
Science and a Christian World View A Christian View
... This is a picture of the world’s largest refracting telescope, found in the University of Chicago’s Yerkes Observatory in Williams Bay, ...
... This is a picture of the world’s largest refracting telescope, found in the University of Chicago’s Yerkes Observatory in Williams Bay, ...
VMC-200L - Vixen North America
... The VMC-200L is a unique design that employs a meniscus corrector lens along with two high-precision spherical mirrors to help eliminate spherical aberration and yield a sharp image with no hint of false color. This is a telescope suitable for observation of all types of celestial objects and offers ...
... The VMC-200L is a unique design that employs a meniscus corrector lens along with two high-precision spherical mirrors to help eliminate spherical aberration and yield a sharp image with no hint of false color. This is a telescope suitable for observation of all types of celestial objects and offers ...
Magnification and Field of View: An Introduction
... Introduction — Telescopes allow us to see things at different scales according to the magnification of a particular telescope–eyepiece combination. In this exercise you will experiment with different eyepieces attached to a telescope. You will see how these alter the size of their fields of view and ...
... Introduction — Telescopes allow us to see things at different scales according to the magnification of a particular telescope–eyepiece combination. In this exercise you will experiment with different eyepieces attached to a telescope. You will see how these alter the size of their fields of view and ...
Telescopes and Astronomical Observations
... Focal Plane Scale Scale is simply determined by the effective focal length “fl” of the telescope. = 206265”/fl(mm) arcsec/mm ...
... Focal Plane Scale Scale is simply determined by the effective focal length “fl” of the telescope. = 206265”/fl(mm) arcsec/mm ...
Introduction to Telescopes
... In this lab we will give you a general introduction to telescopes and what can be seen through them. At future labs, such as CCD imaging, you will have a chance to explore the universe in greater depth. Astronomers use a wide range of instruments to gather and focus electromagnetic radiation (light, ...
... In this lab we will give you a general introduction to telescopes and what can be seen through them. At future labs, such as CCD imaging, you will have a chance to explore the universe in greater depth. Astronomers use a wide range of instruments to gather and focus electromagnetic radiation (light, ...
Radio Telescopes
... surface (many times per second) to compensate for distortions by atmospheric turbulence. ...
... surface (many times per second) to compensate for distortions by atmospheric turbulence. ...
Because the Hubble telescope is located in space
... The Hubble Space Telescope is part of a group of telescopes that orbit Earth. The telescopes allow astronomers to gain information from the full range of electromagnetic radiation. The Compton Gamma-Ray Observatory was sent into orbit in 1991. The Chandra X-Ray Observatory was launched in 1999, and ...
... The Hubble Space Telescope is part of a group of telescopes that orbit Earth. The telescopes allow astronomers to gain information from the full range of electromagnetic radiation. The Compton Gamma-Ray Observatory was sent into orbit in 1991. The Chandra X-Ray Observatory was launched in 1999, and ...
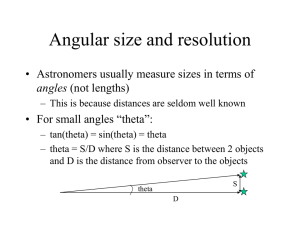
angles_telescopes
... Angular yardsticks • Easy yardstick: your fist – fist held at arms’ length subtends angle of about 5 degrees ...
... Angular yardsticks • Easy yardstick: your fist – fist held at arms’ length subtends angle of about 5 degrees ...
I. Reflective and Refractive Telescopes II. Telescope Optics III
... 9 Telescopes serves three main functions: (1) they are light collectors. The simplest telescopes simply focus light rays to a small area.; (2) Resolve light so that finer details can be seen; (3) Magnification: making objects look bigger (closer) 9 Two main types: refractive and reflective 9 As we ...
... 9 Telescopes serves three main functions: (1) they are light collectors. The simplest telescopes simply focus light rays to a small area.; (2) Resolve light so that finer details can be seen; (3) Magnification: making objects look bigger (closer) 9 Two main types: refractive and reflective 9 As we ...
Document
... Equatorial Mount. The arms of the fork mount point to the North Celestial Pole (North Star). An equatorial mount is a mount for instruments that follows the rotation of the sky (celestial sphere) by having one rotational axis parallel to the Earth's axis of rotation. ...
... Equatorial Mount. The arms of the fork mount point to the North Celestial Pole (North Star). An equatorial mount is a mount for instruments that follows the rotation of the sky (celestial sphere) by having one rotational axis parallel to the Earth's axis of rotation. ...
Tools for Studying Space
... Because the focus of a reflecting telescope is in front of the mirror, an observer must be able to view the image without blocking too much incoming light Most large optical telescopes are reflectors; light does not pass through a mirror so the glass for a reflecting telescope does not have to be of ...
... Because the focus of a reflecting telescope is in front of the mirror, an observer must be able to view the image without blocking too much incoming light Most large optical telescopes are reflectors; light does not pass through a mirror so the glass for a reflecting telescope does not have to be of ...
Section 1
... – Large mirrors allow more light to be gathered – Mirrors are polished, so flaws don’t affect the light – Mirrors can focus all colors of light at the same focal point ...
... – Large mirrors allow more light to be gathered – Mirrors are polished, so flaws don’t affect the light – Mirrors can focus all colors of light at the same focal point ...
