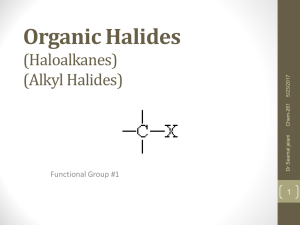Neuman Chapter - Department of Chemistry
... They also show that the relative amounts of elimination and substitution products vary significantly depending on the structure of the substrate. Nucleophile versus Base. When ethoxide ion displaces a leaving group in a SN2 reaction, we call it a nucleophile. When ethoxide ion removes a β-H in an E2 ...
... They also show that the relative amounts of elimination and substitution products vary significantly depending on the structure of the substrate. Nucleophile versus Base. When ethoxide ion displaces a leaving group in a SN2 reaction, we call it a nucleophile. When ethoxide ion removes a β-H in an E2 ...
Heterogeneous catalysis (I)
... In a heterogeneous reaction, the catalyst is in a different phase from the reactants. Normally, the catalyst is a solid and reactants are fluids (liquids or gases). It is characterized by the presence of “active sites” on the catalyst surface. In a homogeneous reaction, the catalyst is in the same p ...
... In a heterogeneous reaction, the catalyst is in a different phase from the reactants. Normally, the catalyst is a solid and reactants are fluids (liquids or gases). It is characterized by the presence of “active sites” on the catalyst surface. In a homogeneous reaction, the catalyst is in the same p ...
Organic Halides (Haloalkanes) (Alkyl Halides)
... (their use is now restricted due to the fact that some of them damage the ozone layer) • polymers such as Teflon (non-stick surfaces as in cookware) and PVC (polyvinylchloride) used plumbing • DDT (dichlorodiphenyltrichloroethane) – now banned pesticide • PCB’s (polychlorinated biphenyls) – electric ...
... (their use is now restricted due to the fact that some of them damage the ozone layer) • polymers such as Teflon (non-stick surfaces as in cookware) and PVC (polyvinylchloride) used plumbing • DDT (dichlorodiphenyltrichloroethane) – now banned pesticide • PCB’s (polychlorinated biphenyls) – electric ...
102 Lecture Ch15
... - no matter how you turn them, they can’t be superimposed • Many organic compounds are also chiral - most biomolecules (amino acids, sugars, etc.) are chiral and usually only one of the stereoisomers is used • In order for a carbon in an organic compound to be chiral, it must have 4 different groups ...
... - no matter how you turn them, they can’t be superimposed • Many organic compounds are also chiral - most biomolecules (amino acids, sugars, etc.) are chiral and usually only one of the stereoisomers is used • In order for a carbon in an organic compound to be chiral, it must have 4 different groups ...
GRIGNARD REAGENTS
... The structures on either side of a straight two-headed arrow are resonance forms of the same chemical entity; they differ only the location of electrons, and can be interconverted by the movement of curly arrows. A carbonyl group is a HYBRID of the two resonance forms shown. ...
... The structures on either side of a straight two-headed arrow are resonance forms of the same chemical entity; they differ only the location of electrons, and can be interconverted by the movement of curly arrows. A carbonyl group is a HYBRID of the two resonance forms shown. ...
9: Formation of Alkenes and Alkynes. Elimination Reactions
... They also show that the relative amounts of elimination and substitution products vary significantly depending on the structure of the substrate. Nucleophile versus Base. When ethoxide ion displaces a leaving group in a SN2 reaction, we call it a nucleophile. When ethoxide ion removes a β-H in an E2 ...
... They also show that the relative amounts of elimination and substitution products vary significantly depending on the structure of the substrate. Nucleophile versus Base. When ethoxide ion displaces a leaving group in a SN2 reaction, we call it a nucleophile. When ethoxide ion removes a β-H in an E2 ...
UNSATURATED HYDROCARBONS
... Unsaturated hydrocarbons are hydrocarbons that have double or triple covalent bonds between adjacent carbon atoms. Those with at least one double bond are called alkenes and those with at least one triple bond are called alkynes. Alkenes with two double bonds are called dienes. ...
... Unsaturated hydrocarbons are hydrocarbons that have double or triple covalent bonds between adjacent carbon atoms. Those with at least one double bond are called alkenes and those with at least one triple bond are called alkynes. Alkenes with two double bonds are called dienes. ...
