* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download BBproject - WordPress.com
Wien bridge oscillator wikipedia , lookup
Crystal radio wikipedia , lookup
Power MOSFET wikipedia , lookup
Electronic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Immunity-aware programming wikipedia , lookup
Transistor–transistor logic wikipedia , lookup
Power electronics wikipedia , lookup
Schmitt trigger wikipedia , lookup
Radio transmitter design wikipedia , lookup
Valve audio amplifier technical specification wikipedia , lookup
Charlieplexing wikipedia , lookup
Operational amplifier wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Surge protector wikipedia , lookup
Two-port network wikipedia , lookup
Current mirror wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Flexible electronics wikipedia , lookup
Index of electronics articles wikipedia , lookup
Valve RF amplifier wikipedia , lookup
Regenerative circuit wikipedia , lookup
RLC circuit wikipedia , lookup
Integrated circuit wikipedia , lookup
Rectiverter wikipedia , lookup
Network analysis (electrical circuits) wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
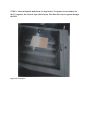
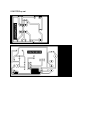
VIVEKANAND EDUCATION SOCIETY’S POLYTECHNIC CHEMBUR,MUMBAI-400071 INFRA RED BASED SECURITY CONTROL SYSTEM A PROJECT REPORT Submitted by AKSHAY BHOPANI AADITYA AUROBINDO VIJAYA KAMBLE ATUL MALUSARE SAURAB KADAM In partial fulfillment for the award of the degree Of DIPLOMA IN ELECTRONICS & TELECOMMUNICATION ENGINEERING Guided by MS. PRAJAKTA KALE ACKNOWLEDGEMENT With a sense of gratitude and respect, I would like to extend my heartiest thanks to my guide Ms. Prajakta Kale for her genuine interest and constant motivation during the entire project duration . I think her for her highly innovative suggestion and active and dedicated involvement throughout the work. I am also thankful to Mr.VikrantJoshi,Principle,V.E.S.Polytechnic for his constant encouragement throughout the course of project work. Lastly , but the most important of all I would like our Lab Assistant Mr.Dinesh Sir for his constant support. He helped us totally in our project work. CONTENTS List of Figures List of Tables ABSTRACT 1.INTRODUCTION 1.1 Timer technology 1.2 IR technology 1.3 Objective of the study: 1.4 Review of the project: 2.DIAGRAMATIC DESCRIPTION 2.1 BLOCK DIAGRAM 3.CIRCUIT DIAGRAM 3.1 Circuit diagram 3.2 Circuit Diagram Working 4.LISTS OF COMPONENTS AND DESCRIPTION 4.1 Components List 4.2 DESCRIPTION OF COMPONENT 4.2.1 IC 555 5.PCB MAKING 5.1 Printed Circuit Board 5.2 PCB Layout Designing 5.3 Making Layout Using EAGLE 5.4 PCB Designing Rules 5.5 PCB Etching 5.6 PCB Drilling 5.7 Drilling Process 5.8 Soldering 5.9 Cold Solder Joints 5.10 Top View of Board 5.11 PCB Layout 6. ALGORITHM, FLOWCHART & PROGRAMMING 6.1 ALGORITHM 6.2 FLOWCHART 6.3 PROGRAMMING 7. TROUBLESHOOTING AND TESTING 7.1 Troubleshooting 7.1.1 Need of Troubleshooting 7.1.2 Steps prior to troubleshooting 7.1.3 Troubleshooting Steps 7.2 TROUBLESHOOTING OF OUR PROBLEMS 8. MERITS , DEMERITS , APPLICATIONS AND FUTURE IMPROVEMENTS 8.1 Merits 8.2 Demerits 8.3 Applications 8.4 Future Improvements CONCLUSION BIBLIOGRAPHY List of Figures Figure2.1: Block Diagram of Project Figure3.1: Circuit diagram Figure5.2: Cleaning of PCB Figure5.3: Dip coat Figure5.4: PCB Oven Figure5.5: UV Exposer Figure5.6: Agitating PCB Figure5.7: Easy Etcher Figure5.10: Top view of board Figure5.11: PCB Layout of project List of Tables Table 4.1: Component list ABSTRACT The novel idea of this project is to provide a cheap and reliable security system using infra red. Also in this project we will be providing live streaming of videos of the area protected by our security system. Here we use mobile phones as a web cam for live streaming videos. It is based on the motion detection and control system action principle. As soon as motion is detected the control system will take appropriate action. It will make home light blink and buzzer activation. Doors would be closed automatically and theft seen would be captured in image. An automatic sms would be send to defined number. So in this way full security will be maintained. It is based on following principle – 1- It is used to sense intrusion. 