The next bullet point down, tells us that the 1 H NMR spectra of
... draw compound 2 as shown. Compound 2 can be named as butan-2-ol as the longest carbon chain contains four carbon atoms and the hydroxyl group is on carbon-2. The fifth bullet point shows us the 1H NMR of compound 3. From the spectrum, we can identify four different peaks, three of which are labelle ...
... draw compound 2 as shown. Compound 2 can be named as butan-2-ol as the longest carbon chain contains four carbon atoms and the hydroxyl group is on carbon-2. The fifth bullet point shows us the 1H NMR of compound 3. From the spectrum, we can identify four different peaks, three of which are labelle ...
heptane
... 8. Are the following pairs enantiomers or diastereomers? Also label each molecule as a D sugar or L sugar. ...
... 8. Are the following pairs enantiomers or diastereomers? Also label each molecule as a D sugar or L sugar. ...
Discussion Sheet 11
... Skill 3: Reactions of alcohols are key C-C bond forming steps in multistep synthesis ...
... Skill 3: Reactions of alcohols are key C-C bond forming steps in multistep synthesis ...
name Page 1 of 6 Multiple Choice. Choose the best answer for the
... Which of the following statements concerning a carbocation is not true? (a) (b) (c) (d) (e) ...
... Which of the following statements concerning a carbocation is not true? (a) (b) (c) (d) (e) ...
Esterification Worksheet
... 4/ Fit a bung and shake vigorously with occasional cooling under the tap or in ice water. Release the HCl gas formed into the fume cupboard every few minutes. 5/ After 15 minutes the solid Benzoate separates out: the solution should be alkaline at the end of the reaction; if not alkaline, or if oily ...
... 4/ Fit a bung and shake vigorously with occasional cooling under the tap or in ice water. Release the HCl gas formed into the fume cupboard every few minutes. 5/ After 15 minutes the solid Benzoate separates out: the solution should be alkaline at the end of the reaction; if not alkaline, or if oily ...
Drawing Organic Structures Functional Groups Constitutional Isomers
... • F > Cl > Br > I 2. C-X bond length • C-I > C-Br > C-Cl > C-F 3. Polarizability of electrons (ease of distribution of electron density) • I > Br > Cl > F ...
... • F > Cl > Br > I 2. C-X bond length • C-I > C-Br > C-Cl > C-F 3. Polarizability of electrons (ease of distribution of electron density) • I > Br > Cl > F ...
File - Dr KHALID SHADID
... • When RCO- groups are named as substituent, they are called alkanoyI or acyl groups. ...
... • When RCO- groups are named as substituent, they are called alkanoyI or acyl groups. ...
File
... Note that the acid obtained has one more carbon atom than the alkyl or aryl halide from which the Grignard reagent is prepared, so the reaction provides a way to increase the length of a carbon chain. ...
... Note that the acid obtained has one more carbon atom than the alkyl or aryl halide from which the Grignard reagent is prepared, so the reaction provides a way to increase the length of a carbon chain. ...
Alcohols I Reading: Wade chapter 10, sections 10-1- 10
... For the chlorinated derivatives of enthanol (ClCH2CH2OH, Cl3CCH2OH), the inductive electron-withdrawing effect of the local halogens enhances the acidity of the parent alcohols; this effect is additive, with trichloroethanol being more acidic than chloroethanol and ethanol. Phenol (an aromatic ring ...
... For the chlorinated derivatives of enthanol (ClCH2CH2OH, Cl3CCH2OH), the inductive electron-withdrawing effect of the local halogens enhances the acidity of the parent alcohols; this effect is additive, with trichloroethanol being more acidic than chloroethanol and ethanol. Phenol (an aromatic ring ...
Chem12 SM Unit 1 Review final new ok revised
... molecule that affect the properties of the compound, such as solubility, melting point, boiling point, and chemical reactivity. Organic molecules are classified according to their functional groups. 99. Methene is not an appropriate name for a compound because the prefix methindicates a single carbo ...
... molecule that affect the properties of the compound, such as solubility, melting point, boiling point, and chemical reactivity. Organic molecules are classified according to their functional groups. 99. Methene is not an appropriate name for a compound because the prefix methindicates a single carbo ...
Blank Final Exam from 2004 - Department of Chemistry | Oregon
... Iron is being reduced and Sulfur is being oxidized Hydrogen is being reduced and Iron is being oxidized Sulfur is being reduced and iron is being oxidized Sulfur is the oxidizing agent and iron is the reducing agent Hydrogen is being oxidized and sulfur is being reduced ...
... Iron is being reduced and Sulfur is being oxidized Hydrogen is being reduced and Iron is being oxidized Sulfur is being reduced and iron is being oxidized Sulfur is the oxidizing agent and iron is the reducing agent Hydrogen is being oxidized and sulfur is being reduced ...
