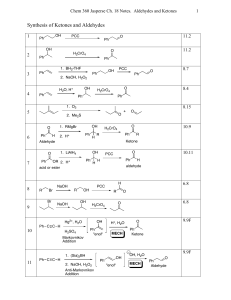
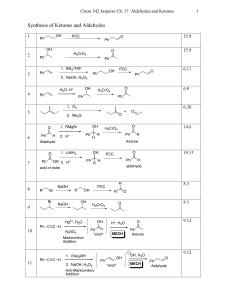
Chapter 2- Acids and Bases
... D) CH3CH2OH can be a Bronsted-Lowry acid, and CH3CH2NH2 can be a Bronsted-Lowry base. E) CH3CH2OH can be a Bronsted-Lowry acid, CH3CH2NH2 can be a Bronsted-Lowry base, and CH3CH2OH can be a Lewis base. Ans: E 31. Which of the following statements is true? A) CH3CH3 can be a Lewis base. B) BBr3 can b ...
... D) CH3CH2OH can be a Bronsted-Lowry acid, and CH3CH2NH2 can be a Bronsted-Lowry base. E) CH3CH2OH can be a Bronsted-Lowry acid, CH3CH2NH2 can be a Bronsted-Lowry base, and CH3CH2OH can be a Lewis base. Ans: E 31. Which of the following statements is true? A) CH3CH3 can be a Lewis base. B) BBr3 can b ...
IOSR Journal of Applied Chemistry (IOSR-JAC)
... Each of the moieties in the mixed ligand complexes undergoes particular vibrations and contributes certain peaks in their IR spectra. The electron delocalization in the chelated CED2- ring leads to the coupling of vibrational modes so that few bands in IR spectra represent pure vibrations. The IR sp ...
... Each of the moieties in the mixed ligand complexes undergoes particular vibrations and contributes certain peaks in their IR spectra. The electron delocalization in the chelated CED2- ring leads to the coupling of vibrational modes so that few bands in IR spectra represent pure vibrations. The IR sp ...
TRANSITION SERIES - New Age International
... The elements Y39 to Cd48 (10 elements) constitute the second transition series whereas La157, Hf72—Hg constitute third transition series. The filling of 4d and 5d orbitals continues as we move from left to right in the periods. The electronic configurations of 4d and 5d transition series are given i ...
... The elements Y39 to Cd48 (10 elements) constitute the second transition series whereas La157, Hf72—Hg constitute third transition series. The filling of 4d and 5d orbitals continues as we move from left to right in the periods. The electronic configurations of 4d and 5d transition series are given i ...
Chemistry of Ti(OiPr)Cl3 with Chloride
... Synthesis of Complexes. The reactions of 6 with chloride, THF, benzaldehyde, or methyl benzoate are outlined in Scheme 1. Two mol equiv of chloride, THF, or benzaldehyde added easily to 6 afforded monomeric six-coordinate complexes [Ti(OiPr)Cl5]2-(HAm+)2 (Am ) NEt3 (7a) or NC5H5 (7b)), Ti(OiPr)Cl3(T ...
... Synthesis of Complexes. The reactions of 6 with chloride, THF, benzaldehyde, or methyl benzoate are outlined in Scheme 1. Two mol equiv of chloride, THF, or benzaldehyde added easily to 6 afforded monomeric six-coordinate complexes [Ti(OiPr)Cl5]2-(HAm+)2 (Am ) NEt3 (7a) or NC5H5 (7b)), Ti(OiPr)Cl3(T ...
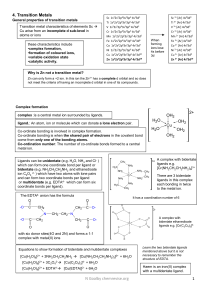
coordination compounds
... w Following rules have to be followed while writing the formula of the complex from IUPAC names. 1. Cation whether simple or complex is written first followed by the anion. 2. The order of formulating a complex ion is reverse to that adopted in naming i.e., the central metal atom is written first fo ...
... w Following rules have to be followed while writing the formula of the complex from IUPAC names. 1. Cation whether simple or complex is written first followed by the anion. 2. The order of formulating a complex ion is reverse to that adopted in naming i.e., the central metal atom is written first fo ...
Module 3 Transition elements - Pearson Schools and FE Colleges
... The transition elements have great importance in both biological and chemical systems. Iron is the key element in haemoglobin, the red pigment in blood which carries oxygen round the body, and plays a role as an important catalyst in the Haber process. Platinum, in cis-platin, is used therapeuticall ...