2- When there is no intrusion the output is low. 3- When there is intrusion the output is high. 4- To indicate intrusion we can connect any circuit. CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION 1.1 Timer technology This integrated circuit is used for timing. Many circuits are composed of timers and the most common of them all is the 555 Integrated Circuit. It is used in many commercially manufactured items such as video recorders and timers.You must understand the basic workings of this important IC. The 555 has eight pins (legs) but the function of two are very important. These are pin two and three. This chip is used in timing circuits. It is a timer. When the switch is pressed a current / voltage goes into the IC through pin two (the input pin). The chip starts counting and when it has finished counting it ‘pulses’ a current or voltage from pin three (the output pin). This voltage from pin three switches a transistor and allows the LED to light.The time from pressing the switch to the LED lighting could be anything from 1 second to twenty minutes. A 555 will switch on a range of components not only LEDs. For example, it can switch on a relay which then allows a second circuit to work.The circuit shown opposite is a simple version of a real 555 circuit. The real circuit includes resistors and capacitors. (See following sheets).The 555 integrated circuit acts as a counter. When activated by current entering in through pin 2, it starts to count for a certain amount of time. When it has finished counting it emits current from pin 3. This usually activates other components such as LEDs or relays.When the push switch is pressed it allows current to flow into pin 2, starting the timing sequence. The combination of the resistor and capacitor determines the length of the timing sequence. In general terms, if the resistor and capacitor values are high the timing sequence is long. If the values are low the timing sequence is short. The transistor acts as a very sensitive switch. When current enters the base electricity can flow from the collector to the emitter. this allows the LED light.The LED lights when current flows through it. In this circuit it indicates when pin three is emitting current. 1.2 IR technology Infrared (IR) technology addresses a broad variety of wireless applications, especially in the areas of sensing and remote control. Today’s newest products, such as cell phones, digital cameras, and DVD players as well as remote controls for every market segment, rely on IR sensing and control devices. For more than 40 years, ROHM Semiconductor has been driving technology advances that have led to a growing number of IR sensing and communication applications. To understand infrared technology, the best starting point is the electromagnetic spectrum. The frequency range and wavelengths of the entire spectrum are shown in Figure 1. The IR portion of the electromagnetic spectrum is usually divided into three regions: the near-, midand far- infrared. The wavelengths for these regions are shown in Table 1. Infrared wavelengths range from red to violet. The frequencies are higher than microwave but shorter than visible light. Focusing on near-infrared devices and applications, PhotoOptic technologies are used for optical sensing and optical communications with numerous general market applications, since light is less complex than RF when implemented as the signal source. Optical sensors are used in industrial, consumer and other applications for sensing movement, position, proximity, ambient light, speed, and direction. Optical wireless communication uses IR data transmission for short range applications, such as computer peripherals and PDAs (personal digital assistants). For optical communication, a modulated IR light beam transmitted by an emitter LED is received by a silicon photodiode. Infrared Data Association (IrDA) standards provide the protocol for these types of communication. Since IR does not penetrate walls, it does not interfere with other signals in indoor environments. IR technology is the most commonly used technique for remotely controlling appliances. Some general applications for IR components include: Office Automation (OA) equipment such as copiers, fax machines, and printers Vending machines Gaming products Home entertainment products Medical / health care equipment Banking terminals such as ATMs Testing equipment such as IC/LSI testers, encoders, and more Types of IR devices To address the variety of sensing applications, products take advantage of several IR technologies including: IR Emitters IR Receivers (sensors) Photointerrupters and Photo Reflectors Tilt Sensors IrDA Communication Modules Remote Control Module Receivers A brief explanation of each shows the commonalities and differences. An IR Emitter is a light emitting diode (LED). Different types of IR LEDs