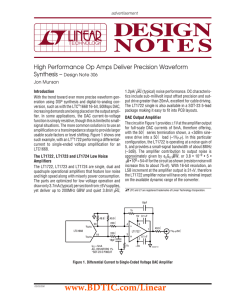
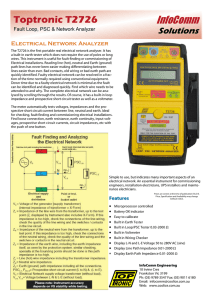
Document
... Components of Electricity are Interrelated • Voltage, current, and resistance must be present to have current flow • Just like water flowing through a hose, changes in voltage, current, and resistance affect each other • That effect is mathematically expressed in ...
... Components of Electricity are Interrelated • Voltage, current, and resistance must be present to have current flow • Just like water flowing through a hose, changes in voltage, current, and resistance affect each other • That effect is mathematically expressed in ...
EE215 Class Problems, Week 5 Solutions All
... Now, we can either find the open circuit voltage or the short circuit current associated with the terminals a and b. We choose to find the open circuit voltage (equal to the Thevenin voltage): ...
... Now, we can either find the open circuit voltage or the short circuit current associated with the terminals a and b. We choose to find the open circuit voltage (equal to the Thevenin voltage): ...
Circuits Test #2 - Review
... V = IR = (2A) (4Ω) = 8V 22. A 9 volt battery produces 4.5 amps across a resistor. What is the resistance? R = V/I = (9V)/(4.5A) = 2Ω 23. If a light in your house (120V) draws 0.5 amps, how much resistance is in the bulb? R = V/I = (120V)/(0.5A) = 240Ω 24. If a light bulb uses 6V and has a resistance ...
... V = IR = (2A) (4Ω) = 8V 22. A 9 volt battery produces 4.5 amps across a resistor. What is the resistance? R = V/I = (9V)/(4.5A) = 2Ω 23. If a light in your house (120V) draws 0.5 amps, how much resistance is in the bulb? R = V/I = (120V)/(0.5A) = 240Ω 24. If a light bulb uses 6V and has a resistance ...
Chapter 5: Series Circuits
... • Voltage dropped across each resistor may be determined by the voltage across any other resistor (or combination of resistors) by using the voltage divider rule expressed as: ...
... • Voltage dropped across each resistor may be determined by the voltage across any other resistor (or combination of resistors) by using the voltage divider rule expressed as: ...
Ohm`s Law - Erie Community College
... Ohm's Law defines the relationships between (P) power, (V) voltage, (A) current, and (R) resistance. One ohm is the resistance value through which one volt will maintain a current of one ampere. Ohm's Law is a very simple and useful tool for analyzing electric circuits. It is used so often in the st ...
... Ohm's Law defines the relationships between (P) power, (V) voltage, (A) current, and (R) resistance. One ohm is the resistance value through which one volt will maintain a current of one ampere. Ohm's Law is a very simple and useful tool for analyzing electric circuits. It is used so often in the st ...
Chapter 9 – Network Theorems
... The total power delivered to a resistive element must be determined using the total current through or the total voltage across the element and cannot be determined by a simple sum of the power levels established by each source. ...
... The total power delivered to a resistive element must be determined using the total current through or the total voltage across the element and cannot be determined by a simple sum of the power levels established by each source. ...
Goodson GC34 Cash Drawer Data Sheet Brochure
... attended to and why. The complete electrical network can be analysed by scrolling through the results. Of course, it has a built-in loop impedance and prospective short circuit tester as well as a voltmeter. ...
... attended to and why. The complete electrical network can be analysed by scrolling through the results. Of course, it has a built-in loop impedance and prospective short circuit tester as well as a voltmeter. ...
Introduction
... – Thevenin’s theorem states that a (linear) one-port network can be replaced with an equivalent circuit consisting of one voltage source in series with one impedance. ...
... – Thevenin’s theorem states that a (linear) one-port network can be replaced with an equivalent circuit consisting of one voltage source in series with one impedance. ...
Network analysis (electrical circuits)

A network, in the context of electronics, is a collection of interconnected components. Network analysis is the process of finding the voltages across, and the currents through, every component in the network. There are many different techniques for calculating these values. However, for the most part, the applied technique assumes that the components of the network are all linear.The methods described in this article are only applicable to linear network analysis, except where explicitly stated.