DNA Technology
... produce a DNA profile DNA profiling is the analysis of DNA fragments to determine whether they come from the same individual. DNA profiling – compares genetic markers from noncoding regions that show variation between individuals and ...
... produce a DNA profile DNA profiling is the analysis of DNA fragments to determine whether they come from the same individual. DNA profiling – compares genetic markers from noncoding regions that show variation between individuals and ...
Defining the tree of life: Archaea`s place in the evolutionary
... transcription, TATA binding protein (TBP) , transcription factors (TFB) and RNA polymerase (RNAP) (Qureshi 1995). Transcription in Archaea occurs 27 bp downstream of a A-box motif that acts as a promoter like eucaryote TATA boxes by binding proteins that aid RNA polymerase binding (Qureshi 1995). T ...
... transcription, TATA binding protein (TBP) , transcription factors (TFB) and RNA polymerase (RNAP) (Qureshi 1995). Transcription in Archaea occurs 27 bp downstream of a A-box motif that acts as a promoter like eucaryote TATA boxes by binding proteins that aid RNA polymerase binding (Qureshi 1995). T ...
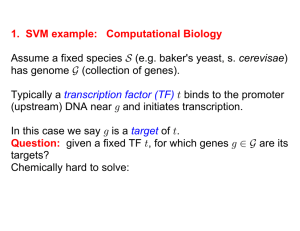
1. SVM example: Computational Biology Assume a fixed species
... With data set H, can we find the right function 0 À J Ä „ " which generalizes the above examples, so that 0 ÐxÑ œ C for all feature vectors? Easier: find a 0 À J Ä real numbers, where 0 ÐxÑ ! if C œ "à 0 ÐxÑ ! if C œ "Þ Resulting predictive accuracy depends on the number of features used, i.e., ...
... With data set H, can we find the right function 0 À J Ä „ " which generalizes the above examples, so that 0 ÐxÑ œ C for all feature vectors? Easier: find a 0 À J Ä real numbers, where 0 ÐxÑ ! if C œ "à 0 ÐxÑ ! if C œ "Þ Resulting predictive accuracy depends on the number of features used, i.e., ...
Phylogenetic, amino acid content and indel analyses
... analysis used (Olsen et al., 1994 ; Ludwig et al., 1994) and which are sometimes in conflict with those defined either by other gene products, e.g. EF-Tu (Ludwig et al., 1994), ATPase β (Ludwig et al., 1994) and RecA (Eisen, 1995), or by whole genome analysis (Tekaia et al., 1999). The classificatio ...
... analysis used (Olsen et al., 1994 ; Ludwig et al., 1994) and which are sometimes in conflict with those defined either by other gene products, e.g. EF-Tu (Ludwig et al., 1994), ATPase β (Ludwig et al., 1994) and RecA (Eisen, 1995), or by whole genome analysis (Tekaia et al., 1999). The classificatio ...
Antibodies for Unfolded Protein Response
... is best known for its role in insulin processing. During ER stress responses and activation of the UPR, PERK functions to inhibit translation of new proteins. Specifically, ER stress causes oligomerization of the ER luminal domain (N-terminal) of PERK, which facilitates the trans-autophosphorylation ...
... is best known for its role in insulin processing. During ER stress responses and activation of the UPR, PERK functions to inhibit translation of new proteins. Specifically, ER stress causes oligomerization of the ER luminal domain (N-terminal) of PERK, which facilitates the trans-autophosphorylation ...
Molecular cloning, characterization and expression analysis of WAG
... highly conserved MADS-MEF2 type protein domain, and the relatively highly conserved Kbox protein domain, and the non-conserved protein domain in the C-terminal region. Despite variation in the nucleotide and amino acid sequences of C-class genes from different plants, these proteins typically contai ...
... highly conserved MADS-MEF2 type protein domain, and the relatively highly conserved Kbox protein domain, and the non-conserved protein domain in the C-terminal region. Despite variation in the nucleotide and amino acid sequences of C-class genes from different plants, these proteins typically contai ...
Slide 1 - E-Learning/An-Najah National University
... mitochondria was not quite the same as the “universal code” that has become so familiar to biologists. In the mitochondrial genomes, what should have been a “stop” codon, UGA, was instead read as the amino acid tryptophan; AUA was read as methionine rather than isoleucine; and AGA and AGG were rea ...
