Test - Hampton Science 8A 8B 8C 8D 8E Stars are classified on the
... Stars are classified on the Hertzsprung - Russell diagram according to their absolute magnitude and their surface temperatures at a given time in a star’s life cycle. What classification would a star have if it was very hot and very bright? ...
... Stars are classified on the Hertzsprung - Russell diagram according to their absolute magnitude and their surface temperatures at a given time in a star’s life cycle. What classification would a star have if it was very hot and very bright? ...
Winter constellations
... the Giant), with the triplets of stars of his belt and sword, and to the upper left the bright red star Betelgeuse. The name means ‘arm of the giant’ in Arabic and it is a red supergiant star about twenty times the mass of the sun. The bottom ‘star’ of Orion’s sword appears slightly fuzzy to the nak ...
... the Giant), with the triplets of stars of his belt and sword, and to the upper left the bright red star Betelgeuse. The name means ‘arm of the giant’ in Arabic and it is a red supergiant star about twenty times the mass of the sun. The bottom ‘star’ of Orion’s sword appears slightly fuzzy to the nak ...
Maksutov
... of dim objects, which are not visible by the human eye. First off, one synchronises the telescope to the park position 1 which is zenith. Near the end of the eyepiece side of the tubus there is a bubble level installed on the side. A second bubble level is installed on the pole which holds the count ...
... of dim objects, which are not visible by the human eye. First off, one synchronises the telescope to the park position 1 which is zenith. Near the end of the eyepiece side of the tubus there is a bubble level installed on the side. A second bubble level is installed on the pole which holds the count ...
handout
... A. First introduced by ___________________ (160 – 127 BC) i. Brightest stars : _________ magnitude ii. Faintest stars ( _____________ eye): _______ magnitude iii. 1st mag stars appear ____________ times brighter than 6th mag stars iv. larger magnitude => _________________ object! B. The magnitude sc ...
... A. First introduced by ___________________ (160 – 127 BC) i. Brightest stars : _________ magnitude ii. Faintest stars ( _____________ eye): _______ magnitude iii. 1st mag stars appear ____________ times brighter than 6th mag stars iv. larger magnitude => _________________ object! B. The magnitude sc ...
Seeing stars in a big way
... through the European Southern Observatory. Which will prove to be the best approach now that astronomers are initiating technical studies for still larger telescopes? Europe has set as its goal a 50–100-metre facility, whereas US astronomers are designing 20–30-metre telescopes. Are the more modest ...
... through the European Southern Observatory. Which will prove to be the best approach now that astronomers are initiating technical studies for still larger telescopes? Europe has set as its goal a 50–100-metre facility, whereas US astronomers are designing 20–30-metre telescopes. Are the more modest ...
File
... contains a diffraction grating that separates visible light into a spectrum of colours (each colour represents a different wavelength in the electromagnetic spectrum). ...
... contains a diffraction grating that separates visible light into a spectrum of colours (each colour represents a different wavelength in the electromagnetic spectrum). ...
Video: National Geographic: Journey to the Edge of the Universe
... 86. How much longer will it take for the message sent in the 1970’s to reach the great cluster? 87. How many civilizations may exist in the Milky Way galaxy? 88. Dark matter could make up more than _________ of all mater in the universe. 89. Why is it thought that dark matter exists? 90. The ...
... 86. How much longer will it take for the message sent in the 1970’s to reach the great cluster? 87. How many civilizations may exist in the Milky Way galaxy? 88. Dark matter could make up more than _________ of all mater in the universe. 89. Why is it thought that dark matter exists? 90. The ...
1” “Sky-Notes” of the Open University Astronomy Club. June 2005. A
... star famous for its striking red colour being fittingly called “Herschel’s Garnet Star”. It is the reddest naked eye star visible from the northern hemisphere. Its colour may show signs of variability. To become a regular variable star observer it is advisable to have your own detailed star charts o ...
... star famous for its striking red colour being fittingly called “Herschel’s Garnet Star”. It is the reddest naked eye star visible from the northern hemisphere. Its colour may show signs of variability. To become a regular variable star observer it is advisable to have your own detailed star charts o ...