are specified based on their packaging.IR Receivers are also called sensors since they detect the wavelength and spectral radiation of the light from the IR emitter. IR receivers are specified by optic features, packaging, special circuitry such as an ambient light filter, wide viewing angle, and more. As a wireless technology, IR has advantages and disadvantages when compared to RF and industrial, scientific, and medical (ISM) (902-928 MHz) band technologies. Advantages include: 1. Higher security: beam directionality helps ensure that data isn’t detected or leaked to nearby devices as it’s transmitted 2. High noise immunity: not as susceptible to signal interference from other devices 3. Few international regulatory constraints 4. Relatively low power requirements: ideal for laptops, cell phones, and personal digital assistants 5. Simple design implementation 1.3 Objective of the study: The main objective of this selecting project is to gain knowledge and experience in developing a real time application. Apart from this, to gain the knowledge of Ne555 timers, IR transmission and reception and the way in which videos can be live streamed. 1.4 Review of the project: Many books have provided valuable information that was very useful for this project. One such book authored byRamakantGayakwadtitled “Op-Amps and Linear Integrated Circuit”. CHAPTER 2 2.1 BLOCK DIAGRAM Our project aims at displaying messages on a LCD by sending messages through a mobile which are transmitted on the lcd through the GSM Module. We know the objective of our project, so we would now proceed to the block diagram of our project which will give us the operation and clear explanation of the signal flow. CHAPTER 3 CIRCUIT DIAGRAM 3.1 Circuit Diagram As we have already gone through the operation of project with the help of block diagram. Now let us have a view of the circuit diagram of our project. 3.1.1 IR Transmitter and Reciev 3.1.2 LED Flasher 3.2 Circuit diagram working 3.2.1 IR Motion detector Here is the circuit diagram of an infrared motion detector that can be used to sense intrusions. Infrared rays reflected from a static object will be in one phase, and the rays reflected from a moving object will be in another phase. The circuit uses this principle to sense the motion. The IC1 (NE 555) is wired as an astablemultivibrator. The IR diode connected at the output of this IC produces infrared beams of frequency 5Khz. These beams are picked by the infrared sensor, photo transistor Q1. At normal condition, that is, when there is no intrusion the output pin (7) of IC2 will be low. When there is an intrusion the phase of the reflected waveforms has a difference in phase and this phase difference will be picked by the IC2. Now the pin 7 of the IC 2 goes high to indicate the intrusion. An LED or a buzzer can be connected at the output of the IC to indicate the intrusion. 3.2.2 LED flasher This circuit uses the 555 timer in an Astable operating mode which generates a continuous output via Pin 3 in the form of a square wave. This turns the LED (D1) on and off. The speed at which the LED (D1) Parts List 1x - NE555 Bipolar Timer 1x - LED (Red) 1x - 470K Resistor (1/4W) 2x - 1K Resistor (1/4W) 1x - 1F Electrolytic Capacitor (16V) 1x - 9V Voltage Battery is turned on and off is set by the values of R1 and R2 CHAPTER 4 LISTS OF COMPONENTS & DESCRIPTION 4.1 Component List SR. NO. 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 TOTALRs. 302 Product Name Resistor 10k ohms 50k ohms 470k ohms 22k ohms 220 ohms 33 ohms 2.2k ohms 1k ohms Capacitors 1 uf 0.1 uf 0.01 uf o.47 uf Diodes IN 4148 IN 4001 1N 4007 IC 555 L14F LM1458 LED IR LED 12*12 PCB board / clad Jumper connectors wires Product cost * Quantity 1*1 1*1 1*1 1*1 1*1 1*1 1*1 1*1 1*1 1*1 1*1 1*1 1*1 1*1 1*1 5*3 80*1 10*2 1*3 10*2 85*1 8*8 4.2 DESCRIPTION OF COMPONENT 4.4.1 IC 555 The LM555 is a highly stable device for generating accurate time delays or oscillation. Additional terminals are provided for triggering or resetting if desired. In the time delay mode of operation, the time is precisely controlled by one external resistor and capacitor. For astable operation as an oscillator, the free running frequency and duty cycle are accurately controlled with two external resistors and one capacitor. The circuit may be triggered and reset on falling waveforms, and the output circuit can source or sink up to 200mA or drive TTL circuits. Features 1.Direct replacement for SE555/NE555 2.Timing from microseconds through hours 3.Operates in both astable and monostable modes 4,Adjustable