Unit 2: Syphilis
... Usually there is a latent period of several weeks between the disappearance of the chancre (primary syphilis) and the onset of signs symptoms and symptoms of secondary syphilis. • The symptoms and signs of secondary syphilis last 2 to 6 (not 8 to 12) weeks before the body's immune system kills most ...
... Usually there is a latent period of several weeks between the disappearance of the chancre (primary syphilis) and the onset of signs symptoms and symptoms of secondary syphilis. • The symptoms and signs of secondary syphilis last 2 to 6 (not 8 to 12) weeks before the body's immune system kills most ...
Overview of HIV CE
... fever, loss of appetite, and swollen lymph glands [glossary]. Opportunistic diseases such as yeast infection may develop. The infected person tests positive on an HIV test. The person can transmit HIV to others. AIDS AIDS is the final and most severe stage of HIV infection. AIDS is diagnosed when th ...
... fever, loss of appetite, and swollen lymph glands [glossary]. Opportunistic diseases such as yeast infection may develop. The infected person tests positive on an HIV test. The person can transmit HIV to others. AIDS AIDS is the final and most severe stage of HIV infection. AIDS is diagnosed when th ...
Infectious Diseases in Finland 2014
... several reminders of this, at home and abroad. Towards the end of March, the WHO issued the first alert concerning an Ebola epidemic in Guinea, West Africa (National Institute of Health and Welfare news 25 March 2014). Almost fifty cases were reported and the epidemic seemed to be spreading further. ...
... several reminders of this, at home and abroad. Towards the end of March, the WHO issued the first alert concerning an Ebola epidemic in Guinea, West Africa (National Institute of Health and Welfare news 25 March 2014). Almost fifty cases were reported and the epidemic seemed to be spreading further. ...
Infectious Diseases in Finland 2011
... culture findings also increased on 2010. Tuberculosis continues to present mainly in the elderly Finns, their infections contracted decades earlier becoming active. One out of four cases of tuberculosis were found among immigrants. The incidence of tuberculosis among children under the age of 5 has ...
... culture findings also increased on 2010. Tuberculosis continues to present mainly in the elderly Finns, their infections contracted decades earlier becoming active. One out of four cases of tuberculosis were found among immigrants. The incidence of tuberculosis among children under the age of 5 has ...
Perelandra Microbial Balancing Program Manual
... M “What tops [Dr.] Hughes’ list of public-health concerns are ‘antibiotic resistant organisms,’ often called ‘killer bacteria.’ Diseases once easily cured with antibiotics—such as pneumonia and meningitis, even children’s ear infections— can now outsmart common drugs. [Dr. Hughes has said:] ‘Today ...
... M “What tops [Dr.] Hughes’ list of public-health concerns are ‘antibiotic resistant organisms,’ often called ‘killer bacteria.’ Diseases once easily cured with antibiotics—such as pneumonia and meningitis, even children’s ear infections— can now outsmart common drugs. [Dr. Hughes has said:] ‘Today ...
What causes tonsillitis?
... breathes, coughs, or sneezes. You may then become infected after breathing in these droplets. Infection can also occur if pathogens get on your skin or on objects that come in contact with the mouth, nose, eyes, or other mucous membranes. Nasal obstruction causes you to breathe through your mouth, w ...
... breathes, coughs, or sneezes. You may then become infected after breathing in these droplets. Infection can also occur if pathogens get on your skin or on objects that come in contact with the mouth, nose, eyes, or other mucous membranes. Nasal obstruction causes you to breathe through your mouth, w ...
Wound infection in clinical practice. An
... ■ Chronic wounds with signs of spreading or systemic* infection† (Figure 4, see page 3) ■ Infected chronic wounds that have not responded to or are deteriorating despite appropriate antimicrobial treatment ■ As required by local surveillance protocols for drug resistant micro-organisms *In patients ...
... ■ Chronic wounds with signs of spreading or systemic* infection† (Figure 4, see page 3) ■ Infected chronic wounds that have not responded to or are deteriorating despite appropriate antimicrobial treatment ■ As required by local surveillance protocols for drug resistant micro-organisms *In patients ...
Infectious Diseases in Finland 2013
... tuberculosis were reported than in earlier years, but those who contracted the disease were younger than before. The fact that one third of cases were identified in foreign-born individuals is indicative of the gradual demographic change in epidemiology, as the number of cases of reactivation in the ...
... tuberculosis were reported than in earlier years, but those who contracted the disease were younger than before. The fact that one third of cases were identified in foreign-born individuals is indicative of the gradual demographic change in epidemiology, as the number of cases of reactivation in the ...
