* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Refraction - Geneva 304
Hubble Space Telescope wikipedia , lookup
Lovell Telescope wikipedia , lookup
James Webb Space Telescope wikipedia , lookup
Allen Telescope Array wikipedia , lookup
Spitzer Space Telescope wikipedia , lookup
International Ultraviolet Explorer wikipedia , lookup
CfA 1.2 m Millimeter-Wave Telescope wikipedia , lookup
Optical telescope wikipedia , lookup
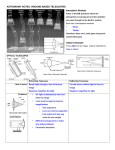
Telescopes Telescopes: Instruments that gather electromagnetic radiation to study astronomical phenomena. The human eye has some shortcomings that ultimately limit that exploration: 1. 2. 3. 4. Limited light-gathering power. Sees only electromagnetic radiation in the visible wavelengths Cannot be used to accumulate light over a long period The eye cannot store an image for future reference Astronomers have developed a variety of instruments and techniques to supplement the human eye. Binoculars Collect more light than the eye: Can see things not visible with the eye A good purchase before telescopes Specifications given in 7x35, 15x45, 10x50 o First number = magnification o Second number = Width in mm of the From 7x35 up to 10x50 power are the best for hand held observations (anything more powerful would shake the images around too much due to hand movements) Can get a good pair from $70 and up Telescopes Optical telescopes may be divided into two general categories: o Refracting telescopes - use lenses o Reflecting telescopes - use mirrors The main purpose of a telescope is to gather light, i.e. to collect and focus photons. We can think of a telescope then as a "light bucket" Refraction Refraction: The change in direction of light propagation at the boundary of two media having different densities. The direction of light propagation is changed at the boundary of glass and air by refraction. Lenses having the right curvature, this principle can be used to gather and focus light Principle of refraction and the refracting telescope Here are Java applets illustrating image formation by a converging lens, and by a diverging lens. Chromatic Aberration Different wavelengths focus at slightly different points. This causes objects like stars to be surrounded by fuzzy, rainbow colored halos. Can be corrected by using a second carefully designed lens mounted behind the main objective lens of the telescope to compensate. Types of Refracting Telescopes Achromatic - basic refractor; 70 to 100 mm objectives Apochromatic - use two or three corrective lenses; up to 180 mm objective; very high quality image Reflection Reflection: The angle of incidence (measured from the perpendicular to the reflecting surface) is equal to the angle of reflection. Principle of reflection and the reflecting telescope Here is a Java applet illustrating the use of a mirror (a diverging or convex mirror in this case) to form an image. The largest optical telescopes are reflecting rather than refracting telescopes: it is easier to build and support large mirrors of high optical quality than large lenses. Types of Reflecting Telescopes Various mirror arrangements are used to transport the light from the focus to an external observer. o Newtonian (more common, longer tube) o Schmidt-Cassegrain (a short tube that uses two reflecting mirrors) o Maksutov-Cassegrain (a variation of the Schmidt-Cassegrain, a bit smaller and more compact) o See figures 4.13 - 4.17 Other Observing Instruments Observing all wavelengths of electromagnetic radiation Includes: Space telescopes; Infrared & Radio telescopes, detectors, and arrays; Ultraviolet, X-, and Gamma Ray telescopes and detectors Famous Telescopes Atmospheric Conditions for Night Viewing Seeing - the steadiness of Earth's atmosphere Transparency - clarity of the Earth's atmosphere Light pollution - glow from lights in cities and towns that 'bleaches out' the darkness of the sky Buying a Telescope Using $100 to $250 department store telescopes is an exercise in frustration! Good quality telescopes and a minimum array of accessories begin around the $300 to $400 mark (save up for a good one, don’t waste your money!) Things to look for: o Stable mount (aluminum or wooden tripods, dobsonian) o Type of movement (pushing tube, slow motion knobs, motor drives) Accessories o Finder scopes (6x30 minimum) o Filters (solar, lunar, and color filters; solar and lunar recommended) o Eyepieces Magnification = focal length of telescope divided by the focal length of the eyepiece Example: 2000mm telescope divided by 25mm eyepiece length = 2000 mm / 25 mm = 80x magnification Usually about 1.25 inches wide; some larger telescopes have 2 inch wide eyepieces $40 to $120, depending on brand Barlow lens - extension attachment for eyepieces - magnifies eyepiece by 2x up to 5x Diagonal - an adapter for viewing at 900