duty cycle 5,Output can source or sink 200 mA 6,Output and supply TTL compatible 7,Temperature stability better than 0.005% per ̊C 8,Normally on and normally off output 9,Available in 8-pin MSOP package Applications Applications 1.Precision timing 2Pulse generation 3.Sequential timing 4.Time delay generation 5.Pulse width modulation 6.Pulse position modulation 7.Linear ramp generat CHAPTER 5 PCB MAKING 5.1 Printed Circuit Board Description: A printed circuit board is used to mechanically & electrically connect electrical components using conductive pathways, tracks traces etched from copper sheets laminated on to conductive substrate. As such, most of today’s PCB is not pushing, if nor exceeding, the limits of classic board design. In mobile telecom for example, interconnect and board dimension are shrinking rapidly, while designs are utilizing fewer, but more complex (and higher pin-count) components. At the same time, boards for networking and computer are getting larger, with more interconnect and plane layers. In order to produce higher quality, more complex products, quicker and more cost efficiently than their competition, companies are taking inventory of their PCB design tools. Understanding which tools best support the needs of design teams is key to determining the proper infrastructure investment, required services, support structure and intellectual skill set of the company. Advanced functionality already exists in today’s leading design tools to solve current and future design challenges. Therefore, companies effectively utilizing the proper design tools have an advantage over those companies using dated technology to design their boards-the inherent ability to automatically solve design challenges without workarounds or short term, inefficient solutions. PCB Materials: Laminate materials: • • FR-4, the most common PCB material. FR-2 • Composite epoxy material, CEM-1,5 • Polyimide. • BT-epoxy. • Cyan ate Ester. • PTFE, Polytetrafluoroethylene(Teflon) • Conductive ink • Heavy copper 5.2 PCB Layout Designing PCB LAYOUT SOFTWARES: • Altium Designer by Altium Limited • Autotrax • EAGLE by Cad Soft • Dip Trace by Novarm • Edwinxp • Free PCB by Allan Wright(open-source Ein2k/XP) • Free routing by alfonswirtz • Cadstar by zuken • CR5000 by zuken • Multisim • Geda, open source PCB software project • OrCAD by cadence • Allergo by cadence • TARGET 3001! • Kicad, open source suite • PADS by mentor graphics • PCB123 design by sunstone circuits • Proteus • Board station by mentor graphics • Expedition enterprise by mentor graphics 5.3 Making Layout Using EAGLE Here is the procedure of designing the layout using eagle software: • Setting up initial settings: this stage of pcb designing involves setting up snaps and visble grid. At this stage the default track and pad sixe should be set. • Set the mechanical elements of the pcb design: It is necessary to import the details for the circuit board outline into the pcb layout software program as soon as possible. It is also necessary to set up any reference marks and holes. These may be required for pick and place machines, of test fixtures during the production process. • Putting all components on the board: At this stage of the pcb layout, the components need to be placed onto the printed circuit board so that they are available to be moved and set I place later. • Creating functional building blocks: At this stage of pcb layout, the components should be moved into their functional blocks so that associated components are close to each other and the circuit can be routed easily later. • Identifying and routing layout critical tracks: Any tracks that are layout critical shoukd be identified and then routed as they are required. By routing these tracks at this stage, then the remained of the design can be implemented around these tracks rather than trying to resolve problems later in the pcb layout. • Routing power and earth rails: Often the earth and power rails may be included as planes, occupying a complete layer of the printed circuit board. This has significant advantage not only in terms of enabling the higher levels of current to be routed easily, but it also significantly reduces any problem with interference on the printed circuit board. • Routing the remaining lines: Usually it is necessary to use the auto-route function on the pcb layout software, it is normal to use the auto-route function’s this may save many days trying to rout the pcb layout manually. • Manually routing any final line on the pcb layout: After the pcb layout software has completed the auto-ranging, there may be routed manually. Alternatively if the design has become too complicated for the space and available numbers of layers, it may be necessary to make some fundamental changes to the board. • Undertaking final tidy up: Once all the design rules should have been followed during the design, it is necessary to do a final check. It is better to catch any problems at this stage rather than once a prototype pcb has been made. Thus we completed the pcblayout designing process. 