Talking Culture: New Boundaries, New Rhetorics of Exclusion in
... Please contact the publisher regarding any further use of this work. Publisher contact information may be obtained at . http://www.jstor.org/action/showPublisher?publisherCode=ucpress. . Each copy of any part of a JSTOR transmission must contain the same copyright notice that appears on the screen o ...
... Please contact the publisher regarding any further use of this work. Publisher contact information may be obtained at . http://www.jstor.org/action/showPublisher?publisherCode=ucpress. . Each copy of any part of a JSTOR transmission must contain the same copyright notice that appears on the screen o ...
CHAPTER 26
... phenotypic variation because they are usually influenced by multiple genes that exist as multiple alleles. A large amount of environmental variation will also increase the overlap between genotypes and phenotypes for polygenic traits. C3. Answer: A normal distribution varies in a symmetrical way aro ...
... phenotypic variation because they are usually influenced by multiple genes that exist as multiple alleles. A large amount of environmental variation will also increase the overlap between genotypes and phenotypes for polygenic traits. C3. Answer: A normal distribution varies in a symmetrical way aro ...
Left-Right Political Spectrum and the Human Gene Pool
... assortative mating as revealed by the shared genome-wide SNPs (single nucleotide polymorphisms) between married couples comparing with random pairs [14]. The study found that married couples had similar genetic make-up comparing with random pairs of individuals. These results were later ascribed ent ...
... assortative mating as revealed by the shared genome-wide SNPs (single nucleotide polymorphisms) between married couples comparing with random pairs [14]. The study found that married couples had similar genetic make-up comparing with random pairs of individuals. These results were later ascribed ent ...
Mechanisms of Evolution 1. In their first attempts to genetically
... from the original population can be lost or over-represented by the new population, depending on the alleles present in the founding members. 12. Natural selection is a process by which organisms with traits well suited to an environment survive and reproduce at a greater rate than organisms less su ...
... from the original population can be lost or over-represented by the new population, depending on the alleles present in the founding members. 12. Natural selection is a process by which organisms with traits well suited to an environment survive and reproduce at a greater rate than organisms less su ...
Chapter 1 The Framework of Biology
... 10.4 More complex patterns of inheritance are an extension of Mendel's basic rules. Other types of inheritance patterns have been discovered since Mendel's initial work. Some alleles show incomplete dominance or co-dominance. Traits which show incomplete dominance have three phenotypes, the heterozy ...
... 10.4 More complex patterns of inheritance are an extension of Mendel's basic rules. Other types of inheritance patterns have been discovered since Mendel's initial work. Some alleles show incomplete dominance or co-dominance. Traits which show incomplete dominance have three phenotypes, the heterozy ...
(lectures 11
... characters that involve “altruism”, in which an individual has a phenotype (such as a behavior) that lowers its own individual fitness but raises the fitness of others? One would think that any allele predisposing the individual to this behavior would be eliminated from the population. The explanati ...
... characters that involve “altruism”, in which an individual has a phenotype (such as a behavior) that lowers its own individual fitness but raises the fitness of others? One would think that any allele predisposing the individual to this behavior would be eliminated from the population. The explanati ...
Lecture 15 Quantitative Genetics II
... When there is genetic variation for a character there will be a resemblance between relatives. Relatives will have more similar trait values to each other than to unrelated individuals. ...
... When there is genetic variation for a character there will be a resemblance between relatives. Relatives will have more similar trait values to each other than to unrelated individuals. ...
a place for behavior in ecological epigenetics
... removed, will improve our understanding of inheritance and, therefore, evolutionary change. As Jablonka suggests, this level of mechanistic understanding promises to lend insight into processes as diverse as domestication and cultural transmission. In addition to characterizing the epigenetic mechan ...
... removed, will improve our understanding of inheritance and, therefore, evolutionary change. As Jablonka suggests, this level of mechanistic understanding promises to lend insight into processes as diverse as domestication and cultural transmission. In addition to characterizing the epigenetic mechan ...
Genetic Drift and Polygenic Inheritance
... a limited number of alleles, while most anthropometric traits are influenced by several loci and also by the environment. These complications must obviously be considered in any interpretation of the effects of mutation, selection, gene flow, and gene drift on metric traits. In particular, random ge ...
... a limited number of alleles, while most anthropometric traits are influenced by several loci and also by the environment. These complications must obviously be considered in any interpretation of the effects of mutation, selection, gene flow, and gene drift on metric traits. In particular, random ge ...
Evolution: Pt I
... • The biological species – “Members of a group of populations that interbreed, or potentially interbreed, with each other under natural conditions to produce viable offspring” ...
... • The biological species – “Members of a group of populations that interbreed, or potentially interbreed, with each other under natural conditions to produce viable offspring” ...
AUXILIARY-2007-0003.GeneticProgramming.
... Both approaches can provide increase in Fitness function. The problem is how good? ...
