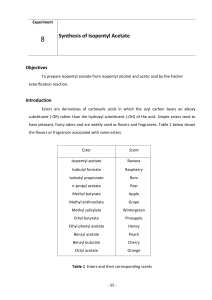
3 Properties Alcohols GOB Structures
... Hand sanitizers containing ethanol as their active ingredient • kill most bacteria and viruses that spread colds and flu. • are approximately 60% (v/v) but can be as high as 85% (v/v). • are highly flammable and produce a transparent, blue flame. • may also contain triclosan, which can accumulate in ...
... Hand sanitizers containing ethanol as their active ingredient • kill most bacteria and viruses that spread colds and flu. • are approximately 60% (v/v) but can be as high as 85% (v/v). • are highly flammable and produce a transparent, blue flame. • may also contain triclosan, which can accumulate in ...
Alcohols
... Give one advantage and one disadvantage of manufacturing ethanol by fermentation rather than by hydration. Do not include energy consumption or cost. Advantage .................................................................................................... ...
... Give one advantage and one disadvantage of manufacturing ethanol by fermentation rather than by hydration. Do not include energy consumption or cost. Advantage .................................................................................................... ...
What are carboxylic acids?
... size are higher than alcohols. The higher boiling points of the carboxylic acids are still caused by hydrogen bonding. In a pure carboxylic acid, hydrogen bonding can occur between two molecules of acid ...
... size are higher than alcohols. The higher boiling points of the carboxylic acids are still caused by hydrogen bonding. In a pure carboxylic acid, hydrogen bonding can occur between two molecules of acid ...
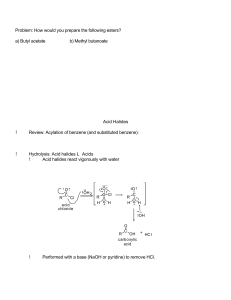
Carboxylic Acid Derivatives and Nitriles
... formation of allylic and benzylic alcohols. You should recall that allylic or benzylic bromides are easy to prepare. The resulting primary halides are generally resistant to substitution by simple hydroxide, so typically the esterification (with potassium acetate) and saponification steps are used t ...
... formation of allylic and benzylic alcohols. You should recall that allylic or benzylic bromides are easy to prepare. The resulting primary halides are generally resistant to substitution by simple hydroxide, so typically the esterification (with potassium acetate) and saponification steps are used t ...
Organic Compounds
... with the alcohol group, which is the –OH group. The names are derived by taking the prefix for the number of carbons it contains and adding the suffix – anol. Ex: 4 carbon alcohol = But-anol or butanol. ...
... with the alcohol group, which is the –OH group. The names are derived by taking the prefix for the number of carbons it contains and adding the suffix – anol. Ex: 4 carbon alcohol = But-anol or butanol. ...
Alcohols - La Salle University
... Naming Diols • Two numbers are needed to locate the two —OH groups. • Use -diol as suffix instead of -ol. ...
... Naming Diols • Two numbers are needed to locate the two —OH groups. • Use -diol as suffix instead of -ol. ...
2.10 Assessed Homework Task - A
... Give one advantage and one disadvantage of manufacturing ethanol by fermentation rather than by hydration. Do not include energy consumption or cost. Advantage .................................................................................................... ...
... Give one advantage and one disadvantage of manufacturing ethanol by fermentation rather than by hydration. Do not include energy consumption or cost. Advantage .................................................................................................... ...
Organic Functional Groups to know ASAP!
... *The following organic functional groups will be studied throughout the course of the year: naming, physical/chemical properties, reactions, mechanisms, & synthesis. *Your first assignment is to become familiar (memorize) the following information so that you can easily work with all material whethe ...
... *The following organic functional groups will be studied throughout the course of the year: naming, physical/chemical properties, reactions, mechanisms, & synthesis. *Your first assignment is to become familiar (memorize) the following information so that you can easily work with all material whethe ...
Document
... C. Phenols have stronger acidic properties than alcohols. D. Phenols undergo substitution reactions easier than the corresponding aromatic hydrocarbons. E. Phenols react with metallic Na, but do not react whit NaOH. 22. The following statements regarding carbonyl compounds are correct: A. The minima ...
... C. Phenols have stronger acidic properties than alcohols. D. Phenols undergo substitution reactions easier than the corresponding aromatic hydrocarbons. E. Phenols react with metallic Na, but do not react whit NaOH. 22. The following statements regarding carbonyl compounds are correct: A. The minima ...
8. Chemistry of cooking
... butanone (a) Name the two products formed by the dehydration of butan-2-ol (b) Name a reagent which could be used to oxidise butan-2-ol to butanone. ...
... butanone (a) Name the two products formed by the dehydration of butan-2-ol (b) Name a reagent which could be used to oxidise butan-2-ol to butanone. ...
alcohols ws 1 - Chesterhouse School
... Glycollic acid and lactic acid each give the reactions of an alcohol group and of a carboxylic acid group. Each compound will react with the other to give an ester. (e) When one molecule of glycollic acid reacts with one molecule of lactic acid, it is possible to form two different esters. Draw the ...
... Glycollic acid and lactic acid each give the reactions of an alcohol group and of a carboxylic acid group. Each compound will react with the other to give an ester. (e) When one molecule of glycollic acid reacts with one molecule of lactic acid, it is possible to form two different esters. Draw the ...
