Stars
... a star, galaxy, or other astronomical object per unit time. Higher levels are positive and increasing numbers • It is “related” to the brightness, which is the luminosity of an object in a given ...
... a star, galaxy, or other astronomical object per unit time. Higher levels are positive and increasing numbers • It is “related” to the brightness, which is the luminosity of an object in a given ...
TAP 403-1: Worked examples – Orbital Motion
... Use Kepler’s third law, T2 r3, to answer this question. Two Earth satellites, A and B, orbit at radii of 7.0 106 m and 2.8 107 m respectively. Which satellite has the longer period of orbit? What is the ratio of orbital radii for the two satellites? What, therefore, is the ratio of the cubes o ...
... Use Kepler’s third law, T2 r3, to answer this question. Two Earth satellites, A and B, orbit at radii of 7.0 106 m and 2.8 107 m respectively. Which satellite has the longer period of orbit? What is the ratio of orbital radii for the two satellites? What, therefore, is the ratio of the cubes o ...
General Introduction 1. Luminosity, Flux and Magnitude The
... The evolution of the Sun is shown schematically in Fig. 7.3. The red giant phase occurs after the interior of the Sun is exhausted of hydrogen and helium burning initiates. The Sun is not massive enough to burn elements beyond He, so after shedding roughly half its mass in a violent wind leading to ...
... The evolution of the Sun is shown schematically in Fig. 7.3. The red giant phase occurs after the interior of the Sun is exhausted of hydrogen and helium burning initiates. The Sun is not massive enough to burn elements beyond He, so after shedding roughly half its mass in a violent wind leading to ...
CElEstron C6 - Astronomy Magazine
... 6x30 finder scope is also included with each, except for the NexStar 6SE, which has a one-power red-dot finder instead. Celestron coats all C6 primary and secondary mirrors with enhanced coatings for better reflectivity and less scattered light. Peak reflectance is 95 percent at a wavelength of 510 ...
... 6x30 finder scope is also included with each, except for the NexStar 6SE, which has a one-power red-dot finder instead. Celestron coats all C6 primary and secondary mirrors with enhanced coatings for better reflectivity and less scattered light. Peak reflectance is 95 percent at a wavelength of 510 ...
aas_scott - Arecibo Observatory
... (NH2CH2COOH). Methanimine has been detected towards Sgr B2, and tentatively in the nearby galaxy, NGC 253, but has never been seen beyond the neighborhood of our Galaxy (i.e. beyond ~5 Mpc). We are conducting a cm-wave molecular line census in Arp 220, the nearest Ultraluminous Infrared Galaxy (ULIR ...
... (NH2CH2COOH). Methanimine has been detected towards Sgr B2, and tentatively in the nearby galaxy, NGC 253, but has never been seen beyond the neighborhood of our Galaxy (i.e. beyond ~5 Mpc). We are conducting a cm-wave molecular line census in Arp 220, the nearest Ultraluminous Infrared Galaxy (ULIR ...
Iceland spar crystals
... • Influence on the development of modern physics (quantum mechanics, relativity, spectroscopy, X-rays,...) • Manufacture of strain-free glass • Materials science; properties of matter at high temperatures • I am not covering these aspects here. • Instead, I will talk about the diverse direct applica ...
... • Influence on the development of modern physics (quantum mechanics, relativity, spectroscopy, X-rays,...) • Manufacture of strain-free glass • Materials science; properties of matter at high temperatures • I am not covering these aspects here. • Instead, I will talk about the diverse direct applica ...
Earth Science Library wk 2 (WP)
... the model was a convenient mathematical tool for determining planetary positions. ...
... the model was a convenient mathematical tool for determining planetary positions. ...
General - Friends of APOD
... Explanation: On June 4, 2010 Regulus, alpha star of the constellation Leo, and wandering planet Mars were at about the same apparent brightness, separated on the sky by 1.5 degrees. An ingenious and creative 10 second exposure from a swinging camera recorded these gyrating trails of the celestial pa ...
... Explanation: On June 4, 2010 Regulus, alpha star of the constellation Leo, and wandering planet Mars were at about the same apparent brightness, separated on the sky by 1.5 degrees. An ingenious and creative 10 second exposure from a swinging camera recorded these gyrating trails of the celestial pa ...
What is an atom?
... This chapter marks a change in the way you will look at nature. Up to this point, you have been thinking about what you can see with your eyes alone or aided by telescopes. In this chapter, you begin using modern astrophysics to search out secrets of the stars that lie beyond what you can see, and t ...
