chemistry - spdm college shirpur
... A student is expected to submit a journal certified by the Head of the Department / Head of the Institution. A student will not be permitted to appear at the practical examination unless he / she produce a certified journal. If the journal is lost ,the student should produce a certificate from Head ...
... A student is expected to submit a journal certified by the Head of the Department / Head of the Institution. A student will not be permitted to appear at the practical examination unless he / she produce a certified journal. If the journal is lost ,the student should produce a certificate from Head ...
Chapter 7 Hydrosilylation of Carbon
... It is well-documented that certain hydrosilanes undergo addition across the carbon-carbon multiple bonds under catalysis by transition metal complexes and the reaction is referred to as the hydrosilylation [1, 2, 3, 4]. Incorporation of chiral ligands into the metal catalyst can, in principle, make ...
... It is well-documented that certain hydrosilanes undergo addition across the carbon-carbon multiple bonds under catalysis by transition metal complexes and the reaction is referred to as the hydrosilylation [1, 2, 3, 4]. Incorporation of chiral ligands into the metal catalyst can, in principle, make ...
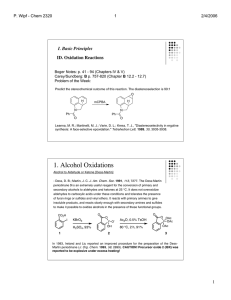
1. Alcohol Oxidations
... For a catalytic protocol, see: Bolm, C.; Magnus, A. S.; Hildebrand, J. P., "Catalytic synthesis of aldehydes and ketones under mild conditions using TEMPO/oxone." Org. Lett. 2000, 2, 1173-1175. TEMPO/NCS allows for the selective oxidation of primary over secondary alcohols: Einhorn, J.; Einhorn, C.; ...
... For a catalytic protocol, see: Bolm, C.; Magnus, A. S.; Hildebrand, J. P., "Catalytic synthesis of aldehydes and ketones under mild conditions using TEMPO/oxone." Org. Lett. 2000, 2, 1173-1175. TEMPO/NCS allows for the selective oxidation of primary over secondary alcohols: Einhorn, J.; Einhorn, C.; ...
reactions of alcohols with alkenes over an aluminum
... Fripiat and Cruz-Cumplido, 1974; Theng, 1974; Thomas et al., 1977; Bittles et al., 1964a, 1964b, 1964c). Recently, renewed interest has been shown in the use of natural and synthetic smectitic clays as highly selective acid catalysts (e.g., Adams et al., 1978, 1979a, 1979b; Ballantine et al., 1981a, ...
... Fripiat and Cruz-Cumplido, 1974; Theng, 1974; Thomas et al., 1977; Bittles et al., 1964a, 1964b, 1964c). Recently, renewed interest has been shown in the use of natural and synthetic smectitic clays as highly selective acid catalysts (e.g., Adams et al., 1978, 1979a, 1979b; Ballantine et al., 1981a, ...
Organic Chemistry Naming Branched Hydrocarbons
... CH3CH3 CH3-CH2-CH2-CH-CH-CH-CH2 –CH3 CH-CH3 CH3 Alkyl groups: 3 methyl groups and 1 ethyl group Alphabetically: ethyl comes before methyl so…. ethyl methyloctane Adding prefixes: none for ethyl, but tri-for the methyl groups so… ethyl trimethyloctane ...
... CH3CH3 CH3-CH2-CH2-CH-CH-CH-CH2 –CH3 CH-CH3 CH3 Alkyl groups: 3 methyl groups and 1 ethyl group Alphabetically: ethyl comes before methyl so…. ethyl methyloctane Adding prefixes: none for ethyl, but tri-for the methyl groups so… ethyl trimethyloctane ...
Orbitals
... Many nucleophilic addition reactions of aldehydes and ketones are catalyzed by acid or base. Bases catalyze hydration by: a. making the carbonyl group more electrophilic b. shifting the equilibrium of the reaction c. making the carbonyl group less electrophilic d. converting the water to hydroxide ...
