The Chemistry of Alkyl Halides - Welcome to people.pharmacy
... In a stereospecific reaction with a given stereochemistry—anti-elimination, in this case—a diastereomeric product requires a diastereomeric starting material (either enantiomer). The easiest path to the answer is to convert the starting material in Eq. 9.40a into its diastereomer by the interchange ...
... In a stereospecific reaction with a given stereochemistry—anti-elimination, in this case—a diastereomeric product requires a diastereomeric starting material (either enantiomer). The easiest path to the answer is to convert the starting material in Eq. 9.40a into its diastereomer by the interchange ...
Reprint - Horizon Research Publishing
... forward synthetic route for the preparation of β-amino alcohols, involve the heating of epoxide with an excess of amine at elevated temperature. Since some functional groups are sensitive to high temperature, a variety of activators such as alkali metal halides, metal perchlorates, metal tetrafluoro ...
... forward synthetic route for the preparation of β-amino alcohols, involve the heating of epoxide with an excess of amine at elevated temperature. Since some functional groups are sensitive to high temperature, a variety of activators such as alkali metal halides, metal perchlorates, metal tetrafluoro ...
ETHERS
... ROH + R'OH )))))))))> ROR + ROR' + R'OR' + H2O However, if one alcohol is t-BuOH, t-Bu-O-R will be the major product owing to rapid formation of t-Bu+ carbocation and inability to form t-Bu-O-t-Bu. ...
... ROH + R'OH )))))))))> ROR + ROR' + R'OR' + H2O However, if one alcohol is t-BuOH, t-Bu-O-R will be the major product owing to rapid formation of t-Bu+ carbocation and inability to form t-Bu-O-t-Bu. ...
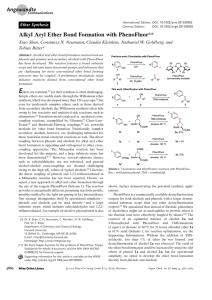
Ir-catalysed formation of C− F bonds. From allylic alcohols to α
... only one constitutional isomer of the product (i.e. 2a 0 was not formed), further screening on this system was performed (Table 2). The best results were obtained using a THF/water mixture of 5 : 1. Less water failed to dissolve SelectF, and more water increased by-product (3a) formation. The cataly ...
... only one constitutional isomer of the product (i.e. 2a 0 was not formed), further screening on this system was performed (Table 2). The best results were obtained using a THF/water mixture of 5 : 1. Less water failed to dissolve SelectF, and more water increased by-product (3a) formation. The cataly ...
Chemistry 5.46 Organic Structure Determination Spring 2004
... (b) Determine the number of protons to which each resonance is coupled. (c) Give the connectivity that must result from the observed splittings. For example, R2CH-CH2-CH2-R’. Explain your reasoning. ...
... (b) Determine the number of protons to which each resonance is coupled. (c) Give the connectivity that must result from the observed splittings. For example, R2CH-CH2-CH2-R’. Explain your reasoning. ...
Solid Manganese Dioxide as an Oxidizing Agent
... Codeinone. -Codeine (201 mg., 0.ti7 mmole) was dissolved in 25 ml. of chloroform and stirred over 600 mg. of manganese dioxidela for 10 minutes. The solution was filtered through a sintered glass funnel, the manganese dioxide washed twice with chloroform, and the filtrates concentrated a t reduced p ...
... Codeinone. -Codeine (201 mg., 0.ti7 mmole) was dissolved in 25 ml. of chloroform and stirred over 600 mg. of manganese dioxidela for 10 minutes. The solution was filtered through a sintered glass funnel, the manganese dioxide washed twice with chloroform, and the filtrates concentrated a t reduced p ...
Online edition for students of organic chemistry lab
... from primary alcohols can be further oxidized to carboxylic acids by some of these oxidizing agents (including HOCl), while the ketones derived from secondary alcohols are stable to further oxidation. The most widely used oxidizing agent is chromic acid, which is prepared by mixing sodium dichromate ...
... from primary alcohols can be further oxidized to carboxylic acids by some of these oxidizing agents (including HOCl), while the ketones derived from secondary alcohols are stable to further oxidation. The most widely used oxidizing agent is chromic acid, which is prepared by mixing sodium dichromate ...
Chapter 1 Structure and Bonding
... 1) Same molecular formula as Alcohol: CnH2n+2O 2) No Hydrogen Bonding is possible in R—O—R 3) Boiling Points are much lower than alcohols, more like haloalkanes 4) Water solubility much less than alcohols a) MeOMe and EtOEt have some water solubility b) Larger ethers are insoluble, very much like al ...