... mitochondria was not quite the same as the “universal code” that has become so familiar to biologists. In the mitochondrial genomes, what should have been a “stop” codon, UGA, was instead read as the amino acid tryptophan; AUA was read as methionine rather than isoleucine; and AGA and AGG were rea ...
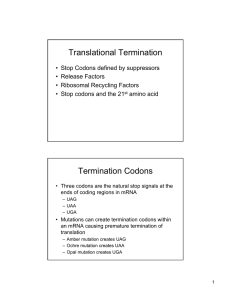
Translational Termination
... • Three codons are the natural stop signals at the ends of coding regions in mRNA – UAG – UAA – UGA ...
... • Three codons are the natural stop signals at the ends of coding regions in mRNA – UAG – UAA – UGA ...
Molecular scissors slice DNA to isolate genes
... individual DNA fragments from a jumbled sample by using the properties of a jelly-like gel. Electrophoresis is like a running race for DNA: it works by passing a current through a gel loaded with DNA fragments at one end. Since DNA has a negative charge, the current causes the DNA segments to move t ...
... individual DNA fragments from a jumbled sample by using the properties of a jelly-like gel. Electrophoresis is like a running race for DNA: it works by passing a current through a gel loaded with DNA fragments at one end. Since DNA has a negative charge, the current causes the DNA segments to move t ...
GO: The Gene Ontology
... • A gene product can have several functions, cellular locations and be involved in many processes • Annotation of a gene product to one ontology is independent from its annotation to other ontologies • Annotations are only to terms reflecting a normal activity or location • Usage of ‘unknown’ GO ter ...
... • A gene product can have several functions, cellular locations and be involved in many processes • Annotation of a gene product to one ontology is independent from its annotation to other ontologies • Annotations are only to terms reflecting a normal activity or location • Usage of ‘unknown’ GO ter ...
Chapter 19 - Great Neck Public Schools
... Don’t memorize this level of detail unless you have nothing else to do. First email me though and I will find you something else to ...
... Don’t memorize this level of detail unless you have nothing else to do. First email me though and I will find you something else to ...
Determination of nucleotide sequences in DNA
... Fig. I. Specificity requirements for DNA polymerase. w i t h , a r e g i o n on t h e D N A b e i n g sequenced ( t h e t e m p l a t e ) . Mononucleotide residues are added sequentially to the 3' end of the primer from the corresponding deoxynucleoside triphosphates, making a complementary copy of ...
... Fig. I. Specificity requirements for DNA polymerase. w i t h , a r e g i o n on t h e D N A b e i n g sequenced ( t h e t e m p l a t e ) . Mononucleotide residues are added sequentially to the 3' end of the primer from the corresponding deoxynucleoside triphosphates, making a complementary copy of ...
New Computational Tools Help Solve Puzzle of RNA Structure
... puzzled over the fact that humans have roughly the same number of protein- and RNA-coding genes as less complex organisms such as worms or fruit flies. New research, however, is showing that the complexity of an organism scales with the number of RNA. The surge of interest in RNA, combined with rapi ...
... puzzled over the fact that humans have roughly the same number of protein- and RNA-coding genes as less complex organisms such as worms or fruit flies. New research, however, is showing that the complexity of an organism scales with the number of RNA. The surge of interest in RNA, combined with rapi ...
Evaluation and Comparison of the GUS, LUC and GFP Reporter
... Green fluorescent protein (GFP) is a 27-kD protein from the jellyfish Aequorea victoria that due to its unique structure, shows a bright green fluorescence when folded correctly and illuminated with UV or blue light (Fig. 1 D; Chalfie et al., 1994). For effective expression in plants, the GFP coding ...
... Green fluorescent protein (GFP) is a 27-kD protein from the jellyfish Aequorea victoria that due to its unique structure, shows a bright green fluorescence when folded correctly and illuminated with UV or blue light (Fig. 1 D; Chalfie et al., 1994). For effective expression in plants, the GFP coding ...
Improved recovery of DNA from polyacrylamide gels after in situ
... Reagent at 60 jC for 30 min. The volume of the DNA solution was decreased from 600 to 20 Al using glassmilk elution according to the manufacturer’s instruction (Geneclean II, Bio101). DNA concentration by ethanol precipitation or using commercially available kits which use chaotropic agents such as ...
