Chapter 20
... Copyright © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. ...
... Copyright © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. ...
CSE280A Class Projects
... The goal of this project is to understand selection signatures in multi-allelic (soft-sweep) and polygenic selection. Start by building a forward simulator that can simulate these kinds of selections. 1. Build a standard forward-simulator for haploid population as follows: assume a Wright-Fisher mod ...
... The goal of this project is to understand selection signatures in multi-allelic (soft-sweep) and polygenic selection. Start by building a forward simulator that can simulate these kinds of selections. 1. Build a standard forward-simulator for haploid population as follows: assume a Wright-Fisher mod ...
Memory - Lone Star College
... Gene-Environment Interaction Both genes and environment affect our traits, but the interaction, the interplay that occurs when the effect of one depends on another, is most important. ...
... Gene-Environment Interaction Both genes and environment affect our traits, but the interaction, the interplay that occurs when the effect of one depends on another, is most important. ...
Evolution - Richfield Public Schools
... Objective: Students will begin to understand the The Theory of Evolution by Natural Selection Test, Grades, Row Wars, ...
... Objective: Students will begin to understand the The Theory of Evolution by Natural Selection Test, Grades, Row Wars, ...
Identification of func
... With ~10 million single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) occurring at >1% in humans, identifying the functionally important SNP can be likened to “finding a needle in a haystack”. It is thus not practical to investigate every SNP for their functionality or disease/drug response association. Our appro ...
... With ~10 million single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) occurring at >1% in humans, identifying the functionally important SNP can be likened to “finding a needle in a haystack”. It is thus not practical to investigate every SNP for their functionality or disease/drug response association. Our appro ...
Question Paper for Competitive Exam : Plant Breeding
... In crossing homozygous dominant and homozygous recessive pea plants, Mendel noted that some genes were not seen in the F1 generation and were seen in only 25% of the F2 generation. What did he call these genes? A ...
... In crossing homozygous dominant and homozygous recessive pea plants, Mendel noted that some genes were not seen in the F1 generation and were seen in only 25% of the F2 generation. What did he call these genes? A ...
Natural Selection
... time travels. You are a scientist interested in the population genetics of extinct animals. Taking advantage of this technological advance, you decide to go to the past 8 million years to conduct a field work in Venezuela to study a population of Phoberomys pattersoni*, the world’s largest extinct r ...
... time travels. You are a scientist interested in the population genetics of extinct animals. Taking advantage of this technological advance, you decide to go to the past 8 million years to conduct a field work in Venezuela to study a population of Phoberomys pattersoni*, the world’s largest extinct r ...
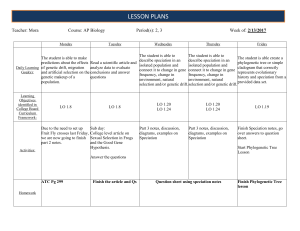
lesson Plans - Lemon Bay High School
... and artificial selection on the conclusions and answer genetic makeup of a ...
... and artificial selection on the conclusions and answer genetic makeup of a ...
population
... • Natural selection acts on individuals, but only populations evolve. • Genetic variations in populations contribute to evolution. • Population genetics is the study of how populations change genetically over time and integrates Mendelian genetics with the Darwinian theory of evolution by natural s ...
... • Natural selection acts on individuals, but only populations evolve. • Genetic variations in populations contribute to evolution. • Population genetics is the study of how populations change genetically over time and integrates Mendelian genetics with the Darwinian theory of evolution by natural s ...
HERE
... Phylogenetic trees and cladograms are graphical representations (models) of evolutionary history that can be tested Speciation and extinction have occurred throughout the Earth’s history. Speciation may occur when two populations become reproductively isolated from each other. Populations of organis ...
... Phylogenetic trees and cladograms are graphical representations (models) of evolutionary history that can be tested Speciation and extinction have occurred throughout the Earth’s history. Speciation may occur when two populations become reproductively isolated from each other. Populations of organis ...
4-26-13 Unit 7 (Evolution) Review
... Divergent evolution- build up of differences between groups which can lead to the development of a new species In other words, two different species that evolved from the same ancestor. Caused by populations of the same species: moving to two different environments or specializing in different areas ...
... Divergent evolution- build up of differences between groups which can lead to the development of a new species In other words, two different species that evolved from the same ancestor. Caused by populations of the same species: moving to two different environments or specializing in different areas ...
Ch. 21 Agents and Hardy
... Phylogenetic trees and cladograms are graphical representations (models) of evolutionary history that can be tested Speciation and extinction have occurred throughout the Earth’s history. Speciation may occur when two populations become reproductively isolated from each other. Populations of organis ...
... Phylogenetic trees and cladograms are graphical representations (models) of evolutionary history that can be tested Speciation and extinction have occurred throughout the Earth’s history. Speciation may occur when two populations become reproductively isolated from each other. Populations of organis ...
Bio112HW3 - Napa Valley College
... c. Genetic drift d. Both a and b 6. Which process changes allele frequencies by chance alone? a. Disruptive selection b. Stabilizing selection c. Genetic drift d. Both a and b 7. Which statement about genetic drift is false? a. It affects allele frequencies the most when populations are small. b. It ...