... 1) Same molecular formula as Alcohol: CnH2n+2O 2) No Hydrogen Bonding is possible in R—O—R 3) Boiling Points are much lower than alcohols, more like haloalkanes 4) Water solubility much less than alcohols a) MeOMe and EtOEt have some water solubility b) Larger ethers are insoluble, very much like al ...
Synthesis of Imidine Hydrochloride and Some
... solution of potassium carbonate at 0 C. The ethereal solution was shaken with (0.01 mole) glycine ethyl ester hydrochloride in 2 ml of water for 1 hr. The ether layer was separated, washed with water, dried over sodium sulphate and the solvent evaporated to afford the crude product. The product was ...
... solution of potassium carbonate at 0 C. The ethereal solution was shaken with (0.01 mole) glycine ethyl ester hydrochloride in 2 ml of water for 1 hr. The ether layer was separated, washed with water, dried over sodium sulphate and the solvent evaporated to afford the crude product. The product was ...
Alkyl Aryl Ether Bond Formation with PhenoFluor
... bond formation is appealing and orthogonal to other crosscoupling approaches. The Mitsunobu reaction has been developed for this purpose, and a large substrate scope has been demonstrated.[6, 7] However, several substrate classes, such as salicylaldehydes, are not tolerated, and general alcohol–alco ...
... bond formation is appealing and orthogonal to other crosscoupling approaches. The Mitsunobu reaction has been developed for this purpose, and a large substrate scope has been demonstrated.[6, 7] However, several substrate classes, such as salicylaldehydes, are not tolerated, and general alcohol–alco ...
Kinetics of Oxidation of Aliphatic Alcohols by Potassium Dichromate
... different oxidizing agents and in various media.1–7 One of the most commonly used oxidants is dichromate and its derivatives. In going through the literature, one finds controversial results regarding the kinetics of these reactions though all studies have proposed similar mechanisms. Some reports s ...
... different oxidizing agents and in various media.1–7 One of the most commonly used oxidants is dichromate and its derivatives. In going through the literature, one finds controversial results regarding the kinetics of these reactions though all studies have proposed similar mechanisms. Some reports s ...
New process of low-temperature methanol synthesis from CO/CO2
... of Cu/ZnO solid catalyst and 2-alcohol solvent catalyst. The primary results showed that when 2-butanol was used as reaction solvent, the one-pass average yield and the selectivity of methanol, in 40 h continuous reaction at temperature as low as 443 K and 5 MPa, were high up to 46.51% and 98.94% re ...
... of Cu/ZnO solid catalyst and 2-alcohol solvent catalyst. The primary results showed that when 2-butanol was used as reaction solvent, the one-pass average yield and the selectivity of methanol, in 40 h continuous reaction at temperature as low as 443 K and 5 MPa, were high up to 46.51% and 98.94% re ...
6.5. alcohols
... Fermentation is done in an absence of air because the presence of air can cause extra reactions to occur. Air oxidises the ethanol produced to ethanoic acid (vinegar). The solution produced by fermentation will only contain around 15% ethanol. Above this concentration of ethanol the yeast will not s ...
... Fermentation is done in an absence of air because the presence of air can cause extra reactions to occur. Air oxidises the ethanol produced to ethanoic acid (vinegar). The solution produced by fermentation will only contain around 15% ethanol. Above this concentration of ethanol the yeast will not s ...
- Wiley Online Library
... copper salt 6. When the leaving group is not oxygen-based, salt metathesis with a metal alkoxide will convert 6 into copper alkoxide 7 from which copper(I) hydride 1 is regenerated by s-bond metathesis with a hydrosilane.[5] Alternatively, functionalization can occur through addition of copper inter ...
... copper salt 6. When the leaving group is not oxygen-based, salt metathesis with a metal alkoxide will convert 6 into copper alkoxide 7 from which copper(I) hydride 1 is regenerated by s-bond metathesis with a hydrosilane.[5] Alternatively, functionalization can occur through addition of copper inter ...
Orbitals - drjosephryan.com
... Acetal and hemiacetal groups are common in carbohydrate chemistry • Glucose, a polyhydroxy aldehyde, undergoes intramolecular nucleophilic addition • Exists primarily as a cyclic hemiacetal ...
... Acetal and hemiacetal groups are common in carbohydrate chemistry • Glucose, a polyhydroxy aldehyde, undergoes intramolecular nucleophilic addition • Exists primarily as a cyclic hemiacetal ...
Document
... recognize an addition reaction, remember that two compounds usually react to form one major product. (Sometimes two isomers are formed.) The product has more atoms bonded to carbon atoms than the organic reactant did. A general example of addition to an alkene is given below. ...
... recognize an addition reaction, remember that two compounds usually react to form one major product. (Sometimes two isomers are formed.) The product has more atoms bonded to carbon atoms than the organic reactant did. A general example of addition to an alkene is given below. ...
