Document
... • Jones Reagent Harsher Oxidant (1° Alcohol Carboxylic Acid) • Alcohol Often Dissolved in Acetone While Jones Reagent Added • Choose Oxidant Based on Desired Carbonyl Functional Group ...
... • Jones Reagent Harsher Oxidant (1° Alcohol Carboxylic Acid) • Alcohol Often Dissolved in Acetone While Jones Reagent Added • Choose Oxidant Based on Desired Carbonyl Functional Group ...
List of Objectives for Chem52
... periodinane, pyridinium chlorochromate (PCC), pyridinium dichromate (PDC), Na2Cr2O7/H2SO4, or CrO3, or KMnO4/NaOH/H2O. (Dess-Martin periodinane, PCC and PDC will oxidize primary alcohols to aldehydes and secondary alcohols to ketones. Chromic acid, chromium trioxide, and permanganate will oxidize pr ...
... periodinane, pyridinium chlorochromate (PCC), pyridinium dichromate (PDC), Na2Cr2O7/H2SO4, or CrO3, or KMnO4/NaOH/H2O. (Dess-Martin periodinane, PCC and PDC will oxidize primary alcohols to aldehydes and secondary alcohols to ketones. Chromic acid, chromium trioxide, and permanganate will oxidize pr ...
Chapter 21 Carboxylic Acid Derivatives
... Solubility • Acid chlorides and anhydrides are too reactive to be used with water or alcohol. • Esters, 3 amides, and nitriles are good polar aprotic solvents. • Solvents commonly used in organic reactions: Ethyl acetate Dimethylformamide (DMF) Acetonitrile Chapter 21 ...
... Solubility • Acid chlorides and anhydrides are too reactive to be used with water or alcohol. • Esters, 3 amides, and nitriles are good polar aprotic solvents. • Solvents commonly used in organic reactions: Ethyl acetate Dimethylformamide (DMF) Acetonitrile Chapter 21 ...
Chem 342 Jasperse Syllabus 1 Organic Chemistry II READING
... What’s Covered in Organic I versus Organic II differs between NDSU and MSUM The following are reading sections and problems associated with one chapter that was covered at MSUM in Organic I but is covered at NDSU in Organic II. Thus, if you are an NDSU student taking Organic II at MSUM, you will end ...
... What’s Covered in Organic I versus Organic II differs between NDSU and MSUM The following are reading sections and problems associated with one chapter that was covered at MSUM in Organic I but is covered at NDSU in Organic II. Thus, if you are an NDSU student taking Organic II at MSUM, you will end ...
Substitution Rxns-a-Sn2-12-quesx
... at the University of Freiburg, in Germany, in collaboration with William L. Hase's group at Texas Tech University, provide direct evidence for this mechanism in the gas phase. However, they also detected an additional, unexpected mechanism. In this new pathway, called the roundabout mechanism, chlor ...
... at the University of Freiburg, in Germany, in collaboration with William L. Hase's group at Texas Tech University, provide direct evidence for this mechanism in the gas phase. However, they also detected an additional, unexpected mechanism. In this new pathway, called the roundabout mechanism, chlor ...
Organic Chemistry Fifth Edition
... Catalytic hydrogenolysis used in industry but conditions difficult or dangerous to duplicate in the laboratory (special catalyst, high temperature, high pressure). ...
... Catalytic hydrogenolysis used in industry but conditions difficult or dangerous to duplicate in the laboratory (special catalyst, high temperature, high pressure). ...
Grignard Reaction
... Victor Grignard, who found that treating a bromoalkane with magnesium metal resulted in the formation of an organometallic adduct where magnesium inserted into the C–Br bond. While making a metal-carbon bond was not new, Grignard found that these reagents (now bearing his name) could react with elec ...
... Victor Grignard, who found that treating a bromoalkane with magnesium metal resulted in the formation of an organometallic adduct where magnesium inserted into the C–Br bond. While making a metal-carbon bond was not new, Grignard found that these reagents (now bearing his name) could react with elec ...
