Discussion Sheet 11
... Alcohols can be made into a variety of leaving groups This opens up possibilities for Sn2 and E2 reactions. ...
... Alcohols can be made into a variety of leaving groups This opens up possibilities for Sn2 and E2 reactions. ...
Chapter16McMurryPPP
... Only alkyl halides can be used (F, Cl, I, Br) Aryl halides and vinylic halides do not react (their carbocations are too hard to form) Will not work with rings containing an amino group substituent or a strongly electronwithdrawing group ...
... Only alkyl halides can be used (F, Cl, I, Br) Aryl halides and vinylic halides do not react (their carbocations are too hard to form) Will not work with rings containing an amino group substituent or a strongly electronwithdrawing group ...
3. Ethers
... •Draw Chloromethyl cyclohexyl ether. •If both groups are the same: •Lastly - for more complicated ethers the term______________may be used as a prefix. •Draw Methoxy butane •Draw Diethoxy benzene •Draw Phenoxy phenol •___________________________________ ether is used as a octane enhancer in petrol. ...
... •Draw Chloromethyl cyclohexyl ether. •If both groups are the same: •Lastly - for more complicated ethers the term______________may be used as a prefix. •Draw Methoxy butane •Draw Diethoxy benzene •Draw Phenoxy phenol •___________________________________ ether is used as a octane enhancer in petrol. ...
Organic Chemistry Fifth Edition
... Alkyl halides are defined as primary if the carbon that the halogen is attached to is directly attached to one other carbon. Similarly if the carbon that the halogen is attached to is directly attached to two carbons then it is a secondary alkyl halide. In tertiary alkyl halides the carbon with the ...
... Alkyl halides are defined as primary if the carbon that the halogen is attached to is directly attached to one other carbon. Similarly if the carbon that the halogen is attached to is directly attached to two carbons then it is a secondary alkyl halide. In tertiary alkyl halides the carbon with the ...
Jonpostwriteup
... precise. A common solution for that problem is the pseudo first order approximation If either (A) or (B) remain constant as the reaction proceeds, then the reaction can be considered pseudo first order because in fact it only depends on the concentration of one reactant. If for example (B) remains c ...
... precise. A common solution for that problem is the pseudo first order approximation If either (A) or (B) remain constant as the reaction proceeds, then the reaction can be considered pseudo first order because in fact it only depends on the concentration of one reactant. If for example (B) remains c ...
Facile Oxidation of Benzyl Alcohols with Sodium Nitrate/p
... shown in Table 1. The oxidation of various benzyl alcohols gave high yields of benzaldehydes in very short reaction times. The competing over-oxidation of benzaldehydes to the corresponding carboxylic acids and any aromatic nitration has not been observed in all cases studied at the present reaction ...
... shown in Table 1. The oxidation of various benzyl alcohols gave high yields of benzaldehydes in very short reaction times. The competing over-oxidation of benzaldehydes to the corresponding carboxylic acids and any aromatic nitration has not been observed in all cases studied at the present reaction ...
AROMATIC CHEMISTRY
... contain 4n + 2 -electrons (Huckel’s Rule), where n is an integer. be cyclic be planar ...
... contain 4n + 2 -electrons (Huckel’s Rule), where n is an integer. be cyclic be planar ...
Variant 1 - Egypt IG Student Room
... the total number of structural isomers, including compound 2, that could be formed by adding a second methyl group to the ring of compound 1, ...
... the total number of structural isomers, including compound 2, that could be formed by adding a second methyl group to the ring of compound 1, ...
Please don`t do problem 31a, but please do problem 32c
... Also self aldol product of acetaldehyde and propionaldehyde ...
... Also self aldol product of acetaldehyde and propionaldehyde ...
Functional Groups - La Salle University
... where R’ is different from R – These can be considered organic derivatives of water in which both hydrogens are replaced by organic groups – The bond angle at oxygen is close to the tetrahedral angle ...
... where R’ is different from R – These can be considered organic derivatives of water in which both hydrogens are replaced by organic groups – The bond angle at oxygen is close to the tetrahedral angle ...
