Infectious Diseases in Industry
... • Reduces the risk of infection and symptoms • Reduces the risk of spreading the flu • Reduces the risk of dangerous complications of influenza • Influenza vaccination of healthy working adults saves $47 per person annually in health care costs and sick days ...
... • Reduces the risk of infection and symptoms • Reduces the risk of spreading the flu • Reduces the risk of dangerous complications of influenza • Influenza vaccination of healthy working adults saves $47 per person annually in health care costs and sick days ...
Disease Transmission
... 6) _____________________: Parasites that come into contact with its host only for certain intervals in order to feed ...
... 6) _____________________: Parasites that come into contact with its host only for certain intervals in order to feed ...
Prevention and control of tick-borne diseases in Europe
... • Antibodies to B. burgdorferi are usually detectable within 4-8 weeks of infection. • Patients with late-stage infection are rarely seronegative and ...
... • Antibodies to B. burgdorferi are usually detectable within 4-8 weeks of infection. • Patients with late-stage infection are rarely seronegative and ...
Vaccine-preventable diseases and immunisation
... Many vaccine-preventable diseases are highly contagious and are readily spread. Workers who are infected with vaccine-preventable diseases may in turn transmit infection to other people at the workplace, their families and the wider community. While vaccination is one of the most effective ways to p ...
... Many vaccine-preventable diseases are highly contagious and are readily spread. Workers who are infected with vaccine-preventable diseases may in turn transmit infection to other people at the workplace, their families and the wider community. While vaccination is one of the most effective ways to p ...
Questions to ask when choosing antibiotics?
... (e.g., serious enterococcal and pseudomonal infections) To prevent the emergence of resistance (e.g., TB, HIV) To achieve additive effects on resistant infections (e.g., PVE, H. pylori) To treat multiple phases (forms) of the same pathogen (e.g., TB, parasitic diseases) When a single antibiotic woul ...
... (e.g., serious enterococcal and pseudomonal infections) To prevent the emergence of resistance (e.g., TB, HIV) To achieve additive effects on resistant infections (e.g., PVE, H. pylori) To treat multiple phases (forms) of the same pathogen (e.g., TB, parasitic diseases) When a single antibiotic woul ...
BSc/Diploma in Medical Laboratory Technology 3 BLT302
... • Direct physical contact with the infected person (touching an infected person or through sexual contact) • Indirect physical contact which is usually by touching contaminated soil or a contaminated surface • Through air, but it can only happen when the microorganism can sustain in the air for a lo ...
... • Direct physical contact with the infected person (touching an infected person or through sexual contact) • Indirect physical contact which is usually by touching contaminated soil or a contaminated surface • Through air, but it can only happen when the microorganism can sustain in the air for a lo ...
Reproductive Diseases in Cattle
... Produced by Agricultural Communications, The Texas A&M University System Educational programs of the Texas Agricultural Extension Service are open to all people without regard to race, color, sex, disability, religion, age or national origin. Issued in furtherance of Cooperative Extension Work in Ag ...
... Produced by Agricultural Communications, The Texas A&M University System Educational programs of the Texas Agricultural Extension Service are open to all people without regard to race, color, sex, disability, religion, age or national origin. Issued in furtherance of Cooperative Extension Work in Ag ...
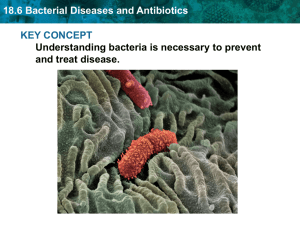
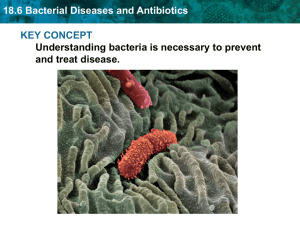
18.6 Bacterial Diseases and Antibiotics
... Antibiotics are used to fight bacterial disease. • Antibiotic: Chemicals that kill or slow the growth of bacteria. – Work by breaking down the cell wall of bacteria. ...
... Antibiotics are used to fight bacterial disease. • Antibiotic: Chemicals that kill or slow the growth of bacteria. – Work by breaking down the cell wall of bacteria. ...
+05020200.Communicable.Diseases
... Employees are encouraged to call in sick and remain at home if they have vomiting, diarrhea, a temperature, or frequent sneezing or coughing. c) The Executive Director reserve the right to request any employee return home and encourage that individual to seek appropriate medical treatment if it is d ...