... Many nucleophilic addition reactions of aldehydes and ketones are catalyzed by acid or base. Bases catalyze hydration by: a. making the carbonyl group more electrophilic b. shifting the equilibrium of the reaction c. making the carbonyl group less electrophilic d. converting the water to hydroxide ...
main types and mechanisms of the reactions in organic chemistry
... Task №3. Give the mechanism of ethylene bromination reaction. Solution. Reactions which undergo -bonds fision, i.e., addition reactions, are typical for compounds which consist of carbon atoms in the state of sp2- or sphybridization. These reactions can pass on radical or onic mechanism depending o ...
... Task №3. Give the mechanism of ethylene bromination reaction. Solution. Reactions which undergo -bonds fision, i.e., addition reactions, are typical for compounds which consist of carbon atoms in the state of sp2- or sphybridization. These reactions can pass on radical or onic mechanism depending o ...
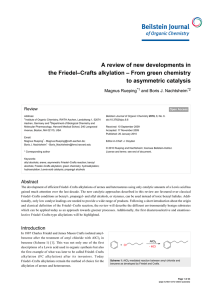
A review of new developments in the Friedel–Crafts - Beilstein
... While FC alkylations with allyl alcohols and benzyl ethers are likely to have the same carbocationic reaction intermediate, the FC alkylation with arenecarbaldehydes 6 has to be different (Scheme 5). Mechanistic investigations revealed that propanediol is necessary for this reaction to proceed. In t ...
... While FC alkylations with allyl alcohols and benzyl ethers are likely to have the same carbocationic reaction intermediate, the FC alkylation with arenecarbaldehydes 6 has to be different (Scheme 5). Mechanistic investigations revealed that propanediol is necessary for this reaction to proceed. In t ...
Chem 350 Jasperse Ch. 6 Summary of Reaction Types, Ch. 4
... Stability/Reactivity/Selectivity Principles 1. Reactant Stability/Reactivity: The more stable the reactant, the less reactive it will be. In terms of rates, this means that the more stable the reactant, the slower it will react. (The concept here is that the more stable the reactant, the more conten ...
... Stability/Reactivity/Selectivity Principles 1. Reactant Stability/Reactivity: The more stable the reactant, the less reactive it will be. In terms of rates, this means that the more stable the reactant, the slower it will react. (The concept here is that the more stable the reactant, the more conten ...
lecture 2 - alcohols-ethers
... commonly seen in reactions of secondary or tertiary alkyl halides or, under strongly acidic conditions, with secondary or tertiary alcohols. ...
... commonly seen in reactions of secondary or tertiary alkyl halides or, under strongly acidic conditions, with secondary or tertiary alcohols. ...
6. Low valent of Vanadium catalyst in organic synthesis
... *the coordination of the phosphorus raises the reduction capability and selectivity. *the bulky reductant is liable to approach the bromide from the less hindered side Toshikazu Hirao,J. Org. Chem., 1993, 58 (23), 6529-6530 ...
... *the coordination of the phosphorus raises the reduction capability and selectivity. *the bulky reductant is liable to approach the bromide from the less hindered side Toshikazu Hirao,J. Org. Chem., 1993, 58 (23), 6529-6530 ...
Chapter 25 Organic and Biological Chemistry
... 1. Find the longest chain in the molecule. 2. Number the chain from the end nearest the first substituent encountered. 3. List the substituents as a prefix along with the number(s) of the carbon(s) to which they are attached. Organic and Biological Chemistry © 2009, Prentice-Hall, Inc. ...
... 1. Find the longest chain in the molecule. 2. Number the chain from the end nearest the first substituent encountered. 3. List the substituents as a prefix along with the number(s) of the carbon(s) to which they are attached. Organic and Biological Chemistry © 2009, Prentice-Hall, Inc. ...
Chapter 25 Organic and Biological Chemistry
... 1. Find the longest chain in the molecule. 2. Number the chain from the end nearest the first substituent encountered. 3. List the substituents as a prefix along with the number(s) of the carbon(s) to which they are attached. Organic and Biological Chemistry © 2009, Prentice-Hall, Inc. ...