Study guide for Tools of Astronomy
... Galaxy, Big Bang, Elliptical galaxy, Spiral galaxy, Irregular galaxy, Light Year, Red shift, Blue shift, Doppler Effect, Milky Way) Know your telescope types Optical – 2 types Refracting – uses convex lenses which cause the light rays to bend, can cause “chromatic aberrations” which cause the image ...
... Galaxy, Big Bang, Elliptical galaxy, Spiral galaxy, Irregular galaxy, Light Year, Red shift, Blue shift, Doppler Effect, Milky Way) Know your telescope types Optical – 2 types Refracting – uses convex lenses which cause the light rays to bend, can cause “chromatic aberrations” which cause the image ...
The Imaging Chain for Optical Astronomy
... • Smaller aperture means less chance of saturation (“overexposure”) on bright sources • Smaller aperture generally means larger field of view – recall F ratio, F=f/D, where f is focal length of collecting element and D is diameter of aperture – for two reflecting telescopes with same F ratio and the ...
... • Smaller aperture means less chance of saturation (“overexposure”) on bright sources • Smaller aperture generally means larger field of view – recall F ratio, F=f/D, where f is focal length of collecting element and D is diameter of aperture – for two reflecting telescopes with same F ratio and the ...
Slide 1
... FOR EXAMPLE, WITH AN 8 INCH (20 CM) TELESCOPE, THE OBJECTIVE AREA WOULD BE: A = PR2 = 314 cm2 FOR AN EYEPIECE 0.2 cm IN DIAMETER A2 = PR2 = 0.0314 cm2 THE RATIO WOULD BE ...
... FOR EXAMPLE, WITH AN 8 INCH (20 CM) TELESCOPE, THE OBJECTIVE AREA WOULD BE: A = PR2 = 314 cm2 FOR AN EYEPIECE 0.2 cm IN DIAMETER A2 = PR2 = 0.0314 cm2 THE RATIO WOULD BE ...
Refraction - Geneva 304
... Here are Java applets illustrating image formation by a converging lens, and by a diverging lens. Chromatic Aberration Different wavelengths focus at slightly different points. This causes objects like stars to be surrounded by fuzzy, rainbow colored halos. Can be corrected by using a second c ...
... Here are Java applets illustrating image formation by a converging lens, and by a diverging lens. Chromatic Aberration Different wavelengths focus at slightly different points. This causes objects like stars to be surrounded by fuzzy, rainbow colored halos. Can be corrected by using a second c ...
Document
... 3. The resolving power of a human eye is about 1 arcminute (1/60 of a degree). A 15-cm (6-inch) telescope has a maximum resolving power of 1 arcsecond (1/3600 of a degree). 4. Astronomical seeing is the blurring and twinkling of the image of an astronomical light source caused by the Earth’s atmosph ...
... 3. The resolving power of a human eye is about 1 arcminute (1/60 of a degree). A 15-cm (6-inch) telescope has a maximum resolving power of 1 arcsecond (1/3600 of a degree). 4. Astronomical seeing is the blurring and twinkling of the image of an astronomical light source caused by the Earth’s atmosph ...
( ) Microscope [Reading Hecht 5.7.3, 5.7.5] Simple microscope (magnifier)
... pupil) sets the diffraction limit. Also, a larger entrance pupil gathers more light, so that faint objects can be detected. Ground based telescopes are limited by atmospheric turbulence, which introduces unavoidable aberrations. One solution is to go into space, above the atmosphere. The configurati ...
... pupil) sets the diffraction limit. Also, a larger entrance pupil gathers more light, so that faint objects can be detected. Ground based telescopes are limited by atmospheric turbulence, which introduces unavoidable aberrations. One solution is to go into space, above the atmosphere. The configurati ...
( ) Microscope Simple microscope (magnifier)
... pupil) sets the diffraction limit. Also, a larger entrance pupil gathers more light, so that faint objects can be detected. Ground based telescopes are limited by atmospheric turbulence, which introduces unavoidable aberrations. One solution is to go into space, above the atmosphere. The configurati ...
... pupil) sets the diffraction limit. Also, a larger entrance pupil gathers more light, so that faint objects can be detected. Ground based telescopes are limited by atmospheric turbulence, which introduces unavoidable aberrations. One solution is to go into space, above the atmosphere. The configurati ...
Optical telescope
An optical telescope is a telescope that gathers and focuses light, mainly from the visible part of the electromagnetic spectrum, to create a magnified image for direct view, or to make a photograph, or to collect data through electronic image sensors.There are three primary types of optical telescope: refractors, which use lenses (dioptrics) reflectors, which use mirrors (catoptrics) catadioptric telescopes, which combine lenses and mirrorsA telescope's light gathering power and ability to resolve small detail is directly related to the diameter (or aperture) of its objective (the primary lens or mirror that collects and focuses the light). The larger the objective, the more light the telescope collects and the finer detail it resolves.People use telescopes and binoculars for activities such as observational astronomy, ornithology, pilotage and reconnaissance, and watching sports or performance arts.





















![( ) Microscope [Reading Hecht 5.7.3, 5.7.5] Simple microscope (magnifier)](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/008906619_1-713a6abc204beda0534960f18d7015c8-300x300.png)
