red shift summary sheet
... bang which has scientific proof! This theory involves a great explosion where everything in the known universe was formed. All the energy and matter found today in the universe expanded from tiny point and formed the galaxies, stars, planets, asteroids, gases, dust and energy. Even today the univers ...
... bang which has scientific proof! This theory involves a great explosion where everything in the known universe was formed. All the energy and matter found today in the universe expanded from tiny point and formed the galaxies, stars, planets, asteroids, gases, dust and energy. Even today the univers ...
Centre of Mass
... is necessary not only to find planets of the size of the earth, but also to detect molecules which form the basis of life. ...
... is necessary not only to find planets of the size of the earth, but also to detect molecules which form the basis of life. ...
Homework 1 – Exercise 1 1/9
... In 1672, an international effort was made to measure the parallax angle of Mars at the time of opposition, when it was closest to Earth. Consider two observers who are separated by a baseline equal to Earth’s diameter. If the difference in their measurements of Mars’s angular position is 33.6’’. Wha ...
... In 1672, an international effort was made to measure the parallax angle of Mars at the time of opposition, when it was closest to Earth. Consider two observers who are separated by a baseline equal to Earth’s diameter. If the difference in their measurements of Mars’s angular position is 33.6’’. Wha ...
Spiral Elliptical Irregular - SMS 8th Grade Astronomy Unit
... The Earth’s Place in the Universe Earth is one of eight (+Pluto!) planets in the solar system We are __________________ million miles away from the sun This is called an Astronomical Unit (AU) (it would take a jet 17 years to travel this far!) Pluto is 39 AU from the sun…How many miles is that? ____ ...
... The Earth’s Place in the Universe Earth is one of eight (+Pluto!) planets in the solar system We are __________________ million miles away from the sun This is called an Astronomical Unit (AU) (it would take a jet 17 years to travel this far!) Pluto is 39 AU from the sun…How many miles is that? ____ ...
Sky Science Review for Test Part A
... Sky Science Review for Test Science 6 S.O. 1 – Recognize that the Sun and stars emit the light by which they are seen, and that most other bodies in space, including Earth’s moon, other planets and their moons, comets and asteroids, are seen by reflected light. Bodies in space that emit (give off) l ...
... Sky Science Review for Test Science 6 S.O. 1 – Recognize that the Sun and stars emit the light by which they are seen, and that most other bodies in space, including Earth’s moon, other planets and their moons, comets and asteroids, are seen by reflected light. Bodies in space that emit (give off) l ...
AST 220 Introduction to Astronomy
... leading to the birth of modern astronomy and its most recent development. Emphasis is placed on the coverage of astronomical instruments and measuring technologies, the solar system, the Milky Way galaxy, important extra galactic objects and cosmology. Laboratory is required. ...
... leading to the birth of modern astronomy and its most recent development. Emphasis is placed on the coverage of astronomical instruments and measuring technologies, the solar system, the Milky Way galaxy, important extra galactic objects and cosmology. Laboratory is required. ...
planet
... planet in the solar system, but because additional objects have been discovered including Eris which is 27% more massive, the IAU reclassified Pluto and the other objects as dwarf planets. The New Horizons spacecraft was launched on January 16, 2006 and will make its closest approach to Pluto on Jul ...
... planet in the solar system, but because additional objects have been discovered including Eris which is 27% more massive, the IAU reclassified Pluto and the other objects as dwarf planets. The New Horizons spacecraft was launched on January 16, 2006 and will make its closest approach to Pluto on Jul ...
slides - Caltech Astronomy
... The ray in the figure has s1 = ∞ intersecting the first surface at y1 and the second at y2 . From two sets of similar right triangles, both sets including either y2 or y1 as one side, y2 / y1 = s2 / s1' = ( s1' - d ) / s1' = s2' / f ' where f ' is the effective focal length of the whole system, and, ...
... The ray in the figure has s1 = ∞ intersecting the first surface at y1 and the second at y2 . From two sets of similar right triangles, both sets including either y2 or y1 as one side, y2 / y1 = s2 / s1' = ( s1' - d ) / s1' = s2' / f ' where f ' is the effective focal length of the whole system, and, ...
Chapter 10
... around the Sun once a year. (Heliocentric model) The Earth’s motion around the Sun is relatively recent ...
... around the Sun once a year. (Heliocentric model) The Earth’s motion around the Sun is relatively recent ...
Content Standards/Performance Indicators: Key Pre
... Understanding the solar system helps you understand Earth’s position in space. The Sun is the star that provides energy for life on Earth. That Earth is part of the Milky Way galaxy. ...
... Understanding the solar system helps you understand Earth’s position in space. The Sun is the star that provides energy for life on Earth. That Earth is part of the Milky Way galaxy. ...
Chapter 6 Telescopes: Portals of Discovery How does your eye form
... • Buy binoculars first (e.g. 7x35) - you get much more for the same money. • Ignore magnification (sales pitch!) • Notice: aperture size, optical quality, portability. • Consumer research: Astronomy, Sky & Tel, Mercury. Astronomy clubs. ...
... • Buy binoculars first (e.g. 7x35) - you get much more for the same money. • Ignore magnification (sales pitch!) • Notice: aperture size, optical quality, portability. • Consumer research: Astronomy, Sky & Tel, Mercury. Astronomy clubs. ...
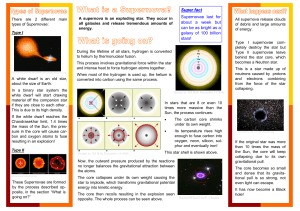
What is a supernova - University of Warwick
... If the white dwarf reaches the Chandrasekhar limit, 1.4 times the mass of the Sun, the pressure in the core will cause carbon and oxygen atoms to fuse resulting in an explosion! ...
