Aroylhydrazone Cu(II) Complexes in keto Form: Structural
... Spectrometry (ESI-MS) and single crystal X-ray crystallography. All compounds act as efficient catalysts towards the peroxidative oxidation of cyclohexane to cyclohexyl hydroperoxide, cyclohexanol and cyclohexanone, under mild conditions. In the presence of an acid promoter, overall yields (based on ...
... Spectrometry (ESI-MS) and single crystal X-ray crystallography. All compounds act as efficient catalysts towards the peroxidative oxidation of cyclohexane to cyclohexyl hydroperoxide, cyclohexanol and cyclohexanone, under mild conditions. In the presence of an acid promoter, overall yields (based on ...
Catalysis by main-group metal - Université Paris-Sud
... alcohols through borrowing hydrogen catalysis (or hydrogen auto transfer),2 has been recognized as one of the most practical methods for the industrial production of substituted alkyl amines. The broad availability of alcohols, combined with the fact that water is the only by-product of such reactio ...
... alcohols through borrowing hydrogen catalysis (or hydrogen auto transfer),2 has been recognized as one of the most practical methods for the industrial production of substituted alkyl amines. The broad availability of alcohols, combined with the fact that water is the only by-product of such reactio ...
motm GLYCINE
... CO2H It’s an aminoacid, right? Yes, glycine is a colourless crystalline solid (decomposing around 230 C), the smallest -amino acid there is, with only two carbon atoms, and a Relative Formula Mass of 75. Why is it called an -amino acid? The amine (NH2) group is bound to the first carbon (alpha ca ...
... CO2H It’s an aminoacid, right? Yes, glycine is a colourless crystalline solid (decomposing around 230 C), the smallest -amino acid there is, with only two carbon atoms, and a Relative Formula Mass of 75. Why is it called an -amino acid? The amine (NH2) group is bound to the first carbon (alpha ca ...
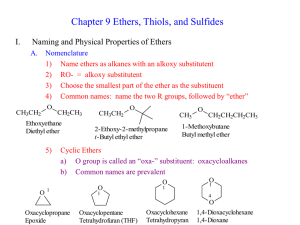
Ch 9 Lecture 2
... 1) Same molecular formula as Alcohol: CnH2n+2O 2) No Hydrogen Bonding is possible in R—O—R 3) Boiling Points are much lower than alcohols, more like haloalkanes 4) Water solubility much less than alcohols a) MeOMe and EtOEt have some water solubility b) Larger ethers are insoluble, very much like al ...
... 1) Same molecular formula as Alcohol: CnH2n+2O 2) No Hydrogen Bonding is possible in R—O—R 3) Boiling Points are much lower than alcohols, more like haloalkanes 4) Water solubility much less than alcohols a) MeOMe and EtOEt have some water solubility b) Larger ethers are insoluble, very much like al ...
as a PDF
... crude oil derived products in various applications. As widely practiced in petrochemical industry, catalyst plays a very important role in the production of basic oleochemicals. Catalytic reactions are abound in the production of oleochemicals: Nickel based catalysts are used in the hydrogenation of ...
... crude oil derived products in various applications. As widely practiced in petrochemical industry, catalyst plays a very important role in the production of basic oleochemicals. Catalytic reactions are abound in the production of oleochemicals: Nickel based catalysts are used in the hydrogenation of ...
9: Formation of Alkenes and Alkynes. Elimination Reactions
... The C-A and C-B bonds break in the elimination reaction, and a second bond forms between the two C's to form a C=C bond. "A-B" in Figure 9.01 may not be an actual reaction product, but we show it this way in this general example in order to keep the chemical bonds on both sides of the equation in ba ...
... The C-A and C-B bonds break in the elimination reaction, and a second bond forms between the two C's to form a C=C bond. "A-B" in Figure 9.01 may not be an actual reaction product, but we show it this way in this general example in order to keep the chemical bonds on both sides of the equation in ba ...
carboxylic acid - Career Launcher
... Acyl group bonded to Y, an electronegative atom or leaving group Includes: Y = halide (acid halides), acyloxy (anhydrides), alkoxy (esters), amine (amides), thiolate (thioesters), phosphate (acyl phosphates) ...
... Acyl group bonded to Y, an electronegative atom or leaving group Includes: Y = halide (acid halides), acyloxy (anhydrides), alkoxy (esters), amine (amides), thiolate (thioesters), phosphate (acyl phosphates) ...
Photosynthetic reaction centers
... their ability to perform electron transfer with a quantum yield of almost unity. This high quantum yield is achieved by the utilization of a number of intermediate electron acceptors (Fig. 1). Within 30 ps after excitation a stable charge separated state is formed in all photosystems. Although the n ...
... their ability to perform electron transfer with a quantum yield of almost unity. This high quantum yield is achieved by the utilization of a number of intermediate electron acceptors (Fig. 1). Within 30 ps after excitation a stable charge separated state is formed in all photosystems. Although the n ...
List of Objectives for Chem52
... *Draw the products and mechanisms (including all electron-pushing arrows, intermediates, and by-products) of nucleophilic aromatic substitution reactions, both through the elimination/ addition mechanism through benzyne and the addition/elimination mechanism (SNAr). Prepare benzyne intermediates thr ...
... *Draw the products and mechanisms (including all electron-pushing arrows, intermediates, and by-products) of nucleophilic aromatic substitution reactions, both through the elimination/ addition mechanism through benzyne and the addition/elimination mechanism (SNAr). Prepare benzyne intermediates thr ...
Future perspectives in catalysis - NRSC
... Catalysis is the quiet force behind the modernization of our chemical industry. It ensures more efficient use of finite natural resources, it helps prevent waste and air pollution, and it makes our industry safer. In the past century, catalysis became the basis of large-scale processes in bulk chemi ...
... Catalysis is the quiet force behind the modernization of our chemical industry. It ensures more efficient use of finite natural resources, it helps prevent waste and air pollution, and it makes our industry safer. In the past century, catalysis became the basis of large-scale processes in bulk chemi ...
09_chapter 4
... lattice oxygen, although onset for desorption begins at as low as ~450°C for all the samples. Copper ferrite exhibits a two stage desorption with a broad low intensity band having an onset of desorption at 430°C and followed by a sharp desorption peak with maxima at ~940°C. Nickel ferrite shows a th ...
... lattice oxygen, although onset for desorption begins at as low as ~450°C for all the samples. Copper ferrite exhibits a two stage desorption with a broad low intensity band having an onset of desorption at 430°C and followed by a sharp desorption peak with maxima at ~940°C. Nickel ferrite shows a th ...
Ring-closing metathesis

Ring-closing metathesis, or RCM, is a widely used variation of olefin metathesis in organic chemistry for the synthesis of various unsaturated rings via the intramolecular metathesis of two terminal alkenes, which forms the cycloalkene as the E- or Z- isomers and volatile ethylene.The most commonly synthesized ring sizes are between 5-7 atoms; however, reported syntheses include 45- up to 90- membered macroheterocycles. These reactions are metal-catalyzed and proceed through a metallacyclobutane intermediate. It was first published by Dider Villemin in 1980 describing the synthesis of an Exaltolide precursor, and later become popularized by Robert H. Grubbs and Richard R. Schrock, who shared the Nobel Prize in Chemistry, along with Yves Chauvin, in 2005 for their combined work in olefin metathesis. RCM is a favorite among organic chemists due to its synthetic utility in the formation of rings, which were previously difficult to access efficiently, and broad substrate scope. Since the only major by-product is ethylene, these reactions may also be considered atom economic, an increasingly important concern in the development of green chemistry.There are several reviews published on ring-closing metathesis.