... Both approaches can provide increase in Fitness function. The problem is how good? ...
here
... one with an omega fixed at 1, a second where each site can be either have an omega between 0 and 1, or an omega of 1, and third a model that uses three omegas as described before for MrBayes. The output is written into a file called Hv1.sites.codeml_out (as directed by the control file). Point out l ...
... one with an omega fixed at 1, a second where each site can be either have an omega between 0 and 1, or an omega of 1, and third a model that uses three omegas as described before for MrBayes. The output is written into a file called Hv1.sites.codeml_out (as directed by the control file). Point out l ...
A comparison of biological and cultural evolution
... The idea of the model of reciprocal altruism, argued mathematically by Trivers (1971), is that it is beneficial for an organism to act in an altruistic manner that temporarily reduces its fitness while increasing another organism’s fitness with the expectation that the other organism will act in a simi ...
... The idea of the model of reciprocal altruism, argued mathematically by Trivers (1971), is that it is beneficial for an organism to act in an altruistic manner that temporarily reduces its fitness while increasing another organism’s fitness with the expectation that the other organism will act in a simi ...
THE QTN PROGRAM AND THE ALLELES THAT MATTER FOR
... the 20th century was that the genes underlying phenotypic variation and divergence were detectable only when they had such dramatic effects as to behave as Mendelian genes, with genotypes inferable from phenotypes. These genes were believed to be of little consequence for evolution, according to Lew ...
... the 20th century was that the genes underlying phenotypic variation and divergence were detectable only when they had such dramatic effects as to behave as Mendelian genes, with genotypes inferable from phenotypes. These genes were believed to be of little consequence for evolution, according to Lew ...
Evolution exam questions
... 15. Blending inheritance was a major stumbling block for the maintenance of genetic variation and Darwin’s theory of evolution via natural selection. The following example will reinforce how our knowledge of inheritance eliminates this stumbling block. 5 pts. A white flowered, small flowered indivi ...
... 15. Blending inheritance was a major stumbling block for the maintenance of genetic variation and Darwin’s theory of evolution via natural selection. The following example will reinforce how our knowledge of inheritance eliminates this stumbling block. 5 pts. A white flowered, small flowered indivi ...
syllabus - Laura A. Ogden
... Understand "culture" as a process of sense-making, Reflect on how cultural difference is constituted and challenged Consider the ways anthropologists use ethnography to translate cultural difference Reflect on the relationship between global & local processes of cultural production On writte ...
... Understand "culture" as a process of sense-making, Reflect on how cultural difference is constituted and challenged Consider the ways anthropologists use ethnography to translate cultural difference Reflect on the relationship between global & local processes of cultural production On writte ...
The cultural evolution of a rule of conduct: Hayek`s epistemology
... fundamental in a field that do not consider strictly profit maximization “the core” of economics. “No society would be viable without some norms and rules of conduct. Such norms and rules are necessary for viability exactly in fields where strictly economic incentives are absent or cannot be create ...
... fundamental in a field that do not consider strictly profit maximization “the core” of economics. “No society would be viable without some norms and rules of conduct. Such norms and rules are necessary for viability exactly in fields where strictly economic incentives are absent or cannot be create ...
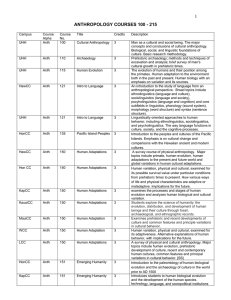
Review of Course Numbers
... Linguistically oriented approaches to human behavior, including ethnolinguistics, sociolinguistics, and psycholinguistics. The way language functions in culture, society, and the cognitive processes. Introduction to the peoples and cultures of the Pacific Islands. Emphasis is on cultural change and ...
... Linguistically oriented approaches to human behavior, including ethnolinguistics, sociolinguistics, and psycholinguistics. The way language functions in culture, society, and the cognitive processes. Introduction to the peoples and cultures of the Pacific Islands. Emphasis is on cultural change and ...
LambSheep - UCSB Economics - University of California, Santa
... Lamb 1 wants to maximize a weighted average of own and Lamb 2’s survival probability, with twice as big a weight for self. Lamb 2 wants to maximize weighted average with greater weight for self. But Lamb 2 is a passive player in this game. Mother loves firstborn, but their interests are partly in co ...
... Lamb 1 wants to maximize a weighted average of own and Lamb 2’s survival probability, with twice as big a weight for self. Lamb 2 wants to maximize weighted average with greater weight for self. But Lamb 2 is a passive player in this game. Mother loves firstborn, but their interests are partly in co ...
Germs, genomes and genealogies
... changing antigenic variation, the hallmark of which is an excess of protein-changing variation (relative to putatively neutral, non-protein changing variation) at antigenic genes during the course of the infection. Such a pattern is seen in HIV-1, particularly in the env gene, by the use of codon-ba ...
... changing antigenic variation, the hallmark of which is an excess of protein-changing variation (relative to putatively neutral, non-protein changing variation) at antigenic genes during the course of the infection. Such a pattern is seen in HIV-1, particularly in the env gene, by the use of codon-ba ...