... This chapter marks a change in the way you will look at nature. Up to this point, you have been thinking about what you can see with your eyes alone or aided by telescopes. In this chapter, you begin using modern astrophysics to search out secrets of the stars that lie beyond what you can see, and t ...
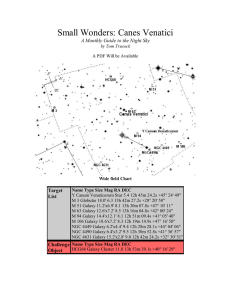
Small Wonders: Canes Venatici
... Canes Venatici is a somewhat small constellation, and may be difficult to find. Flanked on by both Ursa Major and Bootes, Canes is located in a somewhat barren section of the night sky. Canes (whose name means The Hunting Dogs) has been seen as Bootes pets for at least several hundred years, but the ...
... Canes Venatici is a somewhat small constellation, and may be difficult to find. Flanked on by both Ursa Major and Bootes, Canes is located in a somewhat barren section of the night sky. Canes (whose name means The Hunting Dogs) has been seen as Bootes pets for at least several hundred years, but the ...
Chapter 13 Exploring the final frontier
... What velocity would be required by the rock so that it would orbit the Earth and return to the thrower, who is still waiting on Mt Everest? The mass of the Earth is 5.97 × 1024 kg and its mean radius is 6380 km. ...
... What velocity would be required by the rock so that it would orbit the Earth and return to the thrower, who is still waiting on Mt Everest? The mass of the Earth is 5.97 × 1024 kg and its mean radius is 6380 km. ...
to access chapter 16
... temperature, and distance from Earth all play a part in how bright a star looks to us. The dazzling white star Sirius, for example, is the brightest star in the night sky, but it is only the ninth closest star to Earth. It is larger, hotter, and more than 20 times as bright as the Sun. It doesn’t lo ...
... temperature, and distance from Earth all play a part in how bright a star looks to us. The dazzling white star Sirius, for example, is the brightest star in the night sky, but it is only the ninth closest star to Earth. It is larger, hotter, and more than 20 times as bright as the Sun. It doesn’t lo ...
3.6 spectral classes
... carefully determined relative to other stars. Six months later, when Earth’s revolution has carried telescopes halfway around the Sun, the star’s position is measured again. Nearby stars appear to shift back and forth relative to more distant stars as Earth revolves around the Sun. The apparent chan ...
... carefully determined relative to other stars. Six months later, when Earth’s revolution has carried telescopes halfway around the Sun, the star’s position is measured again. Nearby stars appear to shift back and forth relative to more distant stars as Earth revolves around the Sun. The apparent chan ...
Implantable miniature Telescope
... (Table). It is approved for patients 75 years or older with stable, bilateral, end-stage AMD with either geographic atrophy or disciform scarring involving the fovea. Visual acuity criteria include a BCVA of 20/160 to 20/800 in the better-seeing eye. The telescope implant is implanted into one eye a ...
... (Table). It is approved for patients 75 years or older with stable, bilateral, end-stage AMD with either geographic atrophy or disciform scarring involving the fovea. Visual acuity criteria include a BCVA of 20/160 to 20/800 in the better-seeing eye. The telescope implant is implanted into one eye a ...
Practice Midterm 1
... 21. Kepler’s second law, which states that as a planet moves around its orbit it sweeps out equal areas in equal times, means that A) a planet travels faster when it is nearer to the Sun and slower when it is farther from the Sun. B) a planet’s period does not depend on the eccentricity of its orbit ...
... 21. Kepler’s second law, which states that as a planet moves around its orbit it sweeps out equal areas in equal times, means that A) a planet travels faster when it is nearer to the Sun and slower when it is farther from the Sun. B) a planet’s period does not depend on the eccentricity of its orbit ...
Panja_Luukka_3_6_08 - Indico
... temperature. Thus only 90% of the maximal cooling power was used. However, this is a well known problem and can be solved by the next beam test Panja Luukka, Helsinki Institute of Physics ...
... temperature. Thus only 90% of the maximal cooling power was used. However, this is a well known problem and can be solved by the next beam test Panja Luukka, Helsinki Institute of Physics ...
5th Grade – Topic Model - Bundle 4 Stars and the Solar System
... brighter than other stars because it is closer. 5-ESS1-1 Mathematical and Computational Thinking ● Organize simple data sets to reveal patterns that suggest relationships. Students could organize simple data sets to reveal patterns [such as] daily changes in the length and direction of shadows that ...
