Key to Problems for Drug Design Courses (II)
... 5. (a)Whole cell assays are preferred when the nature of the steps in the mechanism of the disease state have not been well defined. They also offer a number of other advantages over biochemical tests. For example, whole cell tests may identify compounds that act at sites other than the target site. ...
... 5. (a)Whole cell assays are preferred when the nature of the steps in the mechanism of the disease state have not been well defined. They also offer a number of other advantages over biochemical tests. For example, whole cell tests may identify compounds that act at sites other than the target site. ...
The New York Times
... risk of relapse and which misspellings are likely to result in drug sensitivities. Q. Are there other diseases where the process might be useful? A. The same medicine we use to treat leukemia is also prescribed for Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis. So that same genetic test could be employed t ...
... risk of relapse and which misspellings are likely to result in drug sensitivities. Q. Are there other diseases where the process might be useful? A. The same medicine we use to treat leukemia is also prescribed for Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis. So that same genetic test could be employed t ...
Name NOTES – FORENSIC SCIENCE DRUGS CHAPTER 9 Drug
... 1. Secretes a sticky resin = hashish 2. Has been used legally and illegally for 3000 years 3. Grows wild – 5-15 feet tall ...
... 1. Secretes a sticky resin = hashish 2. Has been used legally and illegally for 3000 years 3. Grows wild – 5-15 feet tall ...
FREE Sample Here - College Test bank
... bottle of pills that she has been taking. She says that a doctor she no longer sees prescribed them for her. She does not know why she was taking the drug or the name of the drug. What should you do to determine the drug’s name, action, and therapeutic purpose? Answers to Chapter 1 Review 1. Chemica ...
... bottle of pills that she has been taking. She says that a doctor she no longer sees prescribed them for her. She does not know why she was taking the drug or the name of the drug. What should you do to determine the drug’s name, action, and therapeutic purpose? Answers to Chapter 1 Review 1. Chemica ...
Antibody-Drug Conjugates
... Member of the Roche Group (March 2009) Leading biotechnology company : treatment of patients with life-threatening medical conditions ...
... Member of the Roche Group (March 2009) Leading biotechnology company : treatment of patients with life-threatening medical conditions ...
administering-medications-7th-edition-donna-gauwitz
... bottle of pills that she has been taking. She says that a doctor she no longer sees prescribed them for her. She does not know why she was taking the drug or the name of the drug. What should you do to determine the drug’s name, action, and therapeutic purpose? Answers to Chapter 1 Review 1. Chemica ...
... bottle of pills that she has been taking. She says that a doctor she no longer sees prescribed them for her. She does not know why she was taking the drug or the name of the drug. What should you do to determine the drug’s name, action, and therapeutic purpose? Answers to Chapter 1 Review 1. Chemica ...
drug master file: [18f]fdg
... a. pH A small amount of each batch of the final drug product will be spotted on Merck pH paper. The pH will be in the physiological range (4.5-7.5) and will be consistent from batch to batch. b. Sterility The product is delivered in a sterile multi-dose vial. No addition of liquid or aliquotting to ...
... a. pH A small amount of each batch of the final drug product will be spotted on Merck pH paper. The pH will be in the physiological range (4.5-7.5) and will be consistent from batch to batch. b. Sterility The product is delivered in a sterile multi-dose vial. No addition of liquid or aliquotting to ...
Radiopharmaceutical Details: 18F-FDG 1. Name
... a. pH A small amount of each batch of the final drug product will be spotted on Merck pH paper. The pH will be in the physiological range (4.5-7.5) and will be consistent from batch to batch. b. Sterility The product is delivered in a sterile multi-dose vial. No addition of liquid or aliquotting to ...
... a. pH A small amount of each batch of the final drug product will be spotted on Merck pH paper. The pH will be in the physiological range (4.5-7.5) and will be consistent from batch to batch. b. Sterility The product is delivered in a sterile multi-dose vial. No addition of liquid or aliquotting to ...
drug master file: [18f]fdg
... another storage container is permitted. Individual doses are removed from this vial using aseptic techniques and only by trained pharmacy staff or nuclear medicine technicians. During preclinical studies the final drug product was produced utilizing established synthesis procedures [See appended Mas ...
