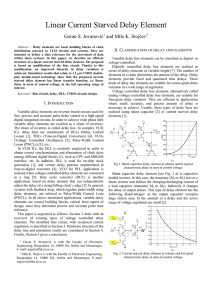
HS3DPG: Hierarchical Simulation for 3D P/G Network
... interconnect delay, and high leakage power. Three-dimensional (3D) integration has been regarded as a promising solution to mitigate these problems mentioned above [1]–[3]. Compared with the traditional 2D integration, the 3D technology can offer many benefits such as the reduction in interconnect wi ...
... interconnect delay, and high leakage power. Three-dimensional (3D) integration has been regarded as a promising solution to mitigate these problems mentioned above [1]–[3]. Compared with the traditional 2D integration, the 3D technology can offer many benefits such as the reduction in interconnect wi ...
Errors Due to Shared Leadwires in Parallel Strain Gage Circuits
... leadwire resistance in this fashion not only solves the initial imbalance and leadwire temperature problems, but also reduces the calibration and crosstalk errors. However, it should be noted that if the resistance of the common leadwire is less than 1/n times that of the individual return leadwires ...
... leadwire resistance in this fashion not only solves the initial imbalance and leadwire temperature problems, but also reduces the calibration and crosstalk errors. However, it should be noted that if the resistance of the common leadwire is less than 1/n times that of the individual return leadwires ...
Methodology for relative location of voltage sag source using
... this work, only the positive sequence voltage is chosen as a variable that could determine the relative location of voltage sags source. Fig. 1.a illustrates a one-line diagram of a radial distribution system. The network is parameterized by impedances between buses, voltage power quality monitors ( ...
... this work, only the positive sequence voltage is chosen as a variable that could determine the relative location of voltage sags source. Fig. 1.a illustrates a one-line diagram of a radial distribution system. The network is parameterized by impedances between buses, voltage power quality monitors ( ...
Nat 4-5 Unit 2 Section 1 pupil notes update Electrical Circuits
... atom is free to wander from one atom to another. When a battery is connected across a conductor these free electrons all move in ________ direction, forming an electric current. In insulators (_________________), the outermost electrons of each atom are tightly bound to the atom. There are no free e ...
... atom is free to wander from one atom to another. When a battery is connected across a conductor these free electrons all move in ________ direction, forming an electric current. In insulators (_________________), the outermost electrons of each atom are tightly bound to the atom. There are no free e ...
INTRODUCTION
... mA without going offscale we can, in theory, set the value of RDB exactly equal to the value of RM 2 . In this case a current of 2 mA flowing through M 2 will split evenly between the branch containing RDB and the branch containing the analog multimeter. Thus the 2 mA current through M 2 will result ...
... mA without going offscale we can, in theory, set the value of RDB exactly equal to the value of RM 2 . In this case a current of 2 mA flowing through M 2 will split evenly between the branch containing RDB and the branch containing the analog multimeter. Thus the 2 mA current through M 2 will result ...
Network analysis (electrical circuits)

A network, in the context of electronics, is a collection of interconnected components. Network analysis is the process of finding the voltages across, and the currents through, every component in the network. There are many different techniques for calculating these values. However, for the most part, the applied technique assumes that the components of the network are all linear.The methods described in this article are only applicable to linear network analysis, except where explicitly stated.