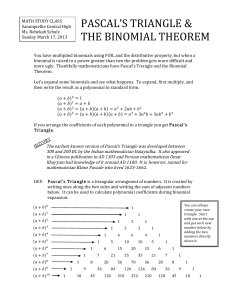
8-1 Geometric Mean
... The geometric mean is created when a proportion is set up, crossmultiplied and solved for x. ...
... The geometric mean is created when a proportion is set up, crossmultiplied and solved for x. ...
Weber problem

In geometry, the Weber problem, named after Alfred Weber, is one of the most famous problems in location theory. It requires finding a point in the plane that minimizes the sum of the transportation costs from this point to n destination points, where different destination points are associated with different costs per unit distance.The Weber problem generalizes the geometric median, which assumes transportation costs per unit distance are the same for all destination points, and the problem of computing the Fermat point, the geometric median of three points. For this reason it is sometimes called the Fermat–Weber problem, although the same name has also been used for the unweighted geometric median problem. The Weber problem is in turn generalized by the attraction–repulsion problem, which allows some of the costs to be negative, so that greater distance from some points is better.