... Employees are encouraged to call in sick and remain at home if they have vomiting, diarrhea, a temperature, or frequent sneezing or coughing. c) The Executive Director reserve the right to request any employee return home and encourage that individual to seek appropriate medical treatment if it is d ...
COMMUNICABLE DISEASES AND INFECTIOUS DISEASE CONTROL
... (AIDS) causes concern about the risk of diseases being transmitted in school. There is no evidence that Hepatitis B and AIDS are spread by casual person-to-person contact. However, organisms which cause these, and other diseases, may be present in body fluids such as blood, urine, feces, vomitus, sa ...
... (AIDS) causes concern about the risk of diseases being transmitted in school. There is no evidence that Hepatitis B and AIDS are spread by casual person-to-person contact. However, organisms which cause these, and other diseases, may be present in body fluids such as blood, urine, feces, vomitus, sa ...
5. Communicable disease surveillance and response
... risk arising from highly pathogenic avian influenza A(H5N1). Over the past year, outbreaks of avian influenza in animals and human infections of the virus continued to be reported in the Region. In the first six months of 2008, a total of eight human A(H5N1) cases have been reported in China and Vie ...
... risk arising from highly pathogenic avian influenza A(H5N1). Over the past year, outbreaks of avian influenza in animals and human infections of the virus continued to be reported in the Region. In the first six months of 2008, a total of eight human A(H5N1) cases have been reported in China and Vie ...
Comprehensive Genomic Study Provides Evidence that
... severe pain caused by infection, dengue now infects 50 million people annually, with 500,000 severe cases of dengue hemorrhagic fever and 22,000 deaths, according to the World Health Organization. There is currently no effective treatment for dengue fever and no preventive vaccine, although there ar ...
... severe pain caused by infection, dengue now infects 50 million people annually, with 500,000 severe cases of dengue hemorrhagic fever and 22,000 deaths, according to the World Health Organization. There is currently no effective treatment for dengue fever and no preventive vaccine, although there ar ...
A New Look At Lyme Disease
... disease symptoms. In the first stage, flulike symptoms and a skin rash develop along the site of the tick bite. The lesion spreads like a small bull’s-eye in most cases, but often recedes after a few weeks. During this stage, symptoms are muscle aches, headache and fatigue. The second stage is a s ...
... disease symptoms. In the first stage, flulike symptoms and a skin rash develop along the site of the tick bite. The lesion spreads like a small bull’s-eye in most cases, but often recedes after a few weeks. During this stage, symptoms are muscle aches, headache and fatigue. The second stage is a s ...
Reply To the Editor—The Gambian study, which is referred to in the
... it was assumed that the prevalence of such infections was similar in control subjects and case patients, in which case no adjustments would be necessary. In our study population, HIV-seronegative control subjects were recruited from local hospitals and clinics and were screened for TB, autoimmune di ...
... it was assumed that the prevalence of such infections was similar in control subjects and case patients, in which case no adjustments would be necessary. In our study population, HIV-seronegative control subjects were recruited from local hospitals and clinics and were screened for TB, autoimmune di ...
ccg.merit.unu.edu
... manufacturing process offers an improvement over an existing drug, biological product, or manufacturing process and the new drug, biological product, or manufacturing process competes with or replaces the existing drug, biological product, or manufacturing process, the Board shall continue to make p ...
... manufacturing process offers an improvement over an existing drug, biological product, or manufacturing process and the new drug, biological product, or manufacturing process competes with or replaces the existing drug, biological product, or manufacturing process, the Board shall continue to make p ...
Diseases and the Human Body Rubella Infectious
... 1) Infectious virus, transmitted to humans through the bite of infected mosquitoes 2) Caused by a virus 3) Symptoms - fever and chills, severe headache, back pain, general muscle aches, nausea, fatigue, and weakness. Affects the LIVER-causes Jaundice 4) Body systems – muscular system, nervous system ...
... 1) Infectious virus, transmitted to humans through the bite of infected mosquitoes 2) Caused by a virus 3) Symptoms - fever and chills, severe headache, back pain, general muscle aches, nausea, fatigue, and weakness. Affects the LIVER-causes Jaundice 4) Body systems – muscular system, nervous system ...
diseases and trees - College of Natural Resources, UC Berkeley
... • If pathogen is host-specific overall density may not be best parameter, but density of susceptible host/race • In some cases opposite may be true especially if alternate hosts are taken into account ...