... brighter than other stars because it is closer. 5-ESS1-1 Mathematical and Computational Thinking ● Organize simple data sets to reveal patterns that suggest relationships. Students could organize simple data sets to reveal patterns [such as] daily changes in the length and direction of shadows that ...
Astronomy 103 Exam 2 Review
... B. DistorLon caused by light passing through the turbulent solar atmosphere C. MoLons of large amounts of gas moving out from the interior of the Sun and then back in D. The Sun’s magneLc field ...
... B. DistorLon caused by light passing through the turbulent solar atmosphere C. MoLons of large amounts of gas moving out from the interior of the Sun and then back in D. The Sun’s magneLc field ...
WebQuest-The-Life-Cycle-of-Stars-1
... 2. You will investigate the process of nuclear fusion explained by Einstein's famous equation E = MC2 and learn how mass in the form of hydrogen atoms is converted to helium and causes a release of energy that makes stars shine. 3. You will also begin to understand the forces involved in stars that ...
... 2. You will investigate the process of nuclear fusion explained by Einstein's famous equation E = MC2 and learn how mass in the form of hydrogen atoms is converted to helium and causes a release of energy that makes stars shine. 3. You will also begin to understand the forces involved in stars that ...
Stars - Weebly
... Life span of a star depends on its size. – Very large, massive stars burn their fuel much faster than smaller stars – Their main sequence may last only a few hundred thousand years – Smaller stars will live on for billions of years because they burn their fuel much more slowly ...
... Life span of a star depends on its size. – Very large, massive stars burn their fuel much faster than smaller stars – Their main sequence may last only a few hundred thousand years – Smaller stars will live on for billions of years because they burn their fuel much more slowly ...
Telescope Basics - UChicago Voices
... to object in the clock-wise direction. • Right ascension: is the angle between the vernal equinox (the intersection of the ecliptic and the celestial equator) and the intersection of the meridian through a celestial object and the celestial equator. RA is measured from 0h to 24h along the celestial ...
... to object in the clock-wise direction. • Right ascension: is the angle between the vernal equinox (the intersection of the ecliptic and the celestial equator) and the intersection of the meridian through a celestial object and the celestial equator. RA is measured from 0h to 24h along the celestial ...
Abundance of Elements
... I. Derive the stellar parameters of M dwarfs using the synthetic spectra in the long wavelength region of the optical spectra (over 8000 Å), which is relatively less contaminated by molecular lines as well as telluric lines. Test the synthetic spectrum for K2 III type star : HD 110014 ...
... I. Derive the stellar parameters of M dwarfs using the synthetic spectra in the long wavelength region of the optical spectra (over 8000 Å), which is relatively less contaminated by molecular lines as well as telluric lines. Test the synthetic spectrum for K2 III type star : HD 110014 ...
Part F
... Metal plates in a sealed box filled with a gas such as helium or neon. As gamma or particle travels through the detector, it ionises the gas between the plates. A trigger system consisting of two PMTs coupled to scintillators above and below box is used to apply high voltage to plates after the part ...
... Metal plates in a sealed box filled with a gas such as helium or neon. As gamma or particle travels through the detector, it ionises the gas between the plates. A trigger system consisting of two PMTs coupled to scintillators above and below box is used to apply high voltage to plates after the part ...
International Ultraviolet Explorer

The International Ultraviolet Explorer (IUE) was an astronomical observatory satellite primarily designed to take ultraviolet spectra. The satellite was a collaborative project between NASA, the UK Science Research Council and the European Space Agency (ESA). The mission was first proposed in early 1964, by a group of scientists in the United Kingdom, and was launched on January 26, 1978 aboard a NASA Delta rocket. The mission lifetime was initially set for 3 years, but in the end it lasted almost 18 years, with the satellite being shut down in 1996. The switch-off occurred for financial reasons, while the telescope was still functioning at near original efficiency.It was the first space observatory to be operated in real time by astronomers who visited the groundstations in the United States and Europe. Astronomers made over 104,000 observations using the IUE, of objects ranging from solar system bodies to distant quasars. Among the significant scientific results from IUE data were the first large scale studies of stellar winds, accurate measurements of the way interstellar dust absorbs light, and measurements of the supernova SN1987A which showed that it defied stellar evolution theories as they then stood. When the mission ended, it was considered the most successful astronomical satellite ever.