Study Guide 2 - Chemistry Teaching Resources
... detailed structure of the molecule, especially the part around the hydroxyl group. In addition to straight-chain and branched structures it is also possible to have rings structures and alcohols with more than one hydroxyl group. This lesson topic looks in more detail at a variety of alcohol structu ...
... detailed structure of the molecule, especially the part around the hydroxyl group. In addition to straight-chain and branched structures it is also possible to have rings structures and alcohols with more than one hydroxyl group. This lesson topic looks in more detail at a variety of alcohol structu ...
AE Tri-Act - aechemie.com
... AE Tri-Act PMETM is a clear, colorless and nearly odorless liquid. It is stable to hydrolysis, temperature and pH. As a result of its good chemical stability, it is highly compatible with all commonly used cosmetic ingredients. Whereas glycerin esters are attacked by lipolytic enzymes, this is not t ...
... AE Tri-Act PMETM is a clear, colorless and nearly odorless liquid. It is stable to hydrolysis, temperature and pH. As a result of its good chemical stability, it is highly compatible with all commonly used cosmetic ingredients. Whereas glycerin esters are attacked by lipolytic enzymes, this is not t ...
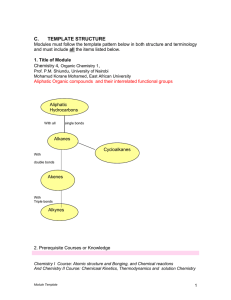
Hydrocarbons
... Alkenes – Uses and sources Alkenes have a double bond present somewhere in their structure. This bond can be snapped open and other elements bonded to it. This makes them quite handy. Sources Alkenes can be created by cracking alkanes Uses Alkenes can be used for fuel They can be used as a building ...
... Alkenes – Uses and sources Alkenes have a double bond present somewhere in their structure. This bond can be snapped open and other elements bonded to it. This makes them quite handy. Sources Alkenes can be created by cracking alkanes Uses Alkenes can be used for fuel They can be used as a building ...
Synthesis of Four Diastereomeric 3,5-Dialkoxy-2,4
... treatment of the dimesylate 24 with 2.4 equiv of methylmagnesium bromide in THF at 0 °C for 10 min afforded the desired diol 25 in 92% yield.11 ...
... treatment of the dimesylate 24 with 2.4 equiv of methylmagnesium bromide in THF at 0 °C for 10 min afforded the desired diol 25 in 92% yield.11 ...
C7 Revision Powerpoint Part 1
... make products such as whisky and brandy; • Genetically modified E. coli bacteria can be used to convert waste biomass from a range of sources into ethanol and recall the optimum conditions for the ...
... make products such as whisky and brandy; • Genetically modified E. coli bacteria can be used to convert waste biomass from a range of sources into ethanol and recall the optimum conditions for the ...
Organic - UCLA Chemistry and Biochemistry
... the characteristic apparent quartet (J = 12 Hz) for Ha that is also seen in the spectrum of Id.' Likewise the stereochemistry of 9b was determined primarily from its highfield 'H NMR spectrum which showed the expected coupling constants for the conformation drawn, namely: Ha dd, J = 11.8, 6.8 Hz;Hb ...
... the characteristic apparent quartet (J = 12 Hz) for Ha that is also seen in the spectrum of Id.' Likewise the stereochemistry of 9b was determined primarily from its highfield 'H NMR spectrum which showed the expected coupling constants for the conformation drawn, namely: Ha dd, J = 11.8, 6.8 Hz;Hb ...
File - Mr. Heff`s Class
... - Molecular formula of benzene, C6H6, is a based on its percent composition and molar mass. - Melting point = 5.5 oC, boiling point = 80.1 oC which is comparable to the boiling of cyclohexane (81.4 0C). - Non-polar molecule and is soluble only in nonpolar solvents. - Benzene has hybrid bonds. - Benz ...
... - Molecular formula of benzene, C6H6, is a based on its percent composition and molar mass. - Melting point = 5.5 oC, boiling point = 80.1 oC which is comparable to the boiling of cyclohexane (81.4 0C). - Non-polar molecule and is soluble only in nonpolar solvents. - Benzene has hybrid bonds. - Benz ...