Chapter 10_Organohalides
... the system allowing for resonance structures to be drawn -system extended over three carbons instead of two ...
... the system allowing for resonance structures to be drawn -system extended over three carbons instead of two ...
Grignard Reaction - OpenBU
... measured. What is critical is that this is done fast to avoid condensation of water onto the surface of the dry ice. IMMEDIATELY add the entire solution of Grignard reagent to the dry ice via a Pasteur pipet as quickly as possible, leaving the unreacted magnesium behind. Bubbling will occur as CO2 r ...
... measured. What is critical is that this is done fast to avoid condensation of water onto the surface of the dry ice. IMMEDIATELY add the entire solution of Grignard reagent to the dry ice via a Pasteur pipet as quickly as possible, leaving the unreacted magnesium behind. Bubbling will occur as CO2 r ...
Grignard Reaction - OpenBU
... measured. What is critical is that this is done fast to avoid condensation of water onto the surface of the dry ice. IMMEDIATELY add the entire solution of Grignard reagent to the dry ice via a Pasteur pipet as quickly as possible, leaving the unreacted magnesium behind. Bubbling will occur as CO2 r ...
... measured. What is critical is that this is done fast to avoid condensation of water onto the surface of the dry ice. IMMEDIATELY add the entire solution of Grignard reagent to the dry ice via a Pasteur pipet as quickly as possible, leaving the unreacted magnesium behind. Bubbling will occur as CO2 r ...
CC 2 097-110..7686hdisk chapter .. Page97
... groups on the benzene ring on electronic excitation (for the photodecarboxylation reactions reported), although it was not clear whether this characteristic is best attributed to its S1 or T1 state or both.† Although ketones classically react via their triplet excited states, typically via Type I an ...
... groups on the benzene ring on electronic excitation (for the photodecarboxylation reactions reported), although it was not clear whether this characteristic is best attributed to its S1 or T1 state or both.† Although ketones classically react via their triplet excited states, typically via Type I an ...
hydroxy- and oxoacids. heterofunctional compounds of benzene
... interconversion between two forms This phenomenon is called tautomerism. Forms which turn one into another are tautomers and their mutual transition are tautomeric transformations. If tautomers are substances with carbonyl and enol groups (for example, isomerism of acetoacetic ester), than tautomeri ...
... interconversion between two forms This phenomenon is called tautomerism. Forms which turn one into another are tautomers and their mutual transition are tautomeric transformations. If tautomers are substances with carbonyl and enol groups (for example, isomerism of acetoacetic ester), than tautomeri ...
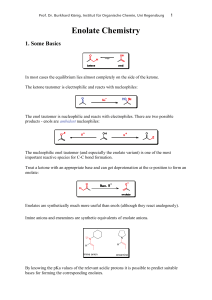
Enolate Chemistry - Institut für Organische Chemie
... One substrate usually has a stronger facial bias than the other and can completely override the facial preference of its partner. In this case one substrate controls the stereochemical outcome entirely. ...
... One substrate usually has a stronger facial bias than the other and can completely override the facial preference of its partner. In this case one substrate controls the stereochemical outcome entirely. ...
Sugar Amino Acids - The Krasavin research group
... Ag2 O, followed by esterification with diazomethane, and final catalytic hydrogenation over Pd/C catalysis to give the final furanoid α-amino acid 5, as the α- or β-anomer, depending on the stereochemistry of starting thiazolyl ketol acetate. This approach was also reported for a galacto-derived pyr ...
... Ag2 O, followed by esterification with diazomethane, and final catalytic hydrogenation over Pd/C catalysis to give the final furanoid α-amino acid 5, as the α- or β-anomer, depending on the stereochemistry of starting thiazolyl ketol acetate. This approach was also reported for a galacto-derived pyr ...
Naming organic compounds
... Indicate the position of the branches with a number, numbering from the end nearest the functional group. If there is more than one branch, the branches are identified in alphabetical order ...