Amino alcohols. XVII. Arylethanolamines
... Seedlings obtained from flats sown in the first week in February were transplanted into the field in’early June in the several years of plantings. Replicated plots were established at the ScottsblufE Field Station in a spacing and yield study under irrigation. HE RENEWED interest in the growing of p ...
... Seedlings obtained from flats sown in the first week in February were transplanted into the field in’early June in the several years of plantings. Replicated plots were established at the ScottsblufE Field Station in a spacing and yield study under irrigation. HE RENEWED interest in the growing of p ...
Lecture 16 Aromatic Diazonium Salts
... In case of primary and secondary aromatic amines, the reaction preferentially takes place at the nitrogen atoms of the diazonium ions. For example, aniline adds to the aromatic diazonium salt to give diazoaminobenzene. ...
... In case of primary and secondary aromatic amines, the reaction preferentially takes place at the nitrogen atoms of the diazonium ions. For example, aniline adds to the aromatic diazonium salt to give diazoaminobenzene. ...
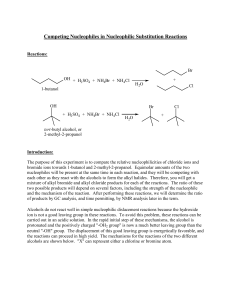
Competing Nucleophiles in Nucleophilic Substitution Reactions
... Experimental Procedure for 1-butanol: The sulfuric acid, ammonium bromide, and ammonium chloride will be provided to you as a solvent-nucleophile medium. One mL of this solution contains 0.42 mL of sulfuric acid, 0.1056 g of ammonium chloride, and 0.1944 g of ammonium bromide. From this information, ...
... Experimental Procedure for 1-butanol: The sulfuric acid, ammonium bromide, and ammonium chloride will be provided to you as a solvent-nucleophile medium. One mL of this solution contains 0.42 mL of sulfuric acid, 0.1056 g of ammonium chloride, and 0.1944 g of ammonium bromide. From this information, ...
ppt
... • In particular, combining carboxylation with hydrogenation reactions may enable the synthesis of multi-carbon ...
... • In particular, combining carboxylation with hydrogenation reactions may enable the synthesis of multi-carbon ...
OxorheniumCatalyzed Deoxydehydration of Sugars and Sugar
... products.[10] While these methods are effective for simple vicinal diols and appear to lay solid foundations in the context of biomass deoxygenation, no system has been reported to have a general efficiency on polyols. The only sugar alcohol employed in this reaction to date is erythritol (C4 sugar ...
... products.[10] While these methods are effective for simple vicinal diols and appear to lay solid foundations in the context of biomass deoxygenation, no system has been reported to have a general efficiency on polyols. The only sugar alcohol employed in this reaction to date is erythritol (C4 sugar ...
Working with Hazardous Chemicals
... Street, Columbia, South Carolina, or may be prepared as follows. A 250-ml., three-necked flask is charged with 89.14 g. (1.001 mole) of 2-amino-2-methylpropanol and cooled in an ice bath. The amine is carefully neutralized with 52.3 g. (1.25 mole) of 90.6% formic acid over a 1-hour period. A magneti ...
... Street, Columbia, South Carolina, or may be prepared as follows. A 250-ml., three-necked flask is charged with 89.14 g. (1.001 mole) of 2-amino-2-methylpropanol and cooled in an ice bath. The amine is carefully neutralized with 52.3 g. (1.25 mole) of 90.6% formic acid over a 1-hour period. A magneti ...
Carbonyl Compounds - Thomas Tallis Science
... dipole–dipole interactions. In addition, these molecules can form hydrogen bonds with each other, due to the slightly positive hydrogen atom of the hydroxyl group. 12 of 38 ...
... dipole–dipole interactions. In addition, these molecules can form hydrogen bonds with each other, due to the slightly positive hydrogen atom of the hydroxyl group. 12 of 38 ...