5.4 PCB Designing Rules • While designing a layout, it must be noted that size of the board should be as small as possible. 2. Before starting, all components should be placed properly so that an accurate measurement of space can be made. 3. The component should not be mounted very close to each other or far away from one another and neither one should ignore the fact that some component need ventilation, which considerably the dimension of the relay and transformer in view of arrangement, the bolting arrangement is also considered. 4. The layout is first drawn on paper then traced on copper plate which finalized with the pen or permanent marker which is efficient and clean with etching. 5. The resistivity also depends on the purity of copper, which is highest for low purity of copper. The high resistance paths are always undesired for soldered connections. 6. The most difficult part of making an operation, it provides greater amount of satisfaction because it is carried out with more care and skill. 7. The board used for project has copper-foil thickness in range of 25 40 75 microns. 8. The soldering quality requires 99.99% efficiency. 9. It is necessary to design copper path extra large. There are two main reasons for this. 10. The copper may be required to carry an extra large overall current. 11. It acts like a kind of a screen or ground plane to minimize the effect of interaction. 12. The first function is to connect the components together in there right sequence with minimum need for interlinking i.e. the jumpers with wire connections. 13. It must be noted, that when layout is done, on the next day it should be dripped in the solution and board is moved continuously right and left after etching perfectly the board is cleaned with water and is drilled. 14. After that holes are drilled with 1mm or 0.8mm drilled. 15. The printed circuit board is now ready for mounting the components on it. 5.5 PCB Etching STEP-1:- After cutting the copper clad sheet to size, the PCB is cleaned with thinner, so that the dust on the PCB is removed and we get a shiny surface. Then we insert the PCB in Dip coat, that is, negative photo resistive material. Figure 5.2 PCB being scrubbed clean Figure 5.3 PCB coated in negative photoresist STEP-2:- The photo resistive material should be made hard on the PCB for which the PCB is kept in the oven for four minutes. Figure 5.4 PCB Oven STEP-3:- After the liquid is made hard, it is kept in the UV exposure for two minutes. In the UV exposure, the circuit is kept with its layout. The ultraviolet rays are passed through the PCB. Figure 5.5: UV Exposer STEP-4:- Thm we have to expose out PCB to nail polish remover solution which is also called as developer liquid. As a result of this an impression of tracks is formed on the PCB. Repeat the STEP-2, in which the PCB is kept in the oven for four minutes. Figure 5.6: Agitating PCB STEP-5:- After removing the PCB from the oven, the tracks on the PCB will be developed. After this the PCB is dipped into the PRITO-ETCH for five minutes. The solution used in the PEORO-ETCH is feriic chloride. Due to this tracks are fully developed on the PCB. Figure 5.7: Easy Etcher STEP-6:- The PCB is then washed in water and cleaned with the help of a cloth. 5.6 PCB Drilling Description: holes through a PCB are typically drilled with tiny drill bits made of solid tungsten carbide. The drilling is performed by the automated drilling machines with placement controlled drill (NCD) files or “Excellon”. The drill file describes the location and size of each drilled hole. These holes are often filled with annular rings (hollow rivets) to create via. Allow the electrical and thermal connection of conductors on opposite sides of PCB. Most common laminate is epoxy filled fiberglass. Drill bit wear is in part due to the fact that glass, being harder than steel on the Mohs scale, can scratch steel. High drill speed necessary for cost effective drilling of hundreds of holes per board causes very high temperatures at the laminate fiber. Copper is softer than