Common Oxidation–Reduction Reactions
... 2) binary compounds of two different halogens: more electronegative halogen gets the oxidation number −1, oxidation number of the less electronegative halogen has to be calculated. ...
... 2) binary compounds of two different halogens: more electronegative halogen gets the oxidation number −1, oxidation number of the less electronegative halogen has to be calculated. ...
Unit 16: Chemistry for Biology Technicians
... displacement of one metal by another and the associated oxidation and reduction equations. Having written reduction and oxidation half equations and overall redox equations for reactions that are easily seen, learners should, in subsequent study, be able to understand redox equilibria and the associ ...
... displacement of one metal by another and the associated oxidation and reduction equations. Having written reduction and oxidation half equations and overall redox equations for reactions that are easily seen, learners should, in subsequent study, be able to understand redox equilibria and the associ ...
HIGHLY SELECTIVE RHODIUM–CATALYZED C–H BORYLATIONS IN
... organoboron starting materials. C–H borylation (activation) has provided an interesting approach to alleviate the requirement for prefunctionalized molecules such as aryl halides to obtain these desired organoboron substrates. We report the first use of a rhodium N–heterocyclic carbene (NHC) complex ...
... organoboron starting materials. C–H borylation (activation) has provided an interesting approach to alleviate the requirement for prefunctionalized molecules such as aryl halides to obtain these desired organoboron substrates. We report the first use of a rhodium N–heterocyclic carbene (NHC) complex ...
Chapter 3 Ligand Effects
... Clearly, there is a need for techniques which provide access to enantiomerically pure compounds. There are a number of methods by which this goal can be achieved19. One can start from naturally occurring enantiomerically pure compounds (the chiral pool). Alternatively, racemic mixtures can be separa ...
... Clearly, there is a need for techniques which provide access to enantiomerically pure compounds. There are a number of methods by which this goal can be achieved19. One can start from naturally occurring enantiomerically pure compounds (the chiral pool). Alternatively, racemic mixtures can be separa ...
20 More About Oxidation–Reduction Reactions
... Notice that the oxidation of either a primary or a secondary alcohol involves removal of a hydrogen from the carbon to which the OH is attached. The carbon bearing the OH group in a tertiary alcohol is not bonded to a hydrogen, so the OH group cannot be oxidized to a carbonyl group. Chromic acid and ...
... Notice that the oxidation of either a primary or a secondary alcohol involves removal of a hydrogen from the carbon to which the OH is attached. The carbon bearing the OH group in a tertiary alcohol is not bonded to a hydrogen, so the OH group cannot be oxidized to a carbonyl group. Chromic acid and ...
Role of Chemical Reaction Engineering in Sustainable
... In this way, n-butane and oxygen are not in direct contact and this leads to minimizing side reactions and higher maleic anhydride selectivity (up to 90 %) is therefore obtained4,6. Figure 4 shows the circulating fluid bed reactor configuration. Again, to enable the use of CFB extensive catalyst dev ...
... In this way, n-butane and oxygen are not in direct contact and this leads to minimizing side reactions and higher maleic anhydride selectivity (up to 90 %) is therefore obtained4,6. Figure 4 shows the circulating fluid bed reactor configuration. Again, to enable the use of CFB extensive catalyst dev ...
Chapter 1
... • Aldehydes and ketones are polar compounds • The carbonyl group is polar – The oxygen end is electronegative – Can hydrogen bond to water – Cannot form intermolecular hydrogen bond ...
... • Aldehydes and ketones are polar compounds • The carbonyl group is polar – The oxygen end is electronegative – Can hydrogen bond to water – Cannot form intermolecular hydrogen bond ...
Theoretical Study of Gas-Phase Reactions of Fe(CO)5 with OH
... (CO)4FeH2 is known to be a weak acid15 and a powerful catalyst for double-bond isomerization reactions.16 Moreover, it is found to decompose readily with liberation of molecular hydrogen17 as in eq 5. Most of these reactions, however, have been reported to proceed either in solution or under conditi ...
