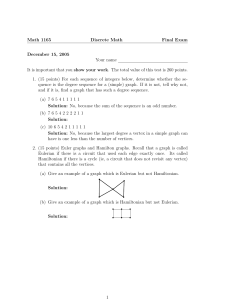
01 - University of South Carolina
... 3. The set of numbers between but not including 2 and 7 can be written as follows: Solution. (a) {x ∈ R | 2 < x < 7} in set builder notation. (b) (2, 7) in interval notation. 4. Explain the differences between the following two sets: A = [−2, 5] and B = (−2, 5). Solution. The set A contains the endp ...
... 3. The set of numbers between but not including 2 and 7 can be written as follows: Solution. (a) {x ∈ R | 2 < x < 7} in set builder notation. (b) (2, 7) in interval notation. 4. Explain the differences between the following two sets: A = [−2, 5] and B = (−2, 5). Solution. The set A contains the endp ...
Math 230.01, Fall 2012: HW 1 Solutions
... e) If M is the maximum of the two numbers, then P (M = 1) + P (M = 2) + P (M = 3) + P (M = 4) = 1, check that your answers for c) and d) satisfy this relationship. SOLUTION: Indeed, if the maximum is equal to i, then the upper face of at least one die must be i (there are two possibilities for which ...
... e) If M is the maximum of the two numbers, then P (M = 1) + P (M = 2) + P (M = 3) + P (M = 4) = 1, check that your answers for c) and d) satisfy this relationship. SOLUTION: Indeed, if the maximum is equal to i, then the upper face of at least one die must be i (there are two possibilities for which ...
Objectives - Katy Tutor
... • Prove that two triangles are congruent using the HL shortcut • Use Corresponding Parts in Congruent Triangles are Congruent (CPCTC) in ...
... • Prove that two triangles are congruent using the HL shortcut • Use Corresponding Parts in Congruent Triangles are Congruent (CPCTC) in ...
practice paper:Class:X:Maths-1
... There is no overall choice. However, internal choice has been provided in one question of 02 marks each, three questions of 03 marks each and two questions of 06 marks each. You have to attempt only one of the alternatives in all such questions. ...
... There is no overall choice. However, internal choice has been provided in one question of 02 marks each, three questions of 03 marks each and two questions of 06 marks each. You have to attempt only one of the alternatives in all such questions. ...
Weber problem

In geometry, the Weber problem, named after Alfred Weber, is one of the most famous problems in location theory. It requires finding a point in the plane that minimizes the sum of the transportation costs from this point to n destination points, where different destination points are associated with different costs per unit distance.The Weber problem generalizes the geometric median, which assumes transportation costs per unit distance are the same for all destination points, and the problem of computing the Fermat point, the geometric median of three points. For this reason it is sometimes called the Fermat–Weber problem, although the same name has also been used for the unweighted geometric median problem. The Weber problem is in turn generalized by the attraction–repulsion problem, which allows some of the costs to be negative, so that greater distance from some points is better.