epoxy and interior conductors may suffer damage during drilling. When very small via are required, drilling the mechanical bits is costly because of high rates of wear and breakage. In this case, the via may be evaporated by lasers. Laser-drilled via typically have an inferior surface finish inside the holes. These holes are called micro via. It is also possible with controlled-depth drilling, laser drilling, or by pre-drilling the individual sheets of the PCB before the lamination, to produce holes that connect only some of the copper layers, rather than passing through the entire board. These holes are called blind via when they connect an internal copper layer to an outer layer, or buried via when they connect two or more internal copper layers and no outer layers. The walls of the holes, for boards with or more layers, are made conductive then plated with the copper to form plated-through holes that electrically connect the conducting layers of the PCB. For multilayer boards those with layers or more, drilling typically produces a smear of the high temperature decomposition products of binding agent in the laminate desmear process, or by plasma-etch. Removing (etching back) the smear also reveals the interior conductors as well. 5.7 Drilling Process 1. First the PCB is placed on the drilling machine and drill bit is inserted. We used the drill bit of 0.8mm. 2. The PCB is placed in such a way that the drill bit is exactly on the top of the place where we need to drill. 3. Then, the machine is turned on and the handle is to pressed down to drill on the PCB. 4. Care should be taken while drilling that PCB is firmly held or else it will come up into the drill bit. 5. After drilling first hole we checked whether the component is getting inserted in the hole or not. Some components like diodes and TSOP had thick leads which were not able to get into the hole. 6. For this we changed the drill bit to 1mm and drilled those holes again so that components were properly inserted. 5.8 Soldering Steps: • For soldering of nay joints first the terminal to be soldered are cleaned to remove oxide film or dirt on it. If required flux is applied on the points to be soldered. • Now the joint to be soldered is heated with the help of soldering iron. Heat applied should be such that when soldered is touched to joint, it must melt quickly. • The joint and the soldering iron are held such that the molten solder should flow smoothly over the joint. • When joint is completely covered with molten solder the soldering iron is removed. • The bright shining solder indicates good soldering. • In case if dry solder join, and air gap remains in between the solder material and joint. It means that soldering is improper. This is removed and again soldering is done. • In case of dry solder join, and air gap remains in between the solder material and joint. It means that soldering is improper. This is removed and again soldering is done. • In this way all the components are soldered on PCB. 5.9 Cold Solder Joints 1. A “cold solder joint” can occur when not enough heat is applied to the component, board, or both. Another common cause is a component moving before the solder has completely cooled and solidified. A cold joint is brittle and prone to physical failure. It is also generally a very high resistance connection which can effect the operation of the circuit or cause it to fail completely. 2. Cold joints can often be recognized by a characteristic grainy, dull gray color, but this is not always the case. A cold joint can often appear as a ball of solder sitting on the pad and joint may even move. Below is the shocking image of every example of a bad solder joint you will ever see. It appears that this FM transmitter kit was assembled using the technique of apply solder to iron then drip onto joint”. If your joints are looking like this, then stop and practice after rereading this page. Note that not a single of these joints is acceptable, but amazingly, the circuit worked. 3. Most cold solder joints can be easily fixed. Generally all that is required to reheat the joint and apply a little more solder. If there is already too much solder on the joint, then the joint will have to be de-soldered and then soldered again. This is done by first removing the old solder with a de-soldering tool or simply by heating it up and flicking it off with the iron. Once the old solder is off, you can re-solder the joint, making sure to heat it thoroughly and keep it still as it cools. 