Solvothermal Synthesis of Polyazomethine Microspheres
... procedure[S1]. In a round-bottomed flask (250mL) equipped with a reflux condenser, a mixture of pnitrobenzaldehyde (7.5 g, 0.05 mol), p-nitroacetophenone(16.5 g, 0.10 mol), ammonium acetate(60.0 g), and glacial acetic acid (150mL) were refluxed for 6 h. After cooled to room temperature, the mixture ...
... procedure[S1]. In a round-bottomed flask (250mL) equipped with a reflux condenser, a mixture of pnitrobenzaldehyde (7.5 g, 0.05 mol), p-nitroacetophenone(16.5 g, 0.10 mol), ammonium acetate(60.0 g), and glacial acetic acid (150mL) were refluxed for 6 h. After cooled to room temperature, the mixture ...
CHEM1102 2014-J-8 June 2014 • Complete the following table
... Ethanol is the weakest acid as its conjugate base is not resonance stabilised. Phenol is a stronger acid as its conjugate base is resonance stabilised – the negative charge can be delocalised into the aromatic ring as shown below. ...
... Ethanol is the weakest acid as its conjugate base is not resonance stabilised. Phenol is a stronger acid as its conjugate base is resonance stabilised – the negative charge can be delocalised into the aromatic ring as shown below. ...
Instructor notes
... this system, methane is converted to methyl bisulfate using a platinum(II) bipyrimidine catalyst in concentrated sulfuric acid. The formal oxidant in this system is SO3. The mechanism for this reaction is quite close to that of the original Shilov reaction, although the details of the C-H activation ...
... this system, methane is converted to methyl bisulfate using a platinum(II) bipyrimidine catalyst in concentrated sulfuric acid. The formal oxidant in this system is SO3. The mechanism for this reaction is quite close to that of the original Shilov reaction, although the details of the C-H activation ...
Air-Stable Trialkylphosphonium Salts
... significant decomposition even after heating [(t-Bu)3PH]BF4 in air at 120 °C for 24 h. In view of the sensitivity of the free phosphines, the air-stability of these salts is particularly remarkable.12 Neither salt is hygroscopic. Applications of [(n-Bu)3PH]BF4. P(n-Bu)3 has been employed in syntheti ...
... significant decomposition even after heating [(t-Bu)3PH]BF4 in air at 120 °C for 24 h. In view of the sensitivity of the free phosphines, the air-stability of these salts is particularly remarkable.12 Neither salt is hygroscopic. Applications of [(n-Bu)3PH]BF4. P(n-Bu)3 has been employed in syntheti ...
T10 SL - MsReenChemistry
... taking place and suggest the identity (name or structure) of these two products. Explain whether or not they can exist as geometrical isomers. ...
... taking place and suggest the identity (name or structure) of these two products. Explain whether or not they can exist as geometrical isomers. ...
215-216 HH W12-notes
... ii) Sodium hypochlorite (NaOCl): Bleach Usually under acidic conditions (e.g., in acetic acid); HOCl (hypochlorous acid) is the actual oxidant. As HOCl is not stable, it has to be generated in situ in the reaction medium. ...
... ii) Sodium hypochlorite (NaOCl): Bleach Usually under acidic conditions (e.g., in acetic acid); HOCl (hypochlorous acid) is the actual oxidant. As HOCl is not stable, it has to be generated in situ in the reaction medium. ...
conversion of the OH group into a better leaving group, and
... Carbocation Rearrangements • Often, when carbocations are intermediates, a less stable carbocation will be converted into a more stable carbocation by a shift of a hydrogen or an alkyl group. This is called a ...
... Carbocation Rearrangements • Often, when carbocations are intermediates, a less stable carbocation will be converted into a more stable carbocation by a shift of a hydrogen or an alkyl group. This is called a ...
Chapter 13. Alcohols, Diols, and Ethers
... ii) Sodium hypochlorite (NaOCl): Bleach Usually under acidic conditions (e.g., in acetic acid); HOCl (hypochlorous acid) is the actual oxidant. As HOCl is not stable, it has to be generated in situ in the reaction medium. ...
... ii) Sodium hypochlorite (NaOCl): Bleach Usually under acidic conditions (e.g., in acetic acid); HOCl (hypochlorous acid) is the actual oxidant. As HOCl is not stable, it has to be generated in situ in the reaction medium. ...
Elias James Corey

Elias James ""E.J."" Corey (born July 12, 1928) is an American organic chemist. In 1990, he won the Nobel Prize in Chemistry ""for his development of the theory and methodology of organic synthesis"", specifically retrosynthetic analysis. Regarded by many as one of the greatest living chemists, he has developed numerous synthetic reagents, methodologies and total syntheses and has advanced the science of organic synthesis considerably.