The global burden of hygiene-related diseases in relation to the
... changes which mean that people with reduced immunity to infection, either due to old age, chronic disease, medial treatments or other factors, now make up an increasing proportion of the global population – maybe as much as 20%. Technological advances and policy changes are being introduced to save ...
... changes which mean that people with reduced immunity to infection, either due to old age, chronic disease, medial treatments or other factors, now make up an increasing proportion of the global population – maybe as much as 20%. Technological advances and policy changes are being introduced to save ...
Schistosomiasis Neena Davisson March 15, 2012
... prevalent in 52 countries of Africa, the Caribbean, the Eastern Mediterranean and South America • S. haematobium – causes urinary schistosomiasis and affects 54 countries in Africa and Eastern Mediterranean • S. japonicum – causes intestinal schistosomiasis in the ...
... prevalent in 52 countries of Africa, the Caribbean, the Eastern Mediterranean and South America • S. haematobium – causes urinary schistosomiasis and affects 54 countries in Africa and Eastern Mediterranean • S. japonicum – causes intestinal schistosomiasis in the ...
Francisella tularensis: an Overview
... form of the disease, tracing transmission to traabout the possible deliberate spread of this ditional farming procedures in Scandinavia such pathogen, this concept is not new. From 1932– as piling hay, which is contaminated with F. 1945, for example, special research units in Ja- ...
... form of the disease, tracing transmission to traabout the possible deliberate spread of this ditional farming procedures in Scandinavia such pathogen, this concept is not new. From 1932– as piling hay, which is contaminated with F. 1945, for example, special research units in Ja- ...
Antibiotic Stewardship
... with the use of antibiotics in long term care residents. • Describe the concept of antibiotic stewardship and identify four core elements of an antibiotic stewardship program. ...
... with the use of antibiotics in long term care residents. • Describe the concept of antibiotic stewardship and identify four core elements of an antibiotic stewardship program. ...
What is syphilis - Cecil County Health Department
... pallidum. It has often been called “the great imitator” because so many of the signs and symptoms are indistinguishable from those of other diseases.
... pallidum. It has often been called “the great imitator” because so many of the signs and symptoms are indistinguishable from those of other diseases.
How common is syphilis?
In the United States, health officials reported over 32,000 cases of syphilis in 2002, including 6,862 cases ...
Infectious Diseases in Finland 2010
... by the fact that more than half of the strains found are resistant to quinolones, forcing the use of thirdgeneration cephalosporins. Tourism to Russia is a key source of cases of syphilis, and its incidence is highest in the hospital districts of southeastern and southern Finland. The number of new ...
... by the fact that more than half of the strains found are resistant to quinolones, forcing the use of thirdgeneration cephalosporins. Tourism to Russia is a key source of cases of syphilis, and its incidence is highest in the hospital districts of southeastern and southern Finland. The number of new ...
Bacillus anthracis and anthrax
... vegetative cells multiply, and a characteristic gelatinous edema develops at the site. This develops into papule within 12-36 hours after infection. The papule changes rapidly to a vesicle, then a pustule (malignant pustule), and finally into a necrotic ulcer from which infection may disseminate, gi ...
... vegetative cells multiply, and a characteristic gelatinous edema develops at the site. This develops into papule within 12-36 hours after infection. The papule changes rapidly to a vesicle, then a pustule (malignant pustule), and finally into a necrotic ulcer from which infection may disseminate, gi ...
Bacteria Battle Back - Addressing Antibiotic
... instead strengthened them, leading to drug-resistant bacteria against which antibiotics are ineffective. Antibiotic resistance was initially found only in hospitals where most antibiotics are still used, but resistance is now a serious problem in the community as well. Infectious diseases that were ...
... instead strengthened them, leading to drug-resistant bacteria against which antibiotics are ineffective. Antibiotic resistance was initially found only in hospitals where most antibiotics are still used, but resistance is now a serious problem in the community as well. Infectious diseases that were ...
Staph Infection Containment in Athletic Departments
... health care provider. Individuals who are immunocompromised or elderly may require medical evaluation even in the absence of these signs. The infection may require a medical procedure called incision and drainage (I&D). The infection may or may not require antibiotics. Infections that fail to clear, ...
... health care provider. Individuals who are immunocompromised or elderly may require medical evaluation even in the absence of these signs. The infection may require a medical procedure called incision and drainage (I&D). The infection may or may not require antibiotics. Infections that fail to clear, ...
Gonorrhea Fact Sheet
... The surest way to avoid transmission of STDs is to abstain from sexual intercourse, or to be in a long-term mutually monogamous relationship with a partner who has been tested and is known to be uninfected. Latex condoms, when used consistently and correctly, can reduce the risk of transmission of g ...