5.10 Top View of Board 5.11 LED Flasher 5.12 IR transmitter 5.13 IR reciever 5.14 PCB Layout CHAPTER 6 ALGORITHM, FLOWCHART & PROGRAMMING 6.1 ALGORITHM 1. Switch on the power supply. 2. Check if the phone is switched on and if it is running the required app. 3. Check if there is an intrusion. 4. Send a positive voltage to LED flasher if there is intrusion 6.2 Flow chart Transmit IR to reciver IF no Is there any intrusion? If yes Positive voltage goes from the receiver to CHAPTER 7 the LED flasher and the LED begins TROUBLESHOOTING AND TESTING flashing. 7.1 Troubleshooting Description: Troubleshooting is a form of solving , often applied to repair failed circuits. It is a logical, schematic search for a source of a problem so that it can be solved, and circuit can be made operational again. Troubleshooting is needed to develop and maintain complex systems where the symptoms of a trouble can have many possible causes. Troubleshooting requires identification of the malfunction(s) or symptoms within the system and confirms the solution so that it can work again. 7.1.1 Need of Troubleshooting 1. Every product, circuit and instruments are designed to give desired output, but there are many problems associated with the design which tend to produce unexpected output. Therefore, for satisfactory performance, it needs to be troubleshooted so that the circuit can be made operational again. 2. Troubleshooting is needed to develop and maintain complex systems where the symptoms of problem can have many possible causes. 3. It is needed for identifying the symptoms and rectifying the problems so that it gives the desired output. 4. Troubleshooting is used in many fields such as engineering, systems administration, electronics, automotive repair and diagnostic medicine. 7.1.2 Steps prior to troubleshooting 1. Before applying power, read the instruction carefully to check we haven’t missed anything, and whether there are any specific instruction for switching on and testing. 2. Check again that we have all polarity sensitive components the right way around , and that all components are in the correct places. Then check whether off board components are connected correctly. 3. Check the underside of board for short circuit between tracks which is common reason for circuit failing to work. 4. When we are sure that everything is correct, apply power and see if the circuit behaves as expected. 7.1.3 Troubleshooting steps 1. Identify the system: Determine what the voltage level in circuit should be so that you know what to look for. 2. Power Check : The first thing to do while checking a defective circuit is to make sure the power cord is plugged in and the fuse is not burnt. In case of battery powered system, make sure the battery is good. 3. Perform sensory check: After power check, observe for the obvious defects. Example, poor solder connection, broken tracks, broken component and burnt out fuses. Also when certain type of component fail, may be able to detect a smell of smoke. Since some failures are detected by their temperature, unplug the circuit and immediately use your sense of touch to detect and overheated component. Always perform sensory check before proceeding with more sophisticated troubleshooting methods. Never touch operating circuit because there may be risk of burn or electric shock. 4. Signal tracing : In this we look for a point in the circuit or a system where we first lose signal or an incorrect signal first occurs. There are 3 ways of signal tracing as given below : a. Method 1: It starts at the input of a circuit where there is the known input signal work towards the output. Check the signal at successive test point until you get incorrect measurement, when it is found, the problem is isolated from the last test point to the present test points. b. Method 2: It starts at the output of the circuit and work towards the input. Check for the voltage at each test point until you get correct measurement. At this point you have isolated problem between the last point & the current test point. c. Method 3: This method is called half splitting. It starts at the middle of the test circuit . If a beginning of test point has a correct signal you know that circuit is working properly from input to that test point. This means that the fault is some ware between test point and the output. Therefore begin signal tracing from test points towards output and get the point at the fault. 