Experiment 4- Alkene
... (ii) Reactions of Alkenes Alkenes, containing a site of unsaturation, undergo electrophilic addition reactions with several reagents such as halogens, oxidizing agents, and sulfuric, halogen, and hypohalous acids. In particular, bromine and oxidizing agents such as permanganate are widely used in qu ...
... (ii) Reactions of Alkenes Alkenes, containing a site of unsaturation, undergo electrophilic addition reactions with several reagents such as halogens, oxidizing agents, and sulfuric, halogen, and hypohalous acids. In particular, bromine and oxidizing agents such as permanganate are widely used in qu ...
Document
... • Atoms other than hydrogen or carbon covalently bonded to a carbon atom in an organic molecule. • Most commonly oxygen, nitrogen, or the halogens. • The presence of a functional group drastically changes the chemical properties of a molecule. ...
... • Atoms other than hydrogen or carbon covalently bonded to a carbon atom in an organic molecule. • Most commonly oxygen, nitrogen, or the halogens. • The presence of a functional group drastically changes the chemical properties of a molecule. ...
Nucleophilic Substitution and b
... •Protonation of alcohol (setting up good leaving group) •For 2o and 3o ionization to yield a carbocation with alkene formation as side product. Attack of nucleophile (second alcohol molecule) on carbocation. • For 1o attack of nucleophile (second alcohol molecule) on the protonated ...
... •Protonation of alcohol (setting up good leaving group) •For 2o and 3o ionization to yield a carbocation with alkene formation as side product. Attack of nucleophile (second alcohol molecule) on carbocation. • For 1o attack of nucleophile (second alcohol molecule) on the protonated ...
Organic Nomenclature - Alkanes, Alkenes, Alkynes
... Organic chemistry centers around the element carbon. Hydrocarbons (compounds made of the elements hydrogen and carbon are the basic building foundation of organic chemistry. Carbon is unique among the elements because it can have up to four bonds per Carbon atom. Numerical Prefixes = Number of Backb ...
... Organic chemistry centers around the element carbon. Hydrocarbons (compounds made of the elements hydrogen and carbon are the basic building foundation of organic chemistry. Carbon is unique among the elements because it can have up to four bonds per Carbon atom. Numerical Prefixes = Number of Backb ...
Background Information
... a “false” positive result due to HCl reacting with the alkene through an electrophlic addition. Phenols and enols will not give a positive result. The alcohol starting material must be sufficiently soluble in aqueous environments (i.e., the Lucas reagent) for the reaction to take place. Therefore, o ...
... a “false” positive result due to HCl reacting with the alkene through an electrophlic addition. Phenols and enols will not give a positive result. The alcohol starting material must be sufficiently soluble in aqueous environments (i.e., the Lucas reagent) for the reaction to take place. Therefore, o ...
Module_16_-_Industrial_and_organic_chemistry
... Burning alcohols You will investigate the burning of 3 different alcohols: Methanol Propanol (propan-1-ol) Hexanol (hexan-1-ol) You will add 50 cm3 of water to the metal can and measure its ...
... Burning alcohols You will investigate the burning of 3 different alcohols: Methanol Propanol (propan-1-ol) Hexanol (hexan-1-ol) You will add 50 cm3 of water to the metal can and measure its ...
document
... Reactions of Alkenes • The C=C double bond is very reactive since it is a centre of electron density. One of the bonds is weaker than the other and this breaks open on reaction leaving the basic carbon chain intact. • Thus alkenes undergo addition reactions and are attacked by electrophiles i.e? • ...
... Reactions of Alkenes • The C=C double bond is very reactive since it is a centre of electron density. One of the bonds is weaker than the other and this breaks open on reaction leaving the basic carbon chain intact. • Thus alkenes undergo addition reactions and are attacked by electrophiles i.e? • ...
ESTERIFICATION Ester Formation Important Vocabulary (review) O
... Reactions between molecular species can be rather slow (especially when compared to the rates of reaction, between ionic species). This lab may help show us this. We know from our work on organic chemistry, that esters are organic molecules of the general form ...
... Reactions between molecular species can be rather slow (especially when compared to the rates of reaction, between ionic species). This lab may help show us this. We know from our work on organic chemistry, that esters are organic molecules of the general form ...
Alcohol

In chemistry, an alcohol is any organic compound in which the hydroxyl functional group (–OH) is bound to a saturated carbon atom. The term alcohol originally referred to the primary alcohol ethyl alcohol (ethanol), the predominant alcohol in alcoholic beverages.The suffix -ol appears in the IUPAC chemical name of all substances where the hydroxyl group is the functional group with the highest priority; in substances where a higher priority group is present the prefix hydroxy- will appear in the IUPAC name. The suffix -ol in non-systematic names (such as paracetamol or cholesterol) also typically indicates that the substance includes a hydroxyl functional group and, so, can be termed an alcohol. But many substances, particularly sugars (examples glucose and sucrose) contain hydroxyl functional groups without using the suffix. An important class of alcohols, of which methanol and ethanol are the simplest members is the saturated straight chain alcohols, the general formula for which is CnH2n+1OH.