... (CO)4FeH2 is known to be a weak acid15 and a powerful catalyst for double-bond isomerization reactions.16 Moreover, it is found to decompose readily with liberation of molecular hydrogen17 as in eq 5. Most of these reactions, however, have been reported to proceed either in solution or under conditi ...
16.18 Summary
... polyethers, called crown ethers, are particularly effective in coordinating with Na+ and K+, and salts of these cations can be dissolved in nonpolar solvents when crown ethers are present. Under these conditions the rates of many reactions that involve anions are accelerated. ...
... polyethers, called crown ethers, are particularly effective in coordinating with Na+ and K+, and salts of these cations can be dissolved in nonpolar solvents when crown ethers are present. Under these conditions the rates of many reactions that involve anions are accelerated. ...
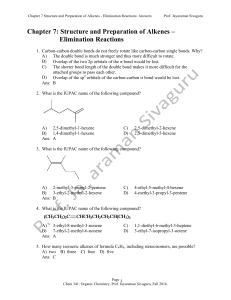
Ch 7 - Practice problem (Answers)
... 24. When a strong base is used in the elimination reaction of an alkyl halide the mechanism, in general, is A) E1. B) E2. C) E1 for tertiary halides, E2 for primary and secondary halides. D) E2 for tertiary halides, E1 for primary and secondary halides. Ans: B 25. Which of the following sets of cond ...
... 24. When a strong base is used in the elimination reaction of an alkyl halide the mechanism, in general, is A) E1. B) E2. C) E1 for tertiary halides, E2 for primary and secondary halides. D) E2 for tertiary halides, E1 for primary and secondary halides. Ans: B 25. Which of the following sets of cond ...
+ ∂ - CHEM171 – Lecture Series Seven : 2012/05
... Reactive centre – encourages either nucleophilic or electrophilic attack. Functional groups will give rise to reactive centres within molecules. For example, if we have a ketone containing the functional group: ∂O ...
... Reactive centre – encourages either nucleophilic or electrophilic attack. Functional groups will give rise to reactive centres within molecules. For example, if we have a ketone containing the functional group: ∂O ...
13_lecture_ppt
... Preparation of aldehydes and ketones • Principal means of preparation is oxidation of the corresponding alcohol – Primary alcohol produces an aldehyde – Secondary alcohol produces a ketone – Tertiary alcohol does not oxidize ...
... Preparation of aldehydes and ketones • Principal means of preparation is oxidation of the corresponding alcohol – Primary alcohol produces an aldehyde – Secondary alcohol produces a ketone – Tertiary alcohol does not oxidize ...
Chap15 - Bakersfield College
... –Much like water in a U-shaped tube, there is constant mixing back and forth through the lower portion of the tube. “reactants” ...
... –Much like water in a U-shaped tube, there is constant mixing back and forth through the lower portion of the tube. “reactants” ...
Ring-closing metathesis

Ring-closing metathesis, or RCM, is a widely used variation of olefin metathesis in organic chemistry for the synthesis of various unsaturated rings via the intramolecular metathesis of two terminal alkenes, which forms the cycloalkene as the E- or Z- isomers and volatile ethylene.The most commonly synthesized ring sizes are between 5-7 atoms; however, reported syntheses include 45- up to 90- membered macroheterocycles. These reactions are metal-catalyzed and proceed through a metallacyclobutane intermediate. It was first published by Dider Villemin in 1980 describing the synthesis of an Exaltolide precursor, and later become popularized by Robert H. Grubbs and Richard R. Schrock, who shared the Nobel Prize in Chemistry, along with Yves Chauvin, in 2005 for their combined work in olefin metathesis. RCM is a favorite among organic chemists due to its synthetic utility in the formation of rings, which were previously difficult to access efficiently, and broad substrate scope. Since the only major by-product is ethylene, these reactions may also be considered atom economic, an increasingly important concern in the development of green chemistry.There are several reviews published on ring-closing metathesis.