HW2_Answers
... 3. Kepler found that the farther a planet was from the Sun, the slower it moved in its orbit. Use what you have learned about an orbit and the Newton’s law of Gravity to explain why Jupiter cannot orbit the Sun as fast as the Earth. Jupiter is farther from the Sun than the Earth. Because of this, th ...
... 3. Kepler found that the farther a planet was from the Sun, the slower it moved in its orbit. Use what you have learned about an orbit and the Newton’s law of Gravity to explain why Jupiter cannot orbit the Sun as fast as the Earth. Jupiter is farther from the Sun than the Earth. Because of this, th ...
!
... Cygnus X-1 is believed to be a black hole. Give two examples of how astronomers can (sometimes) determine whether an X-ray-emitting object is a neutron star or black hole. (2 points)! ...
... Cygnus X-1 is believed to be a black hole. Give two examples of how astronomers can (sometimes) determine whether an X-ray-emitting object is a neutron star or black hole. (2 points)! ...
25drake6s
... The Moon -Mars -- Has atmosphere but too small to have plate tectonics Jupiter -- Too large, has no surface Venus -Earth at 2 AU -- CO2 builds up to try and warm planet, clouds form, block sunlight ...
... The Moon -Mars -- Has atmosphere but too small to have plate tectonics Jupiter -- Too large, has no surface Venus -Earth at 2 AU -- CO2 builds up to try and warm planet, clouds form, block sunlight ...
Astronomy
... 23. What process creates the light emitted by stars? 24. Stars spend most of their lives in this stage: 25. A visual representation of the temperature and luminosity of stars is called: 26. Relatively dark spots on the sun that contains intense magnetic fields are known as: 27. These reactions join ...
... 23. What process creates the light emitted by stars? 24. Stars spend most of their lives in this stage: 25. A visual representation of the temperature and luminosity of stars is called: 26. Relatively dark spots on the sun that contains intense magnetic fields are known as: 27. These reactions join ...
4 x What Powers the Sun? • Need to provide
... Stellar Evolution Here: Evolution through nuclear burning. Minitial > 2M Minitial < 2M ...
... Stellar Evolution Here: Evolution through nuclear burning. Minitial > 2M Minitial < 2M ...
Milky Way Galaxy
... The observable Universe is greater than 12 x 109 light years in radius. (12 x 109 years)(365 days) (24 hr) (60 min) (60 sec) (3 x 108 m ) ( 1 km ) ( year ...
... The observable Universe is greater than 12 x 109 light years in radius. (12 x 109 years)(365 days) (24 hr) (60 min) (60 sec) (3 x 108 m ) ( 1 km ) ( year ...
PowerPoint - Chandra X
... RXJ0822-4300, deduced from 3 Chandra images over 5 years, implies a transverse space velocity of 1,600 km/s for an estimated distance of 7,000 light years. The unusually large space velocity is consistent with the explosion center inferred from proper motions of the oxygen-rich optical filaments, an ...
... RXJ0822-4300, deduced from 3 Chandra images over 5 years, implies a transverse space velocity of 1,600 km/s for an estimated distance of 7,000 light years. The unusually large space velocity is consistent with the explosion center inferred from proper motions of the oxygen-rich optical filaments, an ...
Solar system
... created, including carbon and iron. 2) Gases are pulled together by gravity into clouds called Nebulas. 3) The singularity: All matter is crammed into a tiny point the size of a proton. 4) Protostars are formed: a dense cloud of gas surrounded by a ...
... created, including carbon and iron. 2) Gases are pulled together by gravity into clouds called Nebulas. 3) The singularity: All matter is crammed into a tiny point the size of a proton. 4) Protostars are formed: a dense cloud of gas surrounded by a ...
The First Astronomy…
... What would a purblind member of an ancient civilization see upon looking into the night sky? What would he first notice about what appear to be an infinite amount of stars? Well, after a few hours of looking up at the sky, perhaps man would notice that big reddish star that was in the eastern part o ...