PTT102 Aldehydes and Ketones
... 1. Claisen Condensation Condensation of Two Ester Molecules. The product of a Claisen condensation is a βketo ester. In a Claisen condensation, one molecule of carbonyl compound is the nucleophile and second molecule is electrophile. The new C-C bond connect the α-carbon of one molecule and t ...
... 1. Claisen Condensation Condensation of Two Ester Molecules. The product of a Claisen condensation is a βketo ester. In a Claisen condensation, one molecule of carbonyl compound is the nucleophile and second molecule is electrophile. The new C-C bond connect the α-carbon of one molecule and t ...
PTT102 Aldehydes and Ketones
... 1. Claisen Condensation Condensation of Two Ester Molecules. The product of a Claisen condensation is a βketo ester. In a Claisen condensation, one molecule of carbonyl compound is the nucleophile and second molecule is electrophile. The new C-C bond connect the α-carbon of one molecule and t ...
... 1. Claisen Condensation Condensation of Two Ester Molecules. The product of a Claisen condensation is a βketo ester. In a Claisen condensation, one molecule of carbonyl compound is the nucleophile and second molecule is electrophile. The new C-C bond connect the α-carbon of one molecule and t ...
Full answers
... No. One end of each double bond has two identical groups (methyl or hydrogen) attached to it. Give the structural formula of the organic product formed from (–)-linalool in each of the following reactions. NB: If there is no reaction, write "no reaction". Reagents / Conditions ...
... No. One end of each double bond has two identical groups (methyl or hydrogen) attached to it. Give the structural formula of the organic product formed from (–)-linalool in each of the following reactions. NB: If there is no reaction, write "no reaction". Reagents / Conditions ...
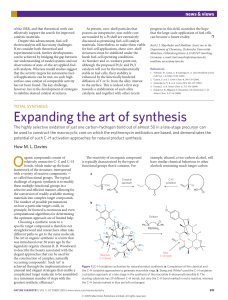
expanding the art of synthesis - Chemistry at Illinois
... group (Fig. 1a). Because the stereochemistry of the alcohol is set, the cyclization can produce only a single three-dimensional form of the cyclized product. In contrast, the new route developed by Stang and White relies on an oxidative cyclization strategy in which one of the numerous C–H bonds is ...
... group (Fig. 1a). Because the stereochemistry of the alcohol is set, the cyclization can produce only a single three-dimensional form of the cyclized product. In contrast, the new route developed by Stang and White relies on an oxidative cyclization strategy in which one of the numerous C–H bonds is ...
File
... 2) Alcohols which have 3 OH goups are called triols CH2OHCHOHCH2OH = 1,2, 3-propanetriol or glycerol or glycerin ...
... 2) Alcohols which have 3 OH goups are called triols CH2OHCHOHCH2OH = 1,2, 3-propanetriol or glycerol or glycerin ...
Topic 8 notes - A
... ammonia does. This would make a series of alternative products called secondary amines. To avoid this, it is necessary to use excess ammonia. b) Elimination of hydrogen halides to make alkenes If haloalkanes are boiled with an ethanolic solution of KOH instead of with an aqueous solution, they will ...
... ammonia does. This would make a series of alternative products called secondary amines. To avoid this, it is necessary to use excess ammonia. b) Elimination of hydrogen halides to make alkenes If haloalkanes are boiled with an ethanolic solution of KOH instead of with an aqueous solution, they will ...
File - Garbally Chemistry
... Halogenation reactions with alkanes involve replacement of one or all of the hydrogens in the alkane. These reactions may produce many products due to the high reactivity of the free radical species. The substitution reaction needs energy to be supplied before the reaction can proceed. Heating or sh ...
... Halogenation reactions with alkanes involve replacement of one or all of the hydrogens in the alkane. These reactions may produce many products due to the high reactivity of the free radical species. The substitution reaction needs energy to be supplied before the reaction can proceed. Heating or sh ...
Document
... Lithium Aluminium Hydride (LiAlH4, LAH) - much more reactive than NaBH4. Incompatible with protic solvents (alcohols, H2O). LiAlH4 (in ether) reduces aldehydes, carboxylic acids, and esters to 1° alcohols and ketones to 2° alcohols. ...
... Lithium Aluminium Hydride (LiAlH4, LAH) - much more reactive than NaBH4. Incompatible with protic solvents (alcohols, H2O). LiAlH4 (in ether) reduces aldehydes, carboxylic acids, and esters to 1° alcohols and ketones to 2° alcohols. ...
BP208P. PHARMACEUTICAL ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
... 2. Detection of elements like Nitrogen, Sulphur and Halogen by Lassaigne’s test 3. Solubility test 4. Functional group test like Phenols, Amides/ Urea, Carbohydrates, Amines, Carboxylic acids, Aldehydes and Ketones, Alcohols, Esters, Aromatic and Halogenated Hydrocarbons, Nitro compounds and Anilide ...
