Conceptual Physics - Southwest High School
... through the loop of the external circuit will pass through a single resistor present in a single branch. When arriving at the branching location or node, a charge makes a choice as to which branch to travel through on its journey back to the low potential terminal. A short comparison and contrast be ...
... through the loop of the external circuit will pass through a single resistor present in a single branch. When arriving at the branching location or node, a charge makes a choice as to which branch to travel through on its journey back to the low potential terminal. A short comparison and contrast be ...
R - UniMAP Portal
... equivalency connected to two sources, the same load voltage and current are produced by both sources. Thevenin’s A method for simplifying a two-terminal theorem linear circuit to an equivalent circuit with only a voltage source in series with a resistance. Voltage source A device that ideally provid ...
... equivalency connected to two sources, the same load voltage and current are produced by both sources. Thevenin’s A method for simplifying a two-terminal theorem linear circuit to an equivalent circuit with only a voltage source in series with a resistance. Voltage source A device that ideally provid ...
Symmetric Gto And Snubber Component Characterization In Pwm
... fall of current ] is significantly less than the storage time ), then the commutation is solely load dependent. Thus, little or no current will be transferred to the snubber diode and the device voltage will not increase positively. Since the device is reverse biased during this interval, the P-dope ...
... fall of current ] is significantly less than the storage time ), then the commutation is solely load dependent. Thus, little or no current will be transferred to the snubber diode and the device voltage will not increase positively. Since the device is reverse biased during this interval, the P-dope ...
Electricity and Measurement Experiments
... 1.6 V coulomb) was “shared” between the globes the charge passed through. The total energy transformed into thermal energy and light as charge travelled along a single path through the circuit was equal to the potential energy change of the charge. In Circuit F, for example, when a coulomb of charge ...
... 1.6 V coulomb) was “shared” between the globes the charge passed through. The total energy transformed into thermal energy and light as charge travelled along a single path through the circuit was equal to the potential energy change of the charge. In Circuit F, for example, when a coulomb of charge ...
DPKC_Mod02_Part01_v06
... Imagine that we have a circuit, and a portion of the circuit can be identified, made up of one or more parts. That portion can be replaced with another set of components, if we do it properly. We call these portions equivalent circuits. Two circuits are considered to be equivalent if they behave the ...
... Imagine that we have a circuit, and a portion of the circuit can be identified, made up of one or more parts. That portion can be replaced with another set of components, if we do it properly. We call these portions equivalent circuits. Two circuits are considered to be equivalent if they behave the ...
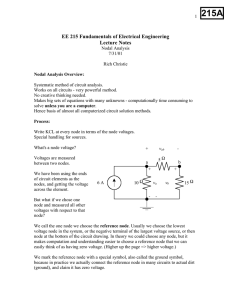
Ch2 Basic Analysis Methods to Circuits
... – The analysis techniques previously (voltage divider, equivalent resistance, etc.) provide an intuitive approach to analyzing circuits – They are not systematic and cannot be easily automated by a ...
... – The analysis techniques previously (voltage divider, equivalent resistance, etc.) provide an intuitive approach to analyzing circuits – They are not systematic and cannot be easily automated by a ...
IEEE013
... the distribution arresters would fare much worse under a higher fault current environment like 6 kA or so since the heating effect is proportional to . The author doubted whether distribution arresters—with or without isolators—represented a viable solution to the overvoltage problem because reclosi ...
... the distribution arresters would fare much worse under a higher fault current environment like 6 kA or so since the heating effect is proportional to . The author doubted whether distribution arresters—with or without isolators—represented a viable solution to the overvoltage problem because reclosi ...
CMOS RF Integrated Circuits Prof. Dr. S. Chatterjee Department of
... when I can transfer the parallel network to series network and vice versa. So therefore, R s has to be equal to R p by 1 plus Q squared, the real part has to be equal to real part and L s has to be equal to L p times Q squared by 1 plus Q squared. What does this mean for us, this means two things, ...
... when I can transfer the parallel network to series network and vice versa. So therefore, R s has to be equal to R p by 1 plus Q squared, the real part has to be equal to real part and L s has to be equal to L p times Q squared by 1 plus Q squared. What does this mean for us, this means two things, ...
Network analysis (electrical circuits)

A network, in the context of electronics, is a collection of interconnected components. Network analysis is the process of finding the voltages across, and the currents through, every component in the network. There are many different techniques for calculating these values. However, for the most part, the applied technique assumes that the components of the network are all linear.The methods described in this article are only applicable to linear network analysis, except where explicitly stated.