Experiment #3: Asymmetric Synthesis – Use of a Chiral Manganese
... Traditionally, olefin epoxidations have been accomplished using a variety of peroxyacids. Since the early 1980's, however, a number of effective transition metal-based catalyst systems have been developed that have significantly extended the scope of these reactions by allowing enantioselective oxyg ...
... Traditionally, olefin epoxidations have been accomplished using a variety of peroxyacids. Since the early 1980's, however, a number of effective transition metal-based catalyst systems have been developed that have significantly extended the scope of these reactions by allowing enantioselective oxyg ...
A GRIGNARD REACTION: SYNTHESIS OF 2-METHYL-2
... 2. The Grignard reagent is mixed with a compound that has an electron-deficient carbonyl carbon. In this case, acetone is used. The electron-rich C attacks the electron-poor C forming a new C-C bond. Simultaneously, the carbonyl oxygen atom takes up one pair of electrons, creating the anion of an al ...
... 2. The Grignard reagent is mixed with a compound that has an electron-deficient carbonyl carbon. In this case, acetone is used. The electron-rich C attacks the electron-poor C forming a new C-C bond. Simultaneously, the carbonyl oxygen atom takes up one pair of electrons, creating the anion of an al ...
File - cpprashanths Chemistry
... ANS: In aqueous solution, KOH is almost completely ionized to give OH- ions which being a strong nucleophile brings about a substitution reaction on alkyl halides to form alcohols. In the aqueous solution, OH- ions are highly solvated (hydrated). This reduces the basic character of OH- ions which f ...
... ANS: In aqueous solution, KOH is almost completely ionized to give OH- ions which being a strong nucleophile brings about a substitution reaction on alkyl halides to form alcohols. In the aqueous solution, OH- ions are highly solvated (hydrated). This reduces the basic character of OH- ions which f ...
2.6 M - Thierry Karsenti
... 5. An alkyne is a compound that has at least one triple bond. A straight-chain alkyne with one triple bond has the formula CnH2n-2. Triple bonds are even more reactive than double bonds. The functional group for an alkyne is the triple bond. 6. Alcohols : These are organic compounds that contain the ...
... 5. An alkyne is a compound that has at least one triple bond. A straight-chain alkyne with one triple bond has the formula CnH2n-2. Triple bonds are even more reactive than double bonds. The functional group for an alkyne is the triple bond. 6. Alcohols : These are organic compounds that contain the ...
Presentation
... (CH3)3C−OH reacts with C6H5MgBr to form benzene, because the alcohol has acidic H atom in its –OH group. Ans: A) benzene ...
... (CH3)3C−OH reacts with C6H5MgBr to form benzene, because the alcohol has acidic H atom in its –OH group. Ans: A) benzene ...
05 Halogen deriv. of hydrocarbons. Alcohols,ethers, esters
... propyl alcohol, because it is cheaper. Isopropyl alcohol is slightly more active than ethyl alcohol against vegetative bacterial growth, but alcohola are largely ineffective against spores. Alcohol ( C2H5OH, ethanol, spiritus vini rectificatus, wine spirit) is a clear, colorless, volatile liquid hav ...
... propyl alcohol, because it is cheaper. Isopropyl alcohol is slightly more active than ethyl alcohol against vegetative bacterial growth, but alcohola are largely ineffective against spores. Alcohol ( C2H5OH, ethanol, spiritus vini rectificatus, wine spirit) is a clear, colorless, volatile liquid hav ...
Nugget
... reactive pro-catalytic and catalytic ruthenium-based systems with carborane counterion. The optimization of the synthetic conditions for the ruthenium carborane complexes leads us in search of the new protonating agents. In addition to the ether and toluene based protonation agents ([H Ln]+ [carbora ...