... another storage container is permitted. Individual doses are removed from this vial using aseptic techniques and only by trained pharmacy staff or nuclear medicine technicians. During preclinical studies the final drug product was produced utilizing established synthesis procedures [See appended Mas ...
URINE DRUG TESTING QUICK REFERENCE
... These guidelines are general; interpretation of detection time must take account of variability of urine specimens, drug metabolism & half-life, patient’s physical condition, fluid intake, method, & frequency of use. ...
... These guidelines are general; interpretation of detection time must take account of variability of urine specimens, drug metabolism & half-life, patient’s physical condition, fluid intake, method, & frequency of use. ...
Element - the simplest form of matter that can exist under normal
... Class Notes 10/6/2009 Elements, Compounds, and Chemical Changes Element - the simplest form of matter that can exist under normal laboratory conditions Elements are pure substances. Elements cannot be separated into simpler substances by chemical means. Elements are the building blocks for all other ...
... Class Notes 10/6/2009 Elements, Compounds, and Chemical Changes Element - the simplest form of matter that can exist under normal laboratory conditions Elements are pure substances. Elements cannot be separated into simpler substances by chemical means. Elements are the building blocks for all other ...
Chempacific Brochuer
... Expansion of the API and fine chemical portfolio is currently ongoing and announcements will be made as new products become available. ...
... Expansion of the API and fine chemical portfolio is currently ongoing and announcements will be made as new products become available. ...
rotherham area prescribing committee
... It has a number of contraindications, cautions, and potential drug interactions. Visual symptoms were the most common adverse effect reported in clinical trials. Ivabradine is much more expensive than the standard treatment options for angina. If a beta-blocker is not appropriate for first-line ther ...
... It has a number of contraindications, cautions, and potential drug interactions. Visual symptoms were the most common adverse effect reported in clinical trials. Ivabradine is much more expensive than the standard treatment options for angina. If a beta-blocker is not appropriate for first-line ther ...
Lecture 2
... drug-receptor interaction • drugs can potentially alter rate of any bodily/brain function • drugs cannot impart entirely new functions to cells • drugs do not create effects, only modify ongoing ones • drugs can allow for effects outside of normal physiological ...
... drug-receptor interaction • drugs can potentially alter rate of any bodily/brain function • drugs cannot impart entirely new functions to cells • drugs do not create effects, only modify ongoing ones • drugs can allow for effects outside of normal physiological ...
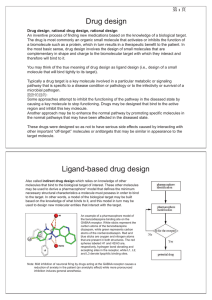
Drug design Ligand-based drug design
... model conformational changes in the biological target that may occur when the small molecule binds to it. This provides semi-quantitative prediction of the binding affinity. Also, knowledge-based scoring function may be used to provide binding affinity estimates. These methods use linear regression, ...
... model conformational changes in the biological target that may occur when the small molecule binds to it. This provides semi-quantitative prediction of the binding affinity. Also, knowledge-based scoring function may be used to provide binding affinity estimates. These methods use linear regression, ...
Drugs Reg - ReillyPsychology
... • Leaves, stems, resin, and flowers form the hemp plant that, when smoked, lower inhibitions and produce feelings of relaxation and mild euphoria • THC (delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol) is the active ingredient ...
... • Leaves, stems, resin, and flowers form the hemp plant that, when smoked, lower inhibitions and produce feelings of relaxation and mild euphoria • THC (delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol) is the active ingredient ...
Household Items That May Contain Mercury
... drugs, hazardous materials personnel may be met with having to make that decision based on a risk versus benefit analysis. It would be very easy to state that the process should never be turn off by qualified personnel waiting for a chemist from the Federal Department of Drug Enforcement (DEA) to ar ...
... drugs, hazardous materials personnel may be met with having to make that decision based on a risk versus benefit analysis. It would be very easy to state that the process should never be turn off by qualified personnel waiting for a chemist from the Federal Department of Drug Enforcement (DEA) to ar ...