... c. Genetic drift d. Both a and b 6. Which process changes allele frequencies by chance alone? a. Disruptive selection b. Stabilizing selection c. Genetic drift d. Both a and b 7. Which statement about genetic drift is false? a. It affects allele frequencies the most when populations are small. b. It ...
Lesson Four, Theory: An Introduction to Mendelian Genetics Lesson
... recognize the phenotypic results of a genetic cross and use this information to infer the inheritance pattern for a trait. ...
... recognize the phenotypic results of a genetic cross and use this information to infer the inheritance pattern for a trait. ...
Chapter 21~The Evolution of Populations
... Evolution Natural selection acts on trait variation, and trait variation is determined by genes. Whether or not a trait gives an advantage depends on the environment. Thus genes, traits, environment, and natural selection are all involved in microevolution. Microevolution occurs when allele fre ...
... Evolution Natural selection acts on trait variation, and trait variation is determined by genes. Whether or not a trait gives an advantage depends on the environment. Thus genes, traits, environment, and natural selection are all involved in microevolution. Microevolution occurs when allele fre ...
population genetics File
... Sometimes one or a few individuals disperse and become the founders of a new, isolated population at some distance from their place of origin. These pioneers are not likely to have all the alleles present in the source population. In some cases, previously rare alleles in the source population ...
... Sometimes one or a few individuals disperse and become the founders of a new, isolated population at some distance from their place of origin. These pioneers are not likely to have all the alleles present in the source population. In some cases, previously rare alleles in the source population ...
Allele Frequencies _ Hardy Weinberg
... Natural Selection which acts on the phenotype rather than the genotype of an organism. ...
... Natural Selection which acts on the phenotype rather than the genotype of an organism. ...
Intro to grass flowers
... duplicate genes acquire debilitating yet complementary mutations that alter one or more subfunctions of the single gene progenitor ...
... duplicate genes acquire debilitating yet complementary mutations that alter one or more subfunctions of the single gene progenitor ...
ppt - Language Log
... The first 30 years of the 20th Century were marked by the accumulation of enormous amounts of information about genetic processes. It was recognized by a number of geneticists that this information provided the missing answers needed to support Darwinian evolution. In 1942, Julian Huxley (grandson o ...
... The first 30 years of the 20th Century were marked by the accumulation of enormous amounts of information about genetic processes. It was recognized by a number of geneticists that this information provided the missing answers needed to support Darwinian evolution. In 1942, Julian Huxley (grandson o ...
7th Evolution Population Genetics.key
... – A change in the DNA sequence that affects genetic information ...
... – A change in the DNA sequence that affects genetic information ...
Ways to look at issues of free will and determinism, baed on current
... endless numbers of these in both 2 -dimensional and 3 -dime nsional systems. Among the simpler results that can be se en in eve n 2 -dimensional models is t hat certain clusters of boxe s c an persist , and can evolve to become safer from c lusters that tend to knock them apart . F or example , they ...
... endless numbers of these in both 2 -dimensional and 3 -dime nsional systems. Among the simpler results that can be se en in eve n 2 -dimensional models is t hat certain clusters of boxe s c an persist , and can evolve to become safer from c lusters that tend to knock them apart . F or example , they ...
Evolution Outline Dec 8-19
... o describe the research and contributions of Lamarck, Wallace and Darwin Selection o compare artificial, natural and sexual selection o describe the three types of natural selection (directional, stabilizing and disruptive) o describe the two types of sexual selection (competition and mate choice) o ...
... o describe the research and contributions of Lamarck, Wallace and Darwin Selection o compare artificial, natural and sexual selection o describe the three types of natural selection (directional, stabilizing and disruptive) o describe the two types of sexual selection (competition and mate choice) o ...
Natural Selection
... occurs when an egg and a sperm unite. Both carry unique traits from the parents into one individual, forming an individual which varies from either parent. – This variation is normally a random event. – In our example, let’s say two mutated animals mate with one another. Let’s look at their offsprin ...
... occurs when an egg and a sperm unite. Both carry unique traits from the parents into one individual, forming an individual which varies from either parent. – This variation is normally a random event. – In our example, let’s say two mutated animals mate with one another. Let’s look at their offsprin ...
Group selection

Group selection is a proposed mechanism of evolution in which natural selection is imagined to act at the level of the group, instead of at the more conventional level of the individual.Early authors such as V. C. Wynne-Edwards and Konrad Lorenz argued that the behavior of animals could affect their survival and reproduction as groups.From the mid 1960s, evolutionary biologists such as John Maynard Smith argued that natural selection acted primarily at the level of the individual. They argued on the basis of mathematical models that individuals would not altruistically sacrifice fitness for the sake of a group. They persuaded the majority of biologists that group selection did not occur, other than in special situations such as the haplodiploid social insects like honeybees (in the Hymenoptera), where kin selection was possible.In 1994 David Sloan Wilson and Elliott Sober argued for multi-level selection, including group selection, on the grounds that groups, like individuals, could compete. In 2010 three authors including E. O. Wilson, known for his work on ants, again revisited the arguments for group selection, provoking a strong rebuttal from a large group of evolutionary biologists. As of yet, there is no clear consensus among biologists regarding the importance of group selection.