... • If pathogen is host-specific overall density may not be best parameter, but density of susceptible host/race • In some cases opposite may be true especially if alternate hosts are taken into account ...
Lesson/Week 4
... rate is larger) during school terms. Such seasonal forcing leads to regular epidemics or more complex dynamics, as the disease oscillates between the high-contact and low-contact solutions. When modelling the spread of HIV it is vital to subdivide the population by sexual orientation and drug use. F ...
... rate is larger) during school terms. Such seasonal forcing leads to regular epidemics or more complex dynamics, as the disease oscillates between the high-contact and low-contact solutions. When modelling the spread of HIV it is vital to subdivide the population by sexual orientation and drug use. F ...
Must be present!
... – Penicillinase-resistant antibiotics (for secondary infection) – Daily eye rinsing – Adequate hydration and nutrition ...
... – Penicillinase-resistant antibiotics (for secondary infection) – Daily eye rinsing – Adequate hydration and nutrition ...
SPEECH BY DR. DEO MTASIWA, DEPUTY PERMANENT
... I feel privileged to be with you today when you are concluding a five-day Epihack intensive work which began on Monday 8th December 2014. This Epihack, which I am told, is the first in Africa and fourth in series is an important event that has brought together 70 health and information technology (I ...
... I feel privileged to be with you today when you are concluding a five-day Epihack intensive work which began on Monday 8th December 2014. This Epihack, which I am told, is the first in Africa and fourth in series is an important event that has brought together 70 health and information technology (I ...
Research Interests
... Christopher Mores, and I have been examining how larval competition in A. aegypti and A. albopictus affects mosquito susceptibility to infection by dengue fever virus (Flaviviridae), an important human pathogen. In addition, I have been investigating how the outcomes of larval competition affect adu ...
... Christopher Mores, and I have been examining how larval competition in A. aegypti and A. albopictus affects mosquito susceptibility to infection by dengue fever virus (Flaviviridae), an important human pathogen. In addition, I have been investigating how the outcomes of larval competition affect adu ...
Latent TB Infection (LTBI) - Colorado Health and Environmental Data
... Evaluate persons for risk factors Test those with a risk factor using the TST or Interferon-gamma release assay (IGRA) Evaluate those with a (+) TST or IGRA by doing a symptom history and chest X-ray Refer to PCP or local public health for treatment recommendations and medication administration ...
... Evaluate persons for risk factors Test those with a risk factor using the TST or Interferon-gamma release assay (IGRA) Evaluate those with a (+) TST or IGRA by doing a symptom history and chest X-ray Refer to PCP or local public health for treatment recommendations and medication administration ...
Neglected tropical diseases

Neglected tropical diseases are a medically diverse group of tropical infections which are especially common in low-income populations in developing regions of Africa, Asia, and the Americas. They are caused by a variety of pathogens such as viruses, bacteria, protozoa and helminths. Different organizations define the set of diseases differently. In sub-Saharan Africa, the impact of these diseases as a group is comparable to malaria and tuberculosis. Some of these diseases have known preventive measures or acute medical treatments which are available in the developed world but which are not universally available in poorer areas. In some cases, the treatments are relatively inexpensive. For example, the treatment for schistosomiasis is USD $0.20 per child per year. Nevertheless, control of neglected diseases is estimated to require funding of between US$2 billion to US$3 billion over the next five to seven years.These diseases are contrasted with the big three diseases (HIV/AIDS, tuberculosis, and malaria), which generally receive greater treatment and research funding. The neglected diseases can also make HIV/AIDS and tuberculosis more deadly. However, some pharmaceutical companies have committed to donating all the drug therapies required, and mass drug administration (for example mass deworming) has been successfully accomplished in several countries.Seventeen neglected tropical diseases are prioritized by WHO. These diseases are common in 149 countries, affecting more than 1.4 billion people (including more than 500 million children) and costing developing economies billions of dollars every year. They resulted in 142,000 deaths in 2013 –down from 204,000 deaths in 1990. Of these 17, two are targeted for eradication (dracunculiasis (guinea-worm disease) by 2015 and yaws by 2020) and four for elimination (blinding trachoma, human African trypanosomiasis, leprosy and lymphatic filariasis by 2020).