... 2. Detection of elements like Nitrogen, Sulphur and Halogen by Lassaigne’s test 3. Solubility test 4. Functional group test like Phenols, Amides/ Urea, Carbohydrates, Amines, Carboxylic acids, Aldehydes and Ketones, Alcohols, Esters, Aromatic and Halogenated Hydrocarbons, Nitro compounds and Anilide ...
Exam 2
... worth studying. Also problems assigned for the text may also be helpful. Chap 9 &10-- Sn2, Sn1, E2 and E1 reactions. -Know the definitions of Sn2, Sn1, E2 and E1. -Be able to depict the reaction coordinate diagrams of each reaction -Be able to draw the mechanism, products and the stereochemical resu ...
... worth studying. Also problems assigned for the text may also be helpful. Chap 9 &10-- Sn2, Sn1, E2 and E1 reactions. -Know the definitions of Sn2, Sn1, E2 and E1. -Be able to depict the reaction coordinate diagrams of each reaction -Be able to draw the mechanism, products and the stereochemical resu ...
Exp 19 - Diphenylacetylene_2015
... 1. Bromination of trans-Stilbene (Preparation of meso-Stilbene Dibromide) Add approximately 180 mg of trans-stilbene (MW = 180 g/mol) and 2.0 mL of dichloromethane (DCM) to a 5 mL conical vial containing a spin vane. Place the vial on the stir-plate in the aluminum block and stir until the stilbene ...
... 1. Bromination of trans-Stilbene (Preparation of meso-Stilbene Dibromide) Add approximately 180 mg of trans-stilbene (MW = 180 g/mol) and 2.0 mL of dichloromethane (DCM) to a 5 mL conical vial containing a spin vane. Place the vial on the stir-plate in the aluminum block and stir until the stilbene ...
Organic Structures
... In general, oxidations go up the levels and reductions go down. So, for example, oxidising a primary alcohol to a carboxylic acid is a change from a Level 1 functional group to a Level 3 functional group. Reducing a ketone to a secondary alcohol is a change from a level 2 functional group to a level ...
... In general, oxidations go up the levels and reductions go down. So, for example, oxidising a primary alcohol to a carboxylic acid is a change from a Level 1 functional group to a Level 3 functional group. Reducing a ketone to a secondary alcohol is a change from a level 2 functional group to a level ...
Haloalkane

The haloalkanes (also known, as halogenoalkanes or alkyl halides) are a group of chemical compounds derived from alkanes containing one or more halogens. They are a subset of the general class of halocarbons, although the distinction is not often made. Haloalkanes are widely used commercially and, consequently, are known under many chemical and commercial names. They are used as flame retardants, fire extinguishants, refrigerants, propellants, solvents, and pharmaceuticals. Subsequent to the widespread use in commerce, many halocarbons have also been shown to be serious pollutants and toxins. For example, the chlorofluorocarbons have been shown to lead to ozone depletion. Methyl bromide is a controversial fumigant. Only haloalkanes which contain chlorine, bromine, and iodine are a threat to the ozone layer, but fluorinated volatile haloalkanes in theory may have activity as greenhouse gases. Methyl iodide, a naturally occurring substance, however, does not have ozone-depleting properties and the United States Environmental Protection Agency has designated the compound a non-ozone layer depleter. For more information, see Halomethane. Haloalkane or alkyl halides are the compounds which have the general formula ″RX″ where R is an alkyl or substituted alkyl group and X is a halogen (F, Cl, Br, I).Haloalkanes have been known for centuries. Chloroethane was produced synthetically in the 15th century. The systematic synthesis of such compounds developed in the 19th century in step with the development of organic chemistry and the understanding of the structure of alkanes. Methods were developed for the selective formation of C-halogen bonds. Especially versatile methods included the addition of halogens to alkenes, hydrohalogenation of alkenes, and the conversion of alcohols to alkyl halides. These methods are so reliable and so easily implemented that haloalkanes became cheaply available for use in industrial chemistry because the halide could be further replaced by other functional groups.While most haloalkanes are human-produced, non-artificial-source haloalkanes do occur on Earth, mostly through enzyme-mediated synthesis by bacteria, fungi, and especially sea macroalgae (seaweeds). More than 1600 halogenated organics have been identified, with bromoalkanes being the most common haloalkanes. Brominated organics in biology range from biologically produced methyl bromide to non-alkane aromatics and unsaturates (indoles, terpenes, acetogenins, and phenols). Halogenated alkanes in land plants are more rare, but do occur, as for example the fluoroacetate produced as a toxin by at least 40 species of known plants. Specific dehalogenase enzymes in bacteria which remove halogens from haloalkanes, are also known.