Solving Right Triangles Using Trigonometric Ratios
... Mathematically proficient students start by explaining to themselves the meaning of a problem and looking for entry points to its solution. They analyze givens, constraints, relationships, and goals. They make conjectures about the form and meaning of the solution and plan a solution pathway rather ...
... Mathematically proficient students start by explaining to themselves the meaning of a problem and looking for entry points to its solution. They analyze givens, constraints, relationships, and goals. They make conjectures about the form and meaning of the solution and plan a solution pathway rather ...
Name - SFP Online!
... 2) In right triangle ABC, the right angle is at C and altitude CD is drawn to hypotenuse AB. If AD = 3 and DB = 9, find AC. ...
... 2) In right triangle ABC, the right angle is at C and altitude CD is drawn to hypotenuse AB. If AD = 3 and DB = 9, find AC. ...
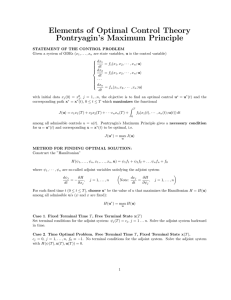
Elements of Optimal Control Theory Pontryagin’s Maximum Principle
... Many insects, such as wasps (including hornets and yellowjackets) live in colonies and have an annual life cycle. Their population consists of two castes: workers and reproductives (the latter comprised of queens and males). At the end of each summer all members of the colony die out except for the ...
... Many insects, such as wasps (including hornets and yellowjackets) live in colonies and have an annual life cycle. Their population consists of two castes: workers and reproductives (the latter comprised of queens and males). At the end of each summer all members of the colony die out except for the ...
Weber problem

In geometry, the Weber problem, named after Alfred Weber, is one of the most famous problems in location theory. It requires finding a point in the plane that minimizes the sum of the transportation costs from this point to n destination points, where different destination points are associated with different costs per unit distance.The Weber problem generalizes the geometric median, which assumes transportation costs per unit distance are the same for all destination points, and the problem of computing the Fermat point, the geometric median of three points. For this reason it is sometimes called the Fermat–Weber problem, although the same name has also been used for the unweighted geometric median problem. The Weber problem is in turn generalized by the attraction–repulsion problem, which allows some of the costs to be negative, so that greater distance from some points is better.