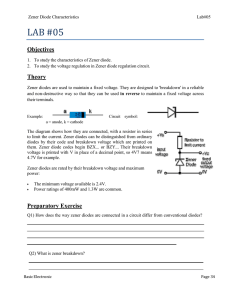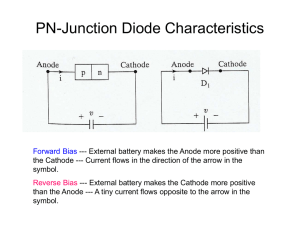
Diode Characteristics
... depletion region of the junction tb is the time to remove the charge stored in the bulk semiconductor material ...
... depletion region of the junction tb is the time to remove the charge stored in the bulk semiconductor material ...
4 - Binus Repository
... The superposition principle applies to phasor responses only if all of the independent sources driving the circuit have the same frequency. That is , when the input sources have the same frequency, we can find the phasor response due to each source acting alone and obtain the total response by addin ...
... The superposition principle applies to phasor responses only if all of the independent sources driving the circuit have the same frequency. That is , when the input sources have the same frequency, we can find the phasor response due to each source acting alone and obtain the total response by addin ...
RB471E
... No copying or reproduction of this document, in part or in whole, is permitted without the consent of ROHM Co.,Ltd. The content specified herein is subject to change for improvement without notice. The content specified herein is for the purpose of introducing ROHM's products (hereinafter "Products" ...
... No copying or reproduction of this document, in part or in whole, is permitted without the consent of ROHM Co.,Ltd. The content specified herein is subject to change for improvement without notice. The content specified herein is for the purpose of introducing ROHM's products (hereinafter "Products" ...
The following should be included in your experimental checklist
... load down the input. (This is similar to the minimal effect that measuring with the scope has on a circuit.) On the output side, the circuit sees the buffer as an ideal source with no internal resistance. The magnitude and frequency of this source is equal to Vin, but the power is supplied by ± VCC. ...
... load down the input. (This is similar to the minimal effect that measuring with the scope has on a circuit.) On the output side, the circuit sees the buffer as an ideal source with no internal resistance. The magnitude and frequency of this source is equal to Vin, but the power is supplied by ± VCC. ...
Period 12 Activity Sheet Solutions: Electric Circuits
... Screw in bulb #3. Bulbs #2 and #3 are now connected in parallel. Bulb #1 is connected in series to the parallel network of bulbs #2 and #3. Close the switch. 1) Are the 3 bulbs equally bright? If not, which one is the brightest? _bulb #1_ 2) Measure the voltage drop across each bulb with a digital m ...
... Screw in bulb #3. Bulbs #2 and #3 are now connected in parallel. Bulb #1 is connected in series to the parallel network of bulbs #2 and #3. Close the switch. 1) Are the 3 bulbs equally bright? If not, which one is the brightest? _bulb #1_ 2) Measure the voltage drop across each bulb with a digital m ...
Ch04220
... and the current through Rp are not the same! 3. The most common mistake made in applying source transformation is not observing the correct polarity of the two sources for equivalence. The polarity of the voltage source vs in one form must be such that it tends to make the current flowing in the dir ...
... and the current through Rp are not the same! 3. The most common mistake made in applying source transformation is not observing the correct polarity of the two sources for equivalence. The polarity of the voltage source vs in one form must be such that it tends to make the current flowing in the dir ...
English - Det
... 2. Remove the communication module from the junction box. Connect external system wiring to the appropriate terminals on the terminal block inside the junction box. See Figure 2 for terminal block location and Figure 3 for terminal identification. The input to the IDC consists of one or more normall ...
... 2. Remove the communication module from the junction box. Connect external system wiring to the appropriate terminals on the terminal block inside the junction box. See Figure 2 for terminal block location and Figure 3 for terminal identification. The input to the IDC consists of one or more normall ...
What is an Electric Circuit?
... 5. Get together with another team that measured voltage on a different type of circuit. Does the graph of voltages look the same for each type of circuit? Explain. [Answer: No. In the parallel circuit, the voltages the same – the battery voltage is the same as each bulb voltage. In the series circui ...
... 5. Get together with another team that measured voltage on a different type of circuit. Does the graph of voltages look the same for each type of circuit? Explain. [Answer: No. In the parallel circuit, the voltages the same – the battery voltage is the same as each bulb voltage. In the series circui ...
Network analysis (electrical circuits)

A network, in the context of electronics, is a collection of interconnected components. Network analysis is the process of finding the voltages across, and the currents through, every component in the network. There are many different techniques for calculating these values. However, for the most part, the applied technique assumes that the components of the network are all linear.The methods described in this article are only applicable to linear network analysis, except where explicitly stated.