Ch-8-Aldehydes and ketones
... Know the structural differences between aldehydes and ketones Know how to draw aldehydes and ketones know the common and IUPAC nomenclature of aldehydes and ketones Know the physical properties of aldehydes and ketones Know how to synthesize an aldehyde or a ketone from a compound without tha ...
... Know the structural differences between aldehydes and ketones Know how to draw aldehydes and ketones know the common and IUPAC nomenclature of aldehydes and ketones Know the physical properties of aldehydes and ketones Know how to synthesize an aldehyde or a ketone from a compound without tha ...
1. Absorption of what type electromagnetic radiation results in
... Which of the following best describes the carbon-chlorine bond of an alkyl ...
... Which of the following best describes the carbon-chlorine bond of an alkyl ...
Group 2-catalysis for the Atom-Efficient Synthesis of Imidazolidine
... cyclisation step proved highly dependent on the substitution pattern of the acetylenic aryl moiety. Ortho-substitution, with substrates such as o-tolylacetylene and 1-naphthylacetylene, resulted in significantly reduced cyclisation rates compared to the parent phenylacetylene (Table 3, entries 2–3) ...
... cyclisation step proved highly dependent on the substitution pattern of the acetylenic aryl moiety. Ortho-substitution, with substrates such as o-tolylacetylene and 1-naphthylacetylene, resulted in significantly reduced cyclisation rates compared to the parent phenylacetylene (Table 3, entries 2–3) ...
PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY/ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
... Write the structural formula of the product of reaction between propanoic acid and ethanol in presence of an acid. Write the general reaction between a carboxylic acid and caustic soda, status the importance of this reaction in industry. ...
... Write the structural formula of the product of reaction between propanoic acid and ethanol in presence of an acid. Write the general reaction between a carboxylic acid and caustic soda, status the importance of this reaction in industry. ...
19.2 preparation of acyl chlorides
... The preparation of a solution of soap by the reaction of fat with water in the presence of base was probably one of the earliest chemical processes discovered by humans. Although the details of this discovery are lost in antiquity, we can imagine early humans finding that water that had been in cont ...
... The preparation of a solution of soap by the reaction of fat with water in the presence of base was probably one of the earliest chemical processes discovered by humans. Although the details of this discovery are lost in antiquity, we can imagine early humans finding that water that had been in cont ...
Alcohols
... تعتمد هذه الطريقة على أن CH3OHيسمى ب Carbinolو تسمى alcoholsكمشتقات منه بذكر أسماء alkylالمستبدلة بدال من ذرات الهيدروجين في مجموعة CH3ثم نكتب كلمة Carbinol ...
... تعتمد هذه الطريقة على أن CH3OHيسمى ب Carbinolو تسمى alcoholsكمشتقات منه بذكر أسماء alkylالمستبدلة بدال من ذرات الهيدروجين في مجموعة CH3ثم نكتب كلمة Carbinol ...
Wolff–Kishner reduction

The Wolff–Kishner reduction is a reaction used in organic chemistry to convert carbonyl functionalities into methylene groups. In the context of complex molecule synthesis, it is most frequently employed to remove a carbonyl group after it has served its synthetic purpose of activating an intermediate in a preceding step. As such, there is no obvious retron for this reaction. Originally reported by Nikolai Kischner in 1911 and Ludwig Wolff in 1912, it has been applied to the total synthesis of scopadulcic acid B, aspidospermidine and dysidiolide.In general, the reaction mechanism first involves the in situ generation of a hydrazone by condensation of hydrazine with the ketone or aldehyde substrate. Sometimes it is however advantageous to use a pre-formed hydrazone as substrate (see modifications). The hydrazone is deprotonated by alkoxide base followed by a concerted, rate-determining step in which a diimide anion is formed. Collapse of this alkyldiimde with loss of N2 leads to formation of an alkylanion which can be protonated by solvent to give the desired product.Because the Wolff–Kishner reduction requires highly basic conditions, it is unsuitable for base-sensitive substrates. However, this method can be superior over the related Clemmensen reduction for acid-sensitive compounds such as pyrroles and for high-molecular weight compounds.