Series and Parallel
... • Resistors added side-by-side • The more paths, the less TOTAL resistance. 1/ Req=1/R1+1/R2+1/R3 • Ex. 2 resistors in parallel with 4Ω each. • Since the circuit offers two equal pathways for charge flow, only 1/2 the charge will choose to pass through a given branch. ...
... • Resistors added side-by-side • The more paths, the less TOTAL resistance. 1/ Req=1/R1+1/R2+1/R3 • Ex. 2 resistors in parallel with 4Ω each. • Since the circuit offers two equal pathways for charge flow, only 1/2 the charge will choose to pass through a given branch. ...
Solve All the Following Problems Problem 1 (15 Marks) A) Discuss
... B) Find the circuit model of the device inside the box shown in the figure if the terminal voltage Vt and terminal current It are measured and it's values tabulated, then you must calculate the power delivered from device to a 10Ω resistor. ...
... B) Find the circuit model of the device inside the box shown in the figure if the terminal voltage Vt and terminal current It are measured and it's values tabulated, then you must calculate the power delivered from device to a 10Ω resistor. ...
diodes - Diga.Me.UK
... It seems the answer lies partly in the usually-invisible detail, like the input and output characteristics the amplifier which follows the 'detector', or of C-MOS circuits, whose outputs have a fairly linear resistance, usually in the region of hundreds of ohms, and whose inputs have carefully craft ...
... It seems the answer lies partly in the usually-invisible detail, like the input and output characteristics the amplifier which follows the 'detector', or of C-MOS circuits, whose outputs have a fairly linear resistance, usually in the region of hundreds of ohms, and whose inputs have carefully craft ...
Branches_Nodes_Loops
... extremes of the series of components. The voltage drop across a resistor is calculated ...
... extremes of the series of components. The voltage drop across a resistor is calculated ...
Potential Dividers
... You will be familiar with the use of a variable resistor to vary current. ...
... You will be familiar with the use of a variable resistor to vary current. ...
The Basics of Series Circuits
... strings of holiday lights that go out completely if one bulb burns out. Although these lights cause hours of frustration during the holidays, they also provide an excellent example of a series circuit. The individual bulbs that make up the string are connected in series, or one after another. When a ...
... strings of holiday lights that go out completely if one bulb burns out. Although these lights cause hours of frustration during the holidays, they also provide an excellent example of a series circuit. The individual bulbs that make up the string are connected in series, or one after another. When a ...
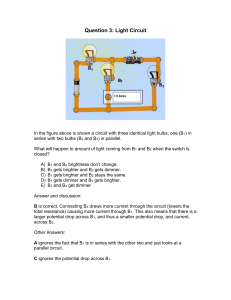
Question 3 - cloudfront.net
... it has an “infinite” resistance. Notes on Demonstration: It is very common for only 20% - 30% of the class to get the correct answer to this question. This can make it very dramatic. There is a problem with the fact that by using light bulbs, we are not strictly dealing with ohmic resistances. Howev ...
... it has an “infinite” resistance. Notes on Demonstration: It is very common for only 20% - 30% of the class to get the correct answer to this question. This can make it very dramatic. There is a problem with the fact that by using light bulbs, we are not strictly dealing with ohmic resistances. Howev ...
PDA
... ranging from 1.8V to 2.6V. The other way is to put a Li-Ion battery and an adapter together. That results in a range from 2.4V to 4.3V for the input voltage. To have a regulated 3.3V input voltage for the controller, the voltage obtained from battery needs another treatment. The conventional method ...
... ranging from 1.8V to 2.6V. The other way is to put a Li-Ion battery and an adapter together. That results in a range from 2.4V to 4.3V for the input voltage. To have a regulated 3.3V input voltage for the controller, the voltage obtained from battery needs another treatment. The conventional method ...
Network analysis (electrical circuits)

A network, in the context of electronics, is a collection of interconnected components. Network analysis is the process of finding the voltages across, and the currents through, every component in the network. There are many different techniques for calculating these values. However, for the most part, the applied technique assumes that the components of the network are all linear.The methods described in this article are only applicable to linear network analysis, except where explicitly stated.

![Electrical Circuits II [Opens in New Window]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/007521861_1-4da59151bb70a291acd72b2f18430da6-300x300.png)