5. Fault analysis: a. Voltage analysis: Afterperforming the visible testing if the problem still persists, then go for voltage analysis. In this method the voltage at different test points is checked. b. resistance analysis: In this analysis, power supply connected to the circuit must be switched when resistance is measured. Resistance analysis is generally used for continuity testing. Eg, check the continuity of PCB track from one test point to other or in case of double sided PCB it helps in checking the connectivity between the holes from both the sides. Similarly this can be used for testing the components such as diode, capacitor and transistor (e.g. open & short). This method requires the instrument such as DMM. c. Signal Analysis: Sometimes its important to observe the nature of the signal at the test point (e.gincase of rectifier). Whereas it is not possible in voltage analysis. By observing the waveform at the test point we can estimate the waveform distortion. For testing the circuit such as rectifier, multi vibrator, amplifier it is important to know the nature. Therefore signal analysis is done. For carrying signal analysis we require CRO. 6. Replace or repair : With the power turned off, replace the defective components or repair defective connections. Turn on the power, check the proper operation of the circuit. 7.2 TROULESHOOTING OF OUR PROBLEMS Testing refers to the initial phase of testing where the module is not yet connected to the wireless medium. This is the part of the testing process wherein we check if the MODEM receives the AT command from the microcontroller and makes its response in form of a new message, an ERROR message, or an OK message (all in form of bit strings). The oscilloscope probes are connected to P3.0 & P3.1 which are internally connected to the Tx& Rx lines of the microcontroller. In this at first we use transformer of 230V 500 mA but as we tested there was lot of voltage at the input of the circuit so there was loading effect & transformer was giving only 7V to the circuit instead of 12V and the bulb was not glowing as it was connected to the relay. So we troubleshooted the problem using the DMM and changed the transformer to 12V, 1A and thus we got proper voltage at the input of the circuit. CHAPTER 8 MERITS, DEMERITS, APPLICATION AND FUTURE IMPROVEMENTS 8.1 Merits 1. SIMPLE & EASY OPERATION 2. LESS EXPENSIVE The total cost of our project is quite less & is easy to initialise&setup even for a common man. 4. POWER EFFICIENT The power requirements of our project are quite less. The maximum power required by the circuit is 12 volts. 5. SMALL SIZE All the circuits are small enough to fit in the palm of an average human. 6. LIVE STREAMING POSSIBLE Live streaming of all the events occurring in the chosen area of application is possible. 8.2 Demerits As there are advantages, there are some limitations of this project. 1. HACKABLE Since the project features an android device it carries a potential to be hacked. 2. FALSE TRIGGER There stands a probability of the system to be falsely triggered. This may occur due to larger than average dust particles, pets, pests like rodents. 3. OWNER MONITORING DEVICES MUST BE SWITCHED ON For live streaming to be possible the owner must have a device(smartphone/pc) switched on. 8.3APPLICATION 1. Offices 2. Safes 3. Homes 4. Garages 5. Exhibits at museums etc. 8.4 Future Improvements With increased knowledge and budget the mobile phone can be replaced by a camera. It can be a point and shoot variant or even a DSLR. As new sensors enter the market they can be integrated into our project. CONCLUSION In India almost 98% of homes don’t have any security system apart from the traditional locks which can be picked very easily. Our project aims to provide a cheap and effective solution to this problem. The versatility of the project means that it can be applied in multiple ways. Safes, garages, homes, exhibits etc can be easily secured using our project. Videos can be streamed directly to the owner or any concerned figure with authority over the object/location under protection. In a situation that the security system fails to contain the thief/thieves the video can be used for facial recognition and later in the trial. The only Pre- requisite for this is that the person receiving the stream has to have his smartphone/pc switched on. Thus we can conclude that this project provides a economically suitable solution to the security problems of people with little disadvantages. BIBLIOGRAPHY Website: 1) http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Wikipedia 2) www.instructables.com 3) www.555timercircuits.com Books: 1) Electronics For you - Magazine 2)Op-Amps and Linear Integrated Circuit by RamakantGayakwad.