... Indicate the position of the branches with a number, numbering from the end nearest the functional group. If there is more than one branch, the branches are identified in alphabetical order ...
Chemistry - Tiwariacademy.net
... SN1 reaction proceeds via the formation of carbocation. The alkyl halide (I) is 3° while (II) is 2°. Therefore, (I) forms 3° carbocation while (II) forms 2° carbocation. Greater the stability of the carbocation, faster is the rate of SN1 reaction. Since 3° carbocation is more stable than 2° carbocat ...
... SN1 reaction proceeds via the formation of carbocation. The alkyl halide (I) is 3° while (II) is 2°. Therefore, (I) forms 3° carbocation while (II) forms 2° carbocation. Greater the stability of the carbocation, faster is the rate of SN1 reaction. Since 3° carbocation is more stable than 2° carbocat ...
Cis/Trans
... 5. hydrogenation of cyclobutene 6. addition of hydrochloric acid to 1-pentene 7. hydrogenation of cyclopentene 8. addition of hydrobromic acid to 1-butene 9. hydration of cyclobutene 10.addition of iodine to 2-hexene 11.water is added to 1-pentene ...
... 5. hydrogenation of cyclobutene 6. addition of hydrochloric acid to 1-pentene 7. hydrogenation of cyclopentene 8. addition of hydrobromic acid to 1-butene 9. hydration of cyclobutene 10.addition of iodine to 2-hexene 11.water is added to 1-pentene ...
amines - Gneet`s
... Electron withdrawing group ( like –NO2, -CN, - X etc) decreases the electron, density of amino group. So that electron releasing tendency of amine and thus its basic strength decreases. In addition to its an electron withdrawing group destabilizes the cation formed after protonation by intensify ...
... Electron withdrawing group ( like –NO2, -CN, - X etc) decreases the electron, density of amino group. So that electron releasing tendency of amine and thus its basic strength decreases. In addition to its an electron withdrawing group destabilizes the cation formed after protonation by intensify ...
Slides
... within an interaction cut-off distance of 7.0. Å are connected via uniform elastic springs. Another structural property CN too have a strong impact on equilibrium dynamics is the CN, which is defined as the number of amino acids (or αcarbons) that coordinate the central amino acid within a first int ...
... within an interaction cut-off distance of 7.0. Å are connected via uniform elastic springs. Another structural property CN too have a strong impact on equilibrium dynamics is the CN, which is defined as the number of amino acids (or αcarbons) that coordinate the central amino acid within a first int ...
Organic Chemistry II Introduction
... Reaction with hydrazine gives hydrazones – Reduction of hydrazone in base yields an alkane – Reduction of hydrazone in acid/Zn yields an alkane Alcohols add to yield acetals Phosphoranes add to aldehydes and ketones to give alkenes (the ...
... Reaction with hydrazine gives hydrazones – Reduction of hydrazone in base yields an alkane – Reduction of hydrazone in acid/Zn yields an alkane Alcohols add to yield acetals Phosphoranes add to aldehydes and ketones to give alkenes (the ...
Petasis reaction

The Petasis reaction (alternatively called the Petasis borono–Mannich (PBM) reaction) is the chemical reaction of an amine, aldehyde, and vinyl- or aryl-boronic acid to form substituted amines.Reported in 1993 by Nicos Petasis as a practical method towards the synthesis of a geometrically pure antifungal agent, naftifine, the Petasis reaction can be described as a variation of the Mannich reaction. Rather than generating an enolate to form the substituted amine product, in the Petasis reaction, the vinyl group of the organoboronic acid serves as the nucleophile. In comparison to other methods of generating allyl amines, the Petasis reaction tolerates a multifunctional scaffold, with a variety of amines and organoboronic acids as potential starting materials. Additionally, the reaction does not require anhydrous or inert conditions. As a mild, selective synthesis, the Petasis reaction is useful in generating α-amino acids, and is utilized in combinatorial chemistry and drug discovery.