... If the white dwarf reaches the Chandrasekhar limit, 1.4 times the mass of the Sun, the pressure in the core will cause carbon and oxygen atoms to fuse resulting in an explosion! ...
Exoplanet, 51 Pegasi b, Solar System, VLT, La Silla. ESOcast
... richest planetary system yet. The system, located over 120 light-years away around the Sun-like star HD 10180, contains at least five exoplanets. There is also tantalising evidence that two more planets may be present in this system, one of which would have the lowest mass ever found. ...
... richest planetary system yet. The system, located over 120 light-years away around the Sun-like star HD 10180, contains at least five exoplanets. There is also tantalising evidence that two more planets may be present in this system, one of which would have the lowest mass ever found. ...
previous mid-term () - Department of Physics and Astronomy
... Stefan-Boltzmann law, and Wien’s displacement law. For example, a red-hot cast iron skillet. c. Maximum emission found toward shorter wavelengths (blue end of spectrum) as temperature increases—i.e., the peak frequency is displaced towards shorter wavelengths. d. Radiation given off at only certain ...
... Stefan-Boltzmann law, and Wien’s displacement law. For example, a red-hot cast iron skillet. c. Maximum emission found toward shorter wavelengths (blue end of spectrum) as temperature increases—i.e., the peak frequency is displaced towards shorter wavelengths. d. Radiation given off at only certain ...
Chapter04
... whenever the two planets pass each other. If there is an arrowhead on each end of the rod, you can show that each planet sees the other in retrograde motion when they pass. Another idea is to ask the students to imagine how we would see Mars move first if the Earth were stationary and Mars moved (st ...
... whenever the two planets pass each other. If there is an arrowhead on each end of the rod, you can show that each planet sees the other in retrograde motion when they pass. Another idea is to ask the students to imagine how we would see Mars move first if the Earth were stationary and Mars moved (st ...
Hertzsprung-Russell Diagram Astronomy Project Purpose: To
... 1.) Determine the stars temperature in Celsius and Kelvin 2.) With the provided formula, determine the star’s luminosity in watts compared to the sun. Example: Betelgeuse is 38000 LSUN, and emits 1.4 x 1031 watts 3.) With the provided formula, determine the star’s radius, and find some way of compar ...
... 1.) Determine the stars temperature in Celsius and Kelvin 2.) With the provided formula, determine the star’s luminosity in watts compared to the sun. Example: Betelgeuse is 38000 LSUN, and emits 1.4 x 1031 watts 3.) With the provided formula, determine the star’s radius, and find some way of compar ...
Week 3: Kepler`s Laws, Light and Matter
... • As we discussed last time, the apparent retrograde motion (a reversal in direction of motion) of the planets is caused by the fact the Earth and the other planets revolve around the Sun at different velocities. The Ptolemaic model of geocentric system, unsuccessfully tried to explain this motion b ...
... • As we discussed last time, the apparent retrograde motion (a reversal in direction of motion) of the planets is caused by the fact the Earth and the other planets revolve around the Sun at different velocities. The Ptolemaic model of geocentric system, unsuccessfully tried to explain this motion b ...
Test#3
... a) they rotate slowly, b) they are a few km in radius c) they have large magnetic fields, d) some of them are observed to be pulsars 28. Which of the following objects can rotate a thousand times per second without being torn apart? a) white dwarf, b) main sequence star, c) red giant, d) neutron sta ...
... a) they rotate slowly, b) they are a few km in radius c) they have large magnetic fields, d) some of them are observed to be pulsars 28. Which of the following objects can rotate a thousand times per second without being torn apart? a) white dwarf, b) main sequence star, c) red giant, d) neutron sta ...
downloadable pdf - University of Florida
... “The shimmering that you see coming off a hot blacktop road in the summer — the upper atmosphere kind of does that with star light,” Eikenberry said. “Speckle imaging kind of freezes that motion out, and you get much better images.” Composed of 17 astronomers and graduate students, the team also cam ...
... “The shimmering that you see coming off a hot blacktop road in the summer — the upper atmosphere kind of does that with star light,” Eikenberry said. “Speckle imaging kind of freezes that motion out, and you get much better images.” Composed of 17 astronomers and graduate students, the team also cam ...
Unit Review Name
... period of time. A. It seemed to match the data that were available. B. The limited technology of the period could not prove it invalid. C. For a long period of time, no one offered a better explanation. D. Scientists lost interest in space studies as other discoveries were made. 12. What is the main ...
... period of time. A. It seemed to match the data that were available. B. The limited technology of the period could not prove it invalid. C. For a long period of time, no one offered a better explanation. D. Scientists lost interest in space studies as other discoveries were made. 12. What is the main ...
International Ultraviolet Explorer

The International Ultraviolet Explorer (IUE) was an astronomical observatory satellite primarily designed to take ultraviolet spectra. The satellite was a collaborative project between NASA, the UK Science Research Council and the European Space Agency (ESA). The mission was first proposed in early 1964, by a group of scientists in the United Kingdom, and was launched on January 26, 1978 aboard a NASA Delta rocket. The mission lifetime was initially set for 3 years, but in the end it lasted almost 18 years, with the satellite being shut down in 1996. The switch-off occurred for financial reasons, while the telescope was still functioning at near original efficiency.It was the first space observatory to be operated in real time by astronomers who visited the groundstations in the United States and Europe. Astronomers made over 104,000 observations using the IUE, of objects ranging from solar system bodies to distant quasars. Among the significant scientific results from IUE data were the first large scale studies of stellar winds, accurate measurements of the way interstellar dust absorbs light, and measurements of the supernova SN1987A which showed that it defied stellar evolution theories as they then stood. When the mission ended, it was considered the most successful astronomical satellite ever.