... The transition elements have great importance in both biological and chemical systems. Iron is the key element in haemoglobin, the red pigment in blood which carries oxygen round the body, and plays a role as an important catalyst in the Haber process. Platinum, in cis-platin, is used therapeuticall ...
Chapter 24 Chemistry of Coordination Compounds
... complex. If the name of the ligand itself has such a prefix, alternatives like bis-, tris-, etc., are used. ...
... complex. If the name of the ligand itself has such a prefix, alternatives like bis-, tris-, etc., are used. ...
Chemistry XII - Kendriya Vidyalaya IIM,Lucknow
... molarity is the number of moles of solute in 1kg of the solvent. 2.State Henry’s law and mention two importants application. Ans- Henry’s law : The pressure of gas over a solution is directly proportional to the mol fraction of the gas dissolve in the mol fraction of the gas dissolve in tje solution ...
... molarity is the number of moles of solute in 1kg of the solvent. 2.State Henry’s law and mention two importants application. Ans- Henry’s law : The pressure of gas over a solution is directly proportional to the mol fraction of the gas dissolve in the mol fraction of the gas dissolve in tje solution ...
PDF w - Erowid
... acids to the corresponding alcohols using sodium borohydride and iodine in THF. We now report that this was found to be an excellent process for the direct reduction of amino acids. The reactions were routinely carried out on a 10-g scale while the reduction of phenylalanine haa been successfdy perf ...
... acids to the corresponding alcohols using sodium borohydride and iodine in THF. We now report that this was found to be an excellent process for the direct reduction of amino acids. The reactions were routinely carried out on a 10-g scale while the reduction of phenylalanine haa been successfdy perf ...
Answers - University of Waterloo
... Ag+(aq) + e− U Ag(s) O2(g) + 2H2O(l) + 4e– U 4 OH–(aq) Cu2+(aq) + 2e− U Cu(s) 2H+(aq) + 2e− U H2(g) Sn2+(aq) + 2e− U Sn(s) Ni2+(aq) + 2e− U Ni(s) Fe2+(aq) + 2e− U Fe(s) Cr3+(aq) + 3e− U Cr(s) Zn2+(aq) + 2e− U Zn(s) 2H2O (l) + 2e− U H2(g) + 2OH−(aq) Al3+(aq) + 3e− U Al(s) ...
... Ag+(aq) + e− U Ag(s) O2(g) + 2H2O(l) + 4e– U 4 OH–(aq) Cu2+(aq) + 2e− U Cu(s) 2H+(aq) + 2e− U H2(g) Sn2+(aq) + 2e− U Sn(s) Ni2+(aq) + 2e− U Ni(s) Fe2+(aq) + 2e− U Fe(s) Cr3+(aq) + 3e− U Cr(s) Zn2+(aq) + 2e− U Zn(s) 2H2O (l) + 2e− U H2(g) + 2OH−(aq) Al3+(aq) + 3e− U Al(s) ...
Organic Chemistry/Fourth Edition: e-Text
... Chloral is trichloroethanal, CCl3CH . Chloral hydrate is the addition product of chloral and water. ...
... Chloral is trichloroethanal, CCl3CH . Chloral hydrate is the addition product of chloral and water. ...
Hydrolases as Catalysts for Green Chemistry and
... reports based on green metrics showed the method to have a greener profile. Another product, trimethylolpropane-oleate, a biolubricant, was produced by lipase-catalysed esterification with high yield, better product quality and a greener profile compared to the process catalysed by other heterogeneo ...
... reports based on green metrics showed the method to have a greener profile. Another product, trimethylolpropane-oleate, a biolubricant, was produced by lipase-catalysed esterification with high yield, better product quality and a greener profile compared to the process catalysed by other heterogeneo ...
Based Nanomaterials: A Platform to Produce Reactive Oxygen
... Upon reaction with 1O2 to form an endoperoxide, the ET process can be precluded by breaking the conjugating structure of the anthracene group, enabling the generation of fluorescence. The detection of 1O2 by DMAX, DPAX and SOSG thus works via a process of weak to strong fluorescence, whose success r ...
