G Rathika Nath.pmd - Oriental Journal of Chemistry
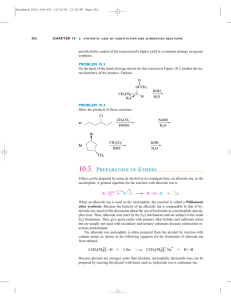
... reactions show a first order dependence on the concentration of both the substrates and the catalyst. The metal complexes having less cross linking at the backbone and ring-activating group near the active site showed high catalytic efficiency. This is only a preliminary study which shows that cross ...
... reactions show a first order dependence on the concentration of both the substrates and the catalyst. The metal complexes having less cross linking at the backbone and ring-activating group near the active site showed high catalytic efficiency. This is only a preliminary study which shows that cross ...
Electrophilic Selenium Catalysis with Electrophilic N
... Functionalization of alkenes is a perpetual goal in organic synthesis. One of the attractive routes to elaborate the carbon–carbon double bond of alkenes is through electrophilic selenium reagent-promoted selenofunctionalization. In this context, several electrophilic organoselenium reagents ArSeX ( ...
... Functionalization of alkenes is a perpetual goal in organic synthesis. One of the attractive routes to elaborate the carbon–carbon double bond of alkenes is through electrophilic selenium reagent-promoted selenofunctionalization. In this context, several electrophilic organoselenium reagents ArSeX ( ...
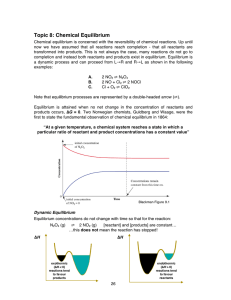
Topic 8: Chemical Equilibrium
... This changes total pressure but not partial pressure – this means that if an inert gas is added at constant volume then it has no effect on the equilibrium position. • Change the volume of the container 3. Change the volume (related to above) When volume decreases, the partial pressures of everythin ...
... This changes total pressure but not partial pressure – this means that if an inert gas is added at constant volume then it has no effect on the equilibrium position. • Change the volume of the container 3. Change the volume (related to above) When volume decreases, the partial pressures of everythin ...
19.19 Summary
... Lithium aluminum hydride reduces esters to alcohols. Two alcohols are formed; the acyl group is reduced to the primary alcohol. ...
... Lithium aluminum hydride reduces esters to alcohols. Two alcohols are formed; the acyl group is reduced to the primary alcohol. ...
Lecture 12 –Octahedral Substitution Reactions
... Change in CFSE – complexes with d3, low spin d6 configurations and d8 exchange ligands slowly. This is because you loose a lot of crystal field stabilization energy when going to 5 co-ordinate. (any geometry is less than octahedral in terms of CFSE). Look at the handout If we compare Al3+ and Cr3+ B ...
... Change in CFSE – complexes with d3, low spin d6 configurations and d8 exchange ligands slowly. This is because you loose a lot of crystal field stabilization energy when going to 5 co-ordinate. (any geometry is less than octahedral in terms of CFSE). Look at the handout If we compare Al3+ and Cr3+ B ...
molybdenum(O)
... the addition of fumaronitrile into the solution does not show any noticeable changes in the chemical shifts, the equilibrium must lie in the direction of FN dissociation. The rate at which the equilibrium is established must be fast com pared to the NMR time scale, so that an average value for the s ...
... the addition of fumaronitrile into the solution does not show any noticeable changes in the chemical shifts, the equilibrium must lie in the direction of FN dissociation. The rate at which the equilibrium is established must be fast com pared to the NMR time scale, so that an average value for the s ...
Organic Chemistry Fifth Edition
... group. More substituted carbon (more positive charge although more sterically hindered) is attacked by a weak nucleophile. Very similar to opening of cyclic bromonium ion. Review that subject. Due to resonance, some positive charge is located on this carbon. ...
... group. More substituted carbon (more positive charge although more sterically hindered) is attacked by a weak nucleophile. Very similar to opening of cyclic bromonium ion. Review that subject. Due to resonance, some positive charge is located on this carbon. ...
Ring-closing metathesis

Ring-closing metathesis, or RCM, is a widely used variation of olefin metathesis in organic chemistry for the synthesis of various unsaturated rings via the intramolecular metathesis of two terminal alkenes, which forms the cycloalkene as the E- or Z- isomers and volatile ethylene.The most commonly synthesized ring sizes are between 5-7 atoms; however, reported syntheses include 45- up to 90- membered macroheterocycles. These reactions are metal-catalyzed and proceed through a metallacyclobutane intermediate. It was first published by Dider Villemin in 1980 describing the synthesis of an Exaltolide precursor, and later become popularized by Robert H. Grubbs and Richard R. Schrock, who shared the Nobel Prize in Chemistry, along with Yves Chauvin, in 2005 for their combined work in olefin metathesis. RCM is a favorite among organic chemists due to its synthetic utility in the formation of rings, which were previously difficult to access efficiently, and broad substrate scope. Since the only major by-product is ethylene, these reactions may also be considered atom economic, an increasingly important concern in the development of green chemistry.There are several reviews published on ring-closing metathesis.