... Reagent at 60 jC for 30 min. The volume of the DNA solution was decreased from 600 to 20 Al using glassmilk elution according to the manufacturer’s instruction (Geneclean II, Bio101). DNA concentration by ethanol precipitation or using commercially available kits which use chaotropic agents such as ...
Design Genes with Ease Using In-Fusion® Cloning
... and synthetic genes (1). This can be accomplished by developing a toolbox of In-Fusion-Ready DNA modules that can be readily joined in infinite combinations. Fragments can include fusion protein partners [Fc, green fluorescent protein (AcGFP1), etc.], epitope tags, linkers, promoters, poly(A) sites, ...
... and synthetic genes (1). This can be accomplished by developing a toolbox of In-Fusion-Ready DNA modules that can be readily joined in infinite combinations. Fragments can include fusion protein partners [Fc, green fluorescent protein (AcGFP1), etc.], epitope tags, linkers, promoters, poly(A) sites, ...
Gene predictions: structural, discovery, functional part 1
... themselves. • Using Glimmer is a two-part process • Train Glimmer with genes from organism that was sequenced, which are known, or strongly believed, to be real genes. • Run trained Glimmer against the entire genome sequence. • This is actually how most ab initio gene predictors—including eukaryotic ...
... themselves. • Using Glimmer is a two-part process • Train Glimmer with genes from organism that was sequenced, which are known, or strongly believed, to be real genes. • Run trained Glimmer against the entire genome sequence. • This is actually how most ab initio gene predictors—including eukaryotic ...
File
... The fluid material of the nucleus is surrounded by the familiar double membrane called the nuclear envelope. DNA, chromatin and chromosomes can be found inside the nucleus. Chromatin is DNA that is combined with proteins, including histone and non-histone proteins. Chromatin is coiled into larger, h ...
... The fluid material of the nucleus is surrounded by the familiar double membrane called the nuclear envelope. DNA, chromatin and chromosomes can be found inside the nucleus. Chromatin is DNA that is combined with proteins, including histone and non-histone proteins. Chromatin is coiled into larger, h ...
Properties of the Genetic Code under Directional, Asymmetric
... genes which code for proteins fulfilling the same functions in different organisms. Furthermore, these genes very often share the same amino-acid residues at the corresponding positions which seems to prove that they have a common ancestor sequence. Such genes are called orthologs. In fact, the degree ...
... genes which code for proteins fulfilling the same functions in different organisms. Furthermore, these genes very often share the same amino-acid residues at the corresponding positions which seems to prove that they have a common ancestor sequence. Such genes are called orthologs. In fact, the degree ...
A significant similarity is the fact that both prokaryotes and
... the nucleus, and is easily seen using a microscope. On the other hand, prokaryotes lack this distinct nucleus and nucleur membrane but instead have a nucleoid, which is an ‘irregularly shaped region within the cell where the genetic information is localised’2 in the form of a, usually circular, doub ...
... the nucleus, and is easily seen using a microscope. On the other hand, prokaryotes lack this distinct nucleus and nucleur membrane but instead have a nucleoid, which is an ‘irregularly shaped region within the cell where the genetic information is localised’2 in the form of a, usually circular, doub ...
Biogenetic Engineering & Manipulating Genes
... 5) How is a cDNA library different from a genomic library? (p. 388390) 6) Name two “vectors” that can be used for gene transfer. 7) Give two examples of a genetically modified crop or animal. 8) Briefly explain the process of gene therapy and give an example how it works. 9) Explain what a clone is ...
... 5) How is a cDNA library different from a genomic library? (p. 388390) 6) Name two “vectors” that can be used for gene transfer. 7) Give two examples of a genetically modified crop or animal. 8) Briefly explain the process of gene therapy and give an example how it works. 9) Explain what a clone is ...
2 An Overview of Nucleic Acid Chemistry, Structure, and Function
... Three helical forms of DNA are recognized to exist: A, B, and Z (27). The B conformation is the dominate form under physiological conditions. In B DNA, the basepairs are stacked 0.34 nm apart, with 10 basepairs per turn of the right-handed double helix and a diameter of approx 2 nm. Like B DNA, the ...
... Three helical forms of DNA are recognized to exist: A, B, and Z (27). The B conformation is the dominate form under physiological conditions. In B DNA, the basepairs are stacked 0.34 nm apart, with 10 basepairs per turn of the right-handed double helix and a diameter of approx 2 nm. Like B DNA, the ...