... Upon reaction with 1O2 to form an endoperoxide, the ET process can be precluded by breaking the conjugating structure of the anthracene group, enabling the generation of fluorescence. The detection of 1O2 by DMAX, DPAX and SOSG thus works via a process of weak to strong fluorescence, whose success r ...
module 5 - StudyWise
... For reactant A as the concentration doubles (B and C staying constant) so does the rate. Therefore the order with respect to reactant A is first order For reactant B compare between experiments 1 and 3 : As the concentration of B doubles (A and C staying constant) the rate quadruples. Therefore the ...
... For reactant A as the concentration doubles (B and C staying constant) so does the rate. Therefore the order with respect to reactant A is first order For reactant B compare between experiments 1 and 3 : As the concentration of B doubles (A and C staying constant) the rate quadruples. Therefore the ...
View/Open - AURA - Alfred University
... nitromethane will not interact with the materials being used in the Ritter reaction. We attempted to optimize a stoichiometric ratio of nitrile to alcohol with benzonitrile and diphenylmethanol in nitromethane. As seen in Scheme 12 and Table 3, the desired amide product (47) was furnished, along wit ...
... nitromethane will not interact with the materials being used in the Ritter reaction. We attempted to optimize a stoichiometric ratio of nitrile to alcohol with benzonitrile and diphenylmethanol in nitromethane. As seen in Scheme 12 and Table 3, the desired amide product (47) was furnished, along wit ...
Carefully detach the last page. It is the Data Sheet.
... Ag+(aq) + e− U Ag(s) O2(g) + 2H2O(l) + 4e– U 4 OH–(aq) Cu2+(aq) + 2e− U Cu(s) 2H+(aq) + 2e− U H2(g) Sn2+(aq) + 2e− U Sn(s) Ni2+(aq) + 2e− U Ni(s) Fe2+(aq) + 2e− U Fe(s) Cr3+(aq) + 3e− U Cr(s) Zn2+(aq) + 2e− U Zn(s) 2H2O (l) + 2e− U H2(g) + 2OH−(aq) Al3+(aq) + 3e− U Al(s) ...
... Ag+(aq) + e− U Ag(s) O2(g) + 2H2O(l) + 4e– U 4 OH–(aq) Cu2+(aq) + 2e− U Cu(s) 2H+(aq) + 2e− U H2(g) Sn2+(aq) + 2e− U Sn(s) Ni2+(aq) + 2e− U Ni(s) Fe2+(aq) + 2e− U Fe(s) Cr3+(aq) + 3e− U Cr(s) Zn2+(aq) + 2e− U Zn(s) 2H2O (l) + 2e− U H2(g) + 2OH−(aq) Al3+(aq) + 3e− U Al(s) ...
Unsymmetrically Bridged Methyl Groups as Intermediates in the
... Protonation of the methylene-bridged, tetracarbonyl species [IrRu(CO)4(µ-CH2)(dppm)2][X] (X ) CF3SO3, BF4) (1) at -90 °C yields the methyl-bridged product [IrRu(CO)4(µ-CH3)(dppm)2][X]2 (X ) CF3SO3, BF4) (3), in which the methyl group is carbon-bound to Ir while engaged in an agostic interaction with ...
... Protonation of the methylene-bridged, tetracarbonyl species [IrRu(CO)4(µ-CH2)(dppm)2][X] (X ) CF3SO3, BF4) (1) at -90 °C yields the methyl-bridged product [IrRu(CO)4(µ-CH3)(dppm)2][X]2 (X ) CF3SO3, BF4) (3), in which the methyl group is carbon-bound to Ir while engaged in an agostic interaction with ...
Hydroformylation

Hydroformylation, also known as oxo synthesis or oxo process, is an important homogeneously catalyzed industrial process for the production of aldehydes from alkenes. This chemical reaction entails the addition of a formyl group (CHO) and a hydrogen atom to a carbon-carbon double bond. This process has undergone continuous growth since its invention in 1938: Production capacity reached 6.6×106 tons in 1995. It is important because the resulting aldehydes are easily converted into many secondary products. For example, the resulting aldehydes are hydrogenated to alcohols that are converted to plasticizers or detergents. Hydroformylation is also used in specialty chemicals, relevant to the organic synthesis of fragrances and natural products. The development of hydroformylation, which originated within the German coal-based industry, is considered one of the premier achievements of 20th-century industrial chemistry.The process typically entails treatment of an alkene with high pressures (between 10 to 100 atmospheres) of carbon monoxide and hydrogen at temperatures between 40 and 200 °C. Transition metal catalysts are required.