... reactive pro-catalytic and catalytic ruthenium-based systems with carborane counterion. The optimization of the synthetic conditions for the ruthenium carborane complexes leads us in search of the new protonating agents. In addition to the ether and toluene based protonation agents ([H Ln]+ [carbora ...
(a) Draw a primary, a secondary, and a tertiary alcohol for the
... Describe the different types of reactions occurring, and give reasons why they are classified as that type. Identify any specific conditions that are needed for the reactions to occur. When propan-1-ol reacts with HCl, a substitution reaction occurs; in this reaction the Cl from HCl replaces the –OH ...
... Describe the different types of reactions occurring, and give reasons why they are classified as that type. Identify any specific conditions that are needed for the reactions to occur. When propan-1-ol reacts with HCl, a substitution reaction occurs; in this reaction the Cl from HCl replaces the –OH ...
No Slide Title
... Naturally Occurring Oxygen-Containing Compounds • Lipids – Fats and Waxes (also called saponifiable lipids) ...
... Naturally Occurring Oxygen-Containing Compounds • Lipids – Fats and Waxes (also called saponifiable lipids) ...
Reaction in
... Conversion of Alcohols to Alkyl Halides and Sulfonate Esters Substitution reactions of activated alcohols (ROH with better LG’s) Dehydration of alcohols via Elimination Reactions Oxidation of Alcohols Nucleophilic Substitution Reactions of Ethers ...
... Conversion of Alcohols to Alkyl Halides and Sulfonate Esters Substitution reactions of activated alcohols (ROH with better LG’s) Dehydration of alcohols via Elimination Reactions Oxidation of Alcohols Nucleophilic Substitution Reactions of Ethers ...
Common aldehydes and ketones
... Nonetheless, the enol form is important for some reactions. Furthermore, the deprotonated intermediate in the interconversion of the two forms, referred to as an enolate anion, is important in carbonyl chemistry, in large part because it is a strong nucleophile. ...
... Nonetheless, the enol form is important for some reactions. Furthermore, the deprotonated intermediate in the interconversion of the two forms, referred to as an enolate anion, is important in carbonyl chemistry, in large part because it is a strong nucleophile. ...
Chapter 7. Alcohols, Thiols, Phenols, Ethers
... There are many examples of the use of Grignard reactions. The example above could be expanded into many variations just by changing the halide and the carbonyl compound. Variations with other types of organometallic compound are also available. The reaction is given in more detail in chapter 8 on al ...
... There are many examples of the use of Grignard reactions. The example above could be expanded into many variations just by changing the halide and the carbonyl compound. Variations with other types of organometallic compound are also available. The reaction is given in more detail in chapter 8 on al ...
10_OrganicChemistryRC
... oxygen atoms which can experience hydrogen bonding with water; therefore, alcohols, phenols, and ethers are more soluble in water than hydrocarbons. Not all alcohols, phenols, or ethers are soluble in water, though. Solubility depends on the number of carbon atoms in these compounds. The more carbon ...
... oxygen atoms which can experience hydrogen bonding with water; therefore, alcohols, phenols, and ethers are more soluble in water than hydrocarbons. Not all alcohols, phenols, or ethers are soluble in water, though. Solubility depends on the number of carbon atoms in these compounds. The more carbon ...
Alcohol

In chemistry, an alcohol is any organic compound in which the hydroxyl functional group (–OH) is bound to a saturated carbon atom. The term alcohol originally referred to the primary alcohol ethyl alcohol (ethanol), the predominant alcohol in alcoholic beverages.The suffix -ol appears in the IUPAC chemical name of all substances where the hydroxyl group is the functional group with the highest priority; in substances where a higher priority group is present the prefix hydroxy- will appear in the IUPAC name. The suffix -ol in non-systematic names (such as paracetamol or cholesterol) also typically indicates that the substance includes a hydroxyl functional group and, so, can be termed an alcohol. But many substances, particularly sugars (examples glucose and sucrose) contain hydroxyl functional groups without using the suffix. An important class of alcohols, of which methanol and ethanol are the simplest members is the saturated straight chain alcohols, the general formula for which is CnH2n+1OH.