) The termination codon always codes for methionine. C) They are not recognized by any tRNA molecules. D) Their conformations do not allow them to fit properly in the A site of the ribosome. ...
RNA Isolation and Technology Applications
... Microarrays for Gene Expression Profiling • Microarrays enable researchers to examine the expression levels of thousands of genes in a single experiment • As many as 50,000 or more unique DNA sequences are spotted on to a glass slide ...
... Microarrays for Gene Expression Profiling • Microarrays enable researchers to examine the expression levels of thousands of genes in a single experiment • As many as 50,000 or more unique DNA sequences are spotted on to a glass slide ...
Chapter 3d
... 1 Initiation: With the help of transcription factors, RNA polymerase binds to the promoter, pries apart the two DNA strands, and initiates mRNA synthesis at the start point on the template strand. ...
... 1 Initiation: With the help of transcription factors, RNA polymerase binds to the promoter, pries apart the two DNA strands, and initiates mRNA synthesis at the start point on the template strand. ...
Translation Definition - Mr. Barrow's Science Center
... The actual process of protein synthesis where mRNA, made during transcription, leaves the nucleus, through nuclear pores located on the nuclear envelope, and attaches to a ribosome The production of a polypeptide (protein) whose amino acid sequence is derived from codon sequences Put a star next to ...
... The actual process of protein synthesis where mRNA, made during transcription, leaves the nucleus, through nuclear pores located on the nuclear envelope, and attaches to a ribosome The production of a polypeptide (protein) whose amino acid sequence is derived from codon sequences Put a star next to ...
Crystal structure of Cas9 in complex with guide RNA and target DNA
... In 2012, biochemical studies revealed that Cas9 is an RNA-guided DNA endonuclease with two nuclease domains (HNH and RuvC) [2] (Fig. 2(a)). The HNH domain cleaves the DNA strand complementary to the 20-nt guide sequence in the crRNAs (cDNA), while the RuvC domain cleaves the noncomplementary DNA str ...
... In 2012, biochemical studies revealed that Cas9 is an RNA-guided DNA endonuclease with two nuclease domains (HNH and RuvC) [2] (Fig. 2(a)). The HNH domain cleaves the DNA strand complementary to the 20-nt guide sequence in the crRNAs (cDNA), while the RuvC domain cleaves the noncomplementary DNA str ...
knockdown
... (siRNAs) which target RNA-degrading enzymes (RNAses) to destroy mRNA transcripts complementary to the siRNAs ...
... (siRNAs) which target RNA-degrading enzymes (RNAses) to destroy mRNA transcripts complementary to the siRNAs ...
Bacterial Regulation
... An operon is a regulatory unit consisting of a few structural genes under the control of one promoter ...
... An operon is a regulatory unit consisting of a few structural genes under the control of one promoter ...
tRNA, rRNA, and RNAi Transfer RNA (tRNA) Characteristics of tRNA
... the presence of modified bases. DHU: dihydrouridine TΨC: Thymine, pseudouracil, cytosine ...
... the presence of modified bases. DHU: dihydrouridine TΨC: Thymine, pseudouracil, cytosine ...
Cell density-dependent gene expression controls luminescence in
... the activator of luminescence gene transcription. The polypeptide consists of two domains. There is a C-terminal helix-turn-helix (H-T-H) containing activator domain extending from about residue 160 to the C-terminal residue, 250. This domain interacts with the transcription initiation complex. The ...
... the activator of luminescence gene transcription. The polypeptide consists of two domains. There is a C-terminal helix-turn-helix (H-T-H) containing activator domain extending from about residue 160 to the C-terminal residue, 250. This domain interacts with the transcription initiation complex. The ...
File
... codon, the ribosome dissociates into its two subunits and falls off the mRNA (which is recycled). -- the peptide/protein chain is released by the tRNA in the P-site into the lumen of the Rough ER (if for export), or into a transition vesicle bound for the Golgi for modifications (if it is to remain ...
... codon, the ribosome dissociates into its two subunits and falls off the mRNA (which is recycled). -- the peptide/protein chain is released by the tRNA in the P-site into the lumen of the Rough ER (if for export), or into a transition vesicle bound for the Golgi for modifications (if it is to remain ...
Concept 14.4: Translation is the RNA
... Molecular Components of Transcription RNA synthesis is catalyzed by RNA polymerase, which pries the DNA strands apart and joins together the RNA nucleotides RNA polymerases assemble polynucleotides in the 5 to 3 direction However, RNA polymerases can start a chain without a primer ...
... Molecular Components of Transcription RNA synthesis is catalyzed by RNA polymerase, which pries the DNA strands apart and joins together the RNA nucleotides RNA polymerases assemble polynucleotides in the 5 to 3 direction However, RNA polymerases can start a chain without a primer ...
BI0I 121 cel]
... State the problem of molecular biology. Compare transcription with translation Describe the 3 species of RNA and discuss their role in gene expression; provide an overview of protein synthesis; compare transcription with translation; describe synthesis of RNA; list the locations in the nucleus where ...
... State the problem of molecular biology. Compare transcription with translation Describe the 3 species of RNA and discuss their role in gene expression; provide an overview of protein synthesis; compare transcription with translation; describe synthesis of RNA; list the locations in the nucleus where ...
Synthese der Oligonukleotide
... Since the discovery that RNA molecules fold into three dimensional objects, which can have catalytic properties the selection of RNA and DNA molecules with specific molecular recognition properties or catalytic capabilities has become a prime focus of research. These molecule are called ribozymes or ...
... Since the discovery that RNA molecules fold into three dimensional objects, which can have catalytic properties the selection of RNA and DNA molecules with specific molecular recognition properties or catalytic capabilities has become a prime focus of research. These molecule are called ribozymes or ...
Cell and Molecular Biology
... Binds and stabilizes the TFIID complex Recruits RNA pol II + TFIIF to the location ...
... Binds and stabilizes the TFIID complex Recruits RNA pol II + TFIIF to the location ...
Inquiry into Life Twelfth Edition
... • All 3 genes are transcribed together producing 1 mRNA, a polycistronic message that starts from a single promoter – Each cistron, or gene, has its own ribosome binding site – Each cistron can be translated by separate ribosomes that bind independently of each other ...
... • All 3 genes are transcribed together producing 1 mRNA, a polycistronic message that starts from a single promoter – Each cistron, or gene, has its own ribosome binding site – Each cistron can be translated by separate ribosomes that bind independently of each other ...



















![BI0I 121 cel]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/004132586_1-822dfb440517eec80339a913dc1e4e97-300x300.png)