... What would a purblind member of an ancient civilization see upon looking into the night sky? What would he first notice about what appear to be an infinite amount of stars? Well, after a few hours of looking up at the sky, perhaps man would notice that big reddish star that was in the eastern part o ...
Stars in our Galaxy
... • Most stars on the H-R diagram fit into a diagonal band. This band is called the main sequence. It contains hot, blue, bright stars in the upper left and cool, red, dim stars in the lower right. • 90% of all stars are main sequence stars but there are a few that don’t fall into this “line” what ar ...
... • Most stars on the H-R diagram fit into a diagonal band. This band is called the main sequence. It contains hot, blue, bright stars in the upper left and cool, red, dim stars in the lower right. • 90% of all stars are main sequence stars but there are a few that don’t fall into this “line” what ar ...
The Big Four:
... HOW TO DETECT A BLACK HOLE • Effects on matter/light outside the horizon – gravitational attraction of other bodies – “dark star” with mass 3M Sun • distinguish from normal star, white dwarf, neutron star ...
... HOW TO DETECT A BLACK HOLE • Effects on matter/light outside the horizon – gravitational attraction of other bodies – “dark star” with mass 3M Sun • distinguish from normal star, white dwarf, neutron star ...
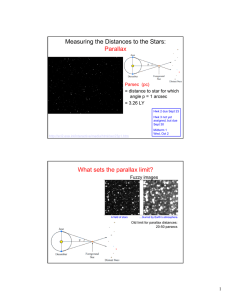
Measuring the Distances to the Stars: Parallax What sets the parallax limit?
... MW Rotation Curve • In principle, for stars, clusters, etc: ...
... MW Rotation Curve • In principle, for stars, clusters, etc: ...
Are Earth-like exoplanets common?
... number of lensing events at any given time of some baseline magnitude. ...
... number of lensing events at any given time of some baseline magnitude. ...
Handout from Allaire Star Party
... S*T*A*R is a registered non-profit educational amateur astronomy society. Meetings are the first Thursday of each month, except July and August, at 8:00 PM at the King of Kings Lutheran Church, 250 Harmony Rd. in Middletown (intersection of Harmony and Cherry Tree Farm Rd.). Membership is open to an ...
... S*T*A*R is a registered non-profit educational amateur astronomy society. Meetings are the first Thursday of each month, except July and August, at 8:00 PM at the King of Kings Lutheran Church, 250 Harmony Rd. in Middletown (intersection of Harmony and Cherry Tree Farm Rd.). Membership is open to an ...
May - Fort Worth Astronomical Society
... the alignment of the five visible planets. However, Yolanda Navarette did manage to "sneak a peak" between clouds of Venus and Saturn and the moon by Jupiter and do an observation report. Yolanda has been diligent all year in her observing projects. Hopefully, the skies will clear over the next two ...
... the alignment of the five visible planets. However, Yolanda Navarette did manage to "sneak a peak" between clouds of Venus and Saturn and the moon by Jupiter and do an observation report. Yolanda has been diligent all year in her observing projects. Hopefully, the skies will clear over the next two ...
International Ultraviolet Explorer

The International Ultraviolet Explorer (IUE) was an astronomical observatory satellite primarily designed to take ultraviolet spectra. The satellite was a collaborative project between NASA, the UK Science Research Council and the European Space Agency (ESA). The mission was first proposed in early 1964, by a group of scientists in the United Kingdom, and was launched on January 26, 1978 aboard a NASA Delta rocket. The mission lifetime was initially set for 3 years, but in the end it lasted almost 18 years, with the satellite being shut down in 1996. The switch-off occurred for financial reasons, while the telescope was still functioning at near original efficiency.It was the first space observatory to be operated in real time by astronomers who visited the groundstations in the United States and Europe. Astronomers made over 104,000 observations using the IUE, of objects ranging from solar system bodies to distant quasars. Among the significant scientific results from IUE data were the first large scale studies of stellar winds, accurate measurements of the way interstellar dust absorbs light, and measurements of the supernova SN1987A which showed that it defied stellar evolution theories as they then stood. When the mission ended, it was considered the most successful astronomical satellite ever.