... 1. Find the longest chain in the molecule. 2. Number the chain from the end nearest the first substituent encountered. 3. List the substituents as a prefix along with the number(s) of the carbon(s) to which they are attached. Organic and Biological Chemistry © 2009, Prentice-Hall, Inc. ...
Chapter 25 Organic and Biological Chemistry
... 1. Find the longest chain in the molecule. 2. Number the chain from the end nearest the first substituent encountered. 3. List the substituents as a prefix along with the number(s) of the carbon(s) to which they are attached. Organic and Biological Chemistry © 2009, Prentice-Hall, Inc. ...
... 1. Find the longest chain in the molecule. 2. Number the chain from the end nearest the first substituent encountered. 3. List the substituents as a prefix along with the number(s) of the carbon(s) to which they are attached. Organic and Biological Chemistry © 2009, Prentice-Hall, Inc. ...
Chapter 25 Organic and Biological Chemistry
... 1. Find the longest chain in the molecule. 2. Number the chain from the end nearest the first substituent encountered. 3. List the substituents as a prefix along with the number(s) of the carbon(s) to which they are attached. Organic and Biological Chemistry © 2009, Prentice-Hall, Inc. ...
... 1. Find the longest chain in the molecule. 2. Number the chain from the end nearest the first substituent encountered. 3. List the substituents as a prefix along with the number(s) of the carbon(s) to which they are attached. Organic and Biological Chemistry © 2009, Prentice-Hall, Inc. ...
Chapter 25 Organic and Biological Chemistry
... 1. Find the longest chain in the molecule. 2. Number the chain from the end nearest the first substituent encountered. 3. List the substituents as a prefix along with the number(s) of the carbon(s) to which they are attached. Organic and Biological Chemistry © 2009, Prentice-Hall, Inc. ...
... 1. Find the longest chain in the molecule. 2. Number the chain from the end nearest the first substituent encountered. 3. List the substituents as a prefix along with the number(s) of the carbon(s) to which they are attached. Organic and Biological Chemistry © 2009, Prentice-Hall, Inc. ...
Chapter 25 Organic and Biological Chemistry
... 1. Find the longest chain in the molecule. 2. Number the chain from the end nearest the first substituent encountered. 3. List the substituents as a prefix along with the number(s) of the carbon(s) to which they are attached. Organic and Biological Chemistry © 2009, Prentice-Hall, Inc. ...
... 1. Find the longest chain in the molecule. 2. Number the chain from the end nearest the first substituent encountered. 3. List the substituents as a prefix along with the number(s) of the carbon(s) to which they are attached. Organic and Biological Chemistry © 2009, Prentice-Hall, Inc. ...
Alcohols phenols ethers
... (R–O/Ar–O) yields another class of compounds known as ‘ethers’, for example, CH3OCH3 (dimethyl ether). ethers as compounds formed by substituting the hydrogen atom of hydroxyl group of an alcohol or phenol by an alkyl or aryl group. Alcohols are organic compounds that have one or more hydroxy (-OH) ...
... (R–O/Ar–O) yields another class of compounds known as ‘ethers’, for example, CH3OCH3 (dimethyl ether). ethers as compounds formed by substituting the hydrogen atom of hydroxyl group of an alcohol or phenol by an alkyl or aryl group. Alcohols are organic compounds that have one or more hydroxy (-OH) ...
File
... Boiling points increase. The alcohols are all primary and hydrogen bond, the only difference is in the length of the carbon chain. The longer the carbon chain the more weak intermolecular forces between the compounds (b) ...
... Boiling points increase. The alcohols are all primary and hydrogen bond, the only difference is in the length of the carbon chain. The longer the carbon chain the more weak intermolecular forces between the compounds (b) ...
Elias James Corey

Elias James ""E.J."" Corey (born July 12, 1928) is an American organic chemist. In 1990, he won the Nobel Prize in Chemistry ""for his development of the theory and methodology of organic synthesis"", specifically retrosynthetic analysis. Regarded by many as one of the greatest living chemists, he has developed numerous synthetic reagents, methodologies and total syntheses and has advanced the science of organic synthesis considerably.