New Phenylglycine-Derived Primary Amine Organocatalysts for the
... is conveniently prepared by direct reduction of phenylglycine with NaBH4/I2 or NaBH4/H2SO4.[21–23] The silyl ether 20 has to the best of our knowledge not been previously reported, but is prepared from amino alcohol 15 in one non-chromatographic step by using the iodine-catalysed silylation with hex ...
... is conveniently prepared by direct reduction of phenylglycine with NaBH4/I2 or NaBH4/H2SO4.[21–23] The silyl ether 20 has to the best of our knowledge not been previously reported, but is prepared from amino alcohol 15 in one non-chromatographic step by using the iodine-catalysed silylation with hex ...
Selective Oxidation Reactions of Natural Compounds with
... Methyltrioxorhenium (CH3ReO3, MTO) in the presence of H2O2 has proven itself as an efficient and versatile oxidation catalyst with interesting selectivity towards natural compounds, which can be oxidized under quite mild conditions [3–21]. In previous work [22] we have observed good regio- and stere ...
... Methyltrioxorhenium (CH3ReO3, MTO) in the presence of H2O2 has proven itself as an efficient and versatile oxidation catalyst with interesting selectivity towards natural compounds, which can be oxidized under quite mild conditions [3–21]. In previous work [22] we have observed good regio- and stere ...
8. Alkynes: An Introduction to Organic Synthesis
... the movement of a proton and are called tautomers Enols rearrange to the isomeric ketone by the rapid transfer of a proton from the hydroxyl to the alkene carbon The keto form is usually so stable compared to the enol that only the keto form can be observed ...
... the movement of a proton and are called tautomers Enols rearrange to the isomeric ketone by the rapid transfer of a proton from the hydroxyl to the alkene carbon The keto form is usually so stable compared to the enol that only the keto form can be observed ...
Free Radical Chemistry and the Preparation of Alkyl
... Oxidations decrease e- density on C (formation of C-O, C-N or C-X bonds) so reactions that form alkyl halides (R-H to R-X) are oxidations ...
... Oxidations decrease e- density on C (formation of C-O, C-N or C-X bonds) so reactions that form alkyl halides (R-H to R-X) are oxidations ...
Rutgers...Ch17 Reactions of Aromatic Compounds
... In the case of toluene, ortho (and para) attack results in the positive charge being spread over two secondary carbons and one tertiary carbon atom (the one bearing the CH3 group). Since the sigma complexes for ortho (and para) attack have resonance forms with tertiary carbons, they are more stable ...
... In the case of toluene, ortho (and para) attack results in the positive charge being spread over two secondary carbons and one tertiary carbon atom (the one bearing the CH3 group). Since the sigma complexes for ortho (and para) attack have resonance forms with tertiary carbons, they are more stable ...
10. Alkyl Halides
... abstract a proton from a carbon next to the leaving group, the C-H begins to break, a new carbon-carbon pi bond begins to form, and the leaving group begins to depart ...
... abstract a proton from a carbon next to the leaving group, the C-H begins to break, a new carbon-carbon pi bond begins to form, and the leaving group begins to depart ...
... In 1995 Grubbs reported new molecularly-well-defined catalysts [Ru(=CHPh)Cl2(PR3)2], R = Ph or Cy (cyclohexyl).8g,h These structures are closely related to the vinylidene ones. The compound with R = Cy [Ru(=CHPh)Cl2(PCy3)2] has been commercialized and is known as the first-generation Grubbs catalyst ...
Alcohols
... Ethanol is the least toxic alcohol, but it is still toxic. The body detoxifies ethanol with NAD catalyzed first by alcohol dehydrogenase (ADH) and second by aldehyde dehydrogenase (ALDH): ethanol acetic acid The reason methanol and ethylene glycol are so toxic to humans is that, when they ...
... Ethanol is the least toxic alcohol, but it is still toxic. The body detoxifies ethanol with NAD catalyzed first by alcohol dehydrogenase (ADH) and second by aldehyde dehydrogenase (ALDH): ethanol acetic acid The reason methanol and ethylene glycol are so toxic to humans is that, when they ...
FUNCTIONALIZATION OF NON-ACTiVATED CARBON ATOMS
... isomers were prepared by our equilibration method. We equilibrated each of the four epimers at different temperatures and established the equilibrium ratio and also the thermodynamical parameters. As expected, the 1413isomer is the most stable one; the ratio 1413H/l4czH is equal to 8 and that of 513 ...
