Research of a New Line Protection Measurement and Controlling
... Algorithm is an important research aspect of microcomputer based protection measurement and controlling device. The main algorithms used by this device are shown as follows. 1) Fourier algorithm It supposes that the sample analog signal is a periodic time function, in addition to fundamental wave, i ...
... Algorithm is an important research aspect of microcomputer based protection measurement and controlling device. The main algorithms used by this device are shown as follows. 1) Fourier algorithm It supposes that the sample analog signal is a periodic time function, in addition to fundamental wave, i ...
Interactive Mobile Simulation of Classical
... application that allows users to construct custom simulations and interact with them through touch gestures. The application allows the user to simultaneously explore electromagnetic induction, circuit theory, electrostatic fields, and elementary particle systems. Since the application allows for a ...
... application that allows users to construct custom simulations and interact with them through touch gestures. The application allows the user to simultaneously explore electromagnetic induction, circuit theory, electrostatic fields, and elementary particle systems. Since the application allows for a ...
Investigation 11
... a) total current in the circuit (IS) b) current through lamp 1 (I1), lamp 2 (I2) and lamp 3 (I3) c) voltage across the battery (VS) d) voltage across lamp 1 (V1), lamp 2 (V2) and lamp 3 (V3) ...
... a) total current in the circuit (IS) b) current through lamp 1 (I1), lamp 2 (I2) and lamp 3 (I3) c) voltage across the battery (VS) d) voltage across lamp 1 (V1), lamp 2 (V2) and lamp 3 (V3) ...
Electrical Circuits 2 (from CPO Physics)
... 20.2 Calculate using network circuits Three bulbs, each with a resistance of 3Ω, are combined in the circuit in the diagram Three volts are applied to the circuit. Calculate the current in each of the bulbs. ...
... 20.2 Calculate using network circuits Three bulbs, each with a resistance of 3Ω, are combined in the circuit in the diagram Three volts are applied to the circuit. Calculate the current in each of the bulbs. ...
Lecture4
... node. The shaded surface encloses a section of the circuit and can be considered as a BIG node ...
... node. The shaded surface encloses a section of the circuit and can be considered as a BIG node ...
PSURGE 30.2 3OkV SURGE TEST SYSTEM ONE SOLUTION
... the superimposition of voltage impulses via coupling capacitors and protection of the power supply on the input side with decoupling ...
... the superimposition of voltage impulses via coupling capacitors and protection of the power supply on the input side with decoupling ...
Lecture 8
... connected end-to-end, they are said to be in series The current is the same in all resistors because any charge that flows through one resistor flows through the other The sum of the potential differences across the resistors is equal to the total potential difference across the ...
... connected end-to-end, they are said to be in series The current is the same in all resistors because any charge that flows through one resistor flows through the other The sum of the potential differences across the resistors is equal to the total potential difference across the ...
3.reactance_and_impedance
... Explain the relationship between AC voltage and AC current in a resistor, capacitor and inductor. Explain why a capacitor causes a phase shift between current and voltage (ICE). Define capacitive reactance. Explain the relationship between capacitive reactance and frequency. Explain why an i ...
... Explain the relationship between AC voltage and AC current in a resistor, capacitor and inductor. Explain why a capacitor causes a phase shift between current and voltage (ICE). Define capacitive reactance. Explain the relationship between capacitive reactance and frequency. Explain why an i ...
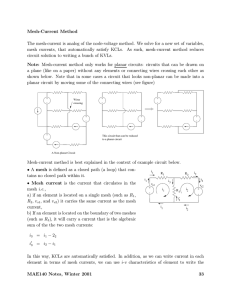
Mesh-Current Method The mesh-current is analog of the node
... Thus, v = va + vb = 5 − 10 = −5 V. Note: Using superposition results in slightly simpler circuits (one element is replaced with either a short or open circuit) but more circuits. In general superposition requires more work than node-voltage or mesh-current methods. Superposition is used: a) If sourc ...
... Thus, v = va + vb = 5 − 10 = −5 V. Note: Using superposition results in slightly simpler circuits (one element is replaced with either a short or open circuit) but more circuits. In general superposition requires more work than node-voltage or mesh-current methods. Superposition is used: a) If sourc ...
Welcome to Physics 220! - BYU Physics and Astronomy
... • Find a combination in series or parallel. • Combine resistors into a single equivalent resistor. •Repeat until there is only one resistor. •The voltage across the resistor is the same as the voltage across the battery. ...
... • Find a combination in series or parallel. • Combine resistors into a single equivalent resistor. •Repeat until there is only one resistor. •The voltage across the resistor is the same as the voltage across the battery. ...
Network analysis (electrical circuits)

A network, in the context of electronics, is a collection of interconnected components. Network analysis is the process of finding the voltages across, and the currents through, every component in the network. There are many different techniques for calculating these values. However, for the most part, the applied technique assumes that the components of the network are all linear.The methods described in this article are only applicable to linear network analysis, except where explicitly stated.