... The surest way to avoid transmission of STDs is to abstain from sexual intercourse, or to be in a long-term mutually monogamous relationship with a partner who has been tested and is known to be uninfected. Latex condoms, when used consistently and correctly, can reduce the risk of transmission of g ...
The impact of introduced diseases in the pre-Treaty period 1790-1840
... The issue of whether the diseases in question were zoonoses, diseases of animal origin, has not been considered in any depth. As Maori did not have any domesticated animals, aside from the dog, many of the infectious diseases, which were mostly zoonoses, might not have existed prior to contact. A mi ...
... The issue of whether the diseases in question were zoonoses, diseases of animal origin, has not been considered in any depth. As Maori did not have any domesticated animals, aside from the dog, many of the infectious diseases, which were mostly zoonoses, might not have existed prior to contact. A mi ...
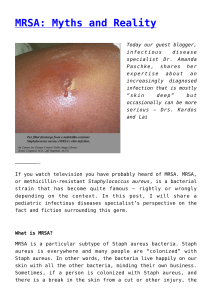
MRSA: Myths and Reality
... areas, so unless people are decontaminated (not advised!) MRSA can’t be eliminated. Should kids with MRSA be excluded from school? Absolutely not. For every one child with a diagnosed MRSA infection there are many more who are colonized with the bacteria, so it does not make sense to exclude a child ...
... areas, so unless people are decontaminated (not advised!) MRSA can’t be eliminated. Should kids with MRSA be excluded from school? Absolutely not. For every one child with a diagnosed MRSA infection there are many more who are colonized with the bacteria, so it does not make sense to exclude a child ...
Cost-Effectiveness of Routine Screening for Sexually Transmitted Diseases Among Inmates in United
... back into the community within 48 hours, so the opportunity to screen and treat those inmates is lost. Therefore, earlier screening, particularly routine screening on intake, may be a more effective strategy to decrease morbidity and the transmission of STDs. Questions remain about which of the many ...
... back into the community within 48 hours, so the opportunity to screen and treat those inmates is lost. Therefore, earlier screening, particularly routine screening on intake, may be a more effective strategy to decrease morbidity and the transmission of STDs. Questions remain about which of the many ...
PLEURAL DISEASE
... Mesothelial cells<5%: tuberculosis possible Lymphocytes >50% : tuberculosis, malignancy, lymphoma, fungus, myxedema ...
... Mesothelial cells<5%: tuberculosis possible Lymphocytes >50% : tuberculosis, malignancy, lymphoma, fungus, myxedema ...
Tuberculosis

Tuberculosis, MTB, or TB (short for tubercle bacillus), in the past also called phthisis, phthisis pulmonalis, or consumption, is a widespread, infectious disease caused by various strains of mycobacteria, usually Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Tuberculosis typically attacks the lungs, but can also affect other parts of the body. It is spread through the air when people who have an active TB infection cough, sneeze, or otherwise transmit respiratory fluids through the air. Most infections do not have symptoms, known as latent tuberculosis. About one in ten latent infections eventually progresses to active disease which, if left untreated, kills more than 50% of those so infected.The classic symptoms of active TB infection are a chronic cough with blood-tinged sputum, fever, night sweats, and weight loss (the last of these giving rise to the formerly common term for the disease, ""consumption""). Infection of other organs causes a wide range of symptoms. Diagnosis of active TB relies on radiology (commonly chest X-rays), as well as microscopic examination and microbiological culture of body fluids. Diagnosis of latent TB relies on the tuberculin skin test (TST) and/or blood tests. Treatment is difficult and requires administration of multiple antibiotics over a long period of time. Household, workplace and social contacts are also screened and treated if necessary. Antibiotic resistance is a growing problem in multiple drug-resistant tuberculosis (MDR-TB) infections. Prevention relies on early detection and treatment of cases and on screening programs and vaccination with the bacillus Calmette-Guérin vaccine.One-third of the world's population is thought to have been infected with M. tuberculosis, and new infections occur in about 1% of the population each year. In 2007, an estimated 13.7 million chronic cases were active globally, while in 2013, an estimated 9 million new cases occurred. In 2013 there were between 1.3 and 1.5 million associated deaths, most of which occurred in developing countries. The total number of tuberculosis cases has been decreasing since 2006, and new cases have decreased since 2002. The rate of tuberculosis in different areas varies across the globe; about 80% of the population in many Asian and African countries tests positive in tuberculin tests, while only 5–10% of the United States population tests positive. More people in the developing world contract tuberculosis because of a poor immune system, largely due to high rates of HIV infection and the corresponding development of AIDS.