... isomers were prepared by our equilibration method. We equilibrated each of the four epimers at different temperatures and established the equilibrium ratio and also the thermodynamical parameters. As expected, the 1413isomer is the most stable one; the ratio 1413H/l4czH is equal to 8 and that of 513 ...
Microsoft Word - Open Access Repository of Indian Theses
... regiochemistry. The methodology was further extended to the ring opening of aliphatic epoxides and substituted styrene oxide with amines to afford the corresponding products in good yields. Chapter IV. Aza-Michael Addition Reactions using Recyclable Copper Catalysts The conjugate addition (1,4-addit ...
... regiochemistry. The methodology was further extended to the ring opening of aliphatic epoxides and substituted styrene oxide with amines to afford the corresponding products in good yields. Chapter IV. Aza-Michael Addition Reactions using Recyclable Copper Catalysts The conjugate addition (1,4-addit ...
PDF aldehydes and ketones
... Addition of NaHSO3 to carbonyl/ aldehydic carbon gives solid adduct; these are sulfonates that are water soluble. Only RCHO, methyl ketones, and cyclic ketones react. Carbonyl compounds can be regenerated on treating the adduct with acid or base. R C ...
... Addition of NaHSO3 to carbonyl/ aldehydic carbon gives solid adduct; these are sulfonates that are water soluble. Only RCHO, methyl ketones, and cyclic ketones react. Carbonyl compounds can be regenerated on treating the adduct with acid or base. R C ...
6. Low valent of Vanadium catalyst in organic synthesis
... As the amount of allyl bromide increased, the yield of the coupling product 1a decreased gradually while the amount of 3 increased. ...
... As the amount of allyl bromide increased, the yield of the coupling product 1a decreased gradually while the amount of 3 increased. ...
Evolution Alters the Enzymatic Reaction Coordinate of Dihydrofolate
... cofactors NADPH and folic acid, which is a substrate mimic. This structure was solved to a resolution of 1.20 Å by Wright et al. (PDB code 4M6K).26 To create a reactive complex to study hydride transfer using the coordinates of folic acid, we changed the protonation states of N1, N8, and protonated ...
... cofactors NADPH and folic acid, which is a substrate mimic. This structure was solved to a resolution of 1.20 Å by Wright et al. (PDB code 4M6K).26 To create a reactive complex to study hydride transfer using the coordinates of folic acid, we changed the protonation states of N1, N8, and protonated ...
Exam I F06 Q - UC Davis Canvas
... CLOSED BOOK EXAM! No books, notes, or additional scrap paper are permitted. All information required is contained on the exam. Place all work in the space provided. If you require additional space, use the back of the exam. A scientific calculator may be used (if it is a programmable calculator, its ...
... CLOSED BOOK EXAM! No books, notes, or additional scrap paper are permitted. All information required is contained on the exam. Place all work in the space provided. If you require additional space, use the back of the exam. A scientific calculator may be used (if it is a programmable calculator, its ...
Student Learning Outcomes (broken down by chapter…basically the
... Predict the major products of the dehydration of alcohols and describe the relative rates at which alcohols undergo dehydration. Predict the products of the reactions of alcohols with oxidizing reagents. Propose mechanisms for the dehydration reactions of alcohols. Predict the major products of the ...
... Predict the major products of the dehydration of alcohols and describe the relative rates at which alcohols undergo dehydration. Predict the products of the reactions of alcohols with oxidizing reagents. Propose mechanisms for the dehydration reactions of alcohols. Predict the major products of the ...
Ene reaction

The ene reaction (also known as the Alder-ene reaction) is a chemical reaction between an alkene with an allylic hydrogen (the ene) and a compound containing a multiple bond (the enophile), in order to form a new σ-bond with migration of the ene double bond and 1,5 hydrogen shift. The product is a substituted alkene with the double bond shifted to the allylic position.This transformation is a group transfer pericyclic reaction, and therefore, usually requires highly activated substrates and/or high temperatures. Nonetheless, the reaction is compatible with a wide variety of functional groups that can be appended to the ene and enophile moieties. Also,many useful Lewis acid-catalyzed ene reactions have been developed which can afford high yields and selectivities at significantly lower temperatures, making the ene reaction a useful C–C forming tool for the synthesis of complex molecules and natural products.