FRAGMENT-BASED DRUG DESIGN: WHY IT'S SO IMPORTANT
... chemical space3-5, while high-throughput screening (HTS) has efficiently coupled specific targets to compound screening files. By industrialising the screening process, HTS gives rapid access to a multitude of new data on selected targets. THE IMPORTANCE OF LIBRARIES OF DRUG-LIKE COMPOUNDS However, ...
... chemical space3-5, while high-throughput screening (HTS) has efficiently coupled specific targets to compound screening files. By industrialising the screening process, HTS gives rapid access to a multitude of new data on selected targets. THE IMPORTANCE OF LIBRARIES OF DRUG-LIKE COMPOUNDS However, ...
Importance of Molecular Simulation for Studying Structural Properties
... chemistry, drug design, computational biology and materials science for studying molecular systems ranging from small chemical systems to large biological molecules and material assemblies. The simplest calculations can be performed by hand, but inevitably computers are required to perform molecular ...
... chemistry, drug design, computational biology and materials science for studying molecular systems ranging from small chemical systems to large biological molecules and material assemblies. The simplest calculations can be performed by hand, but inevitably computers are required to perform molecular ...
INTRODUCTION TO PHARMACOLOGY
... Binding to plasma proteins such as albumin- this will limit access to cellular compartments ...
... Binding to plasma proteins such as albumin- this will limit access to cellular compartments ...
PHAR 303 PHARMACEUTICAL CHEMISTRY I
... Rational drug design is a more focused approach that uses greater knowledge (structural information) about the drug receptor (targets) or one of its natural ligands as a basis to design, identify, or create drug “leads.” Testing is usually done with one or two models (e.g., specific receptor systems ...
... Rational drug design is a more focused approach that uses greater knowledge (structural information) about the drug receptor (targets) or one of its natural ligands as a basis to design, identify, or create drug “leads.” Testing is usually done with one or two models (e.g., specific receptor systems ...
Moisture Transfer between Formulation Components in a
... Disease induction in animal models (e.g. cancer) ...
... Disease induction in animal models (e.g. cancer) ...
Drug discovery
In the fields of medicine, biotechnology and pharmacology, drug discovery is the process by which new candidate medications are discovered. Historically, drugs were discovered through identifying the active ingredient from traditional remedies or by serendipitous discovery. Later chemical libraries of synthetic small molecules, natural products or extracts were screened in intact cells or whole organisms to identify substances that have a desirable therapeutic effect in a process known as classical pharmacology. Since sequencing of the human genome which allowed rapid cloning and synthesis of large quantities of purified proteins, it has become common practice to use high throughput screening of large compounds libraries against isolated biological targets which are hypothesized to be disease modifying in a process known as reverse pharmacology. Hits from these screens are then tested in cells and then in animals for efficacy.Modern drug discovery involves the identification of screening hits, medicinal chemistry and optimization of those hits to increase the affinity, selectivity (to reduce the potential of side effects), efficacy/potency, metabolic stability (to increase the half-life), and oral bioavailability. Once a compound that fulfills all of these requirements has been identified, it will begin the process of drug development prior to clinical trials. One or more of these steps may, but not necessarily, involve computer-aided drug design. Modern drug discovery is thus usually a capital-intensive process that involves large investments by pharmaceutical industry corporations as well as national governments (who provide grants and loan guarantees). Despite advances in technology and understanding of biological systems, drug discovery is still a lengthy, ""expensive, difficult, and inefficient process"" with low rate of new therapeutic discovery. In 2010, the research and development cost of each new molecular entity (NME) was approximately US$1.8 billion. Drug discovery is done by pharmaceutical companies, with research assistance from universities. The ""final product"" of drug discovery is a patent on the potential drug. The drug requires very expensive Phase I, II and III clinical trials, and most of them fail. Small companies have a critical role, often then selling the rights to larger companies that have the resources to run the clinical trials.Discovering drugs that may be a commercial success, or a public health success, involves a complex interaction between investors, industry, academia, patent laws, regulatory exclusivity, marketing and the need to balance secrecy with communication. Meanwhile, for disorders whose rarity means that no large commercial success or public health effect can be expected, the orphan drug funding process ensures that people who experience those disorders can have some hope of pharmacotherapeutic advances.






![drug master file: [18f]fdg](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/009298981_1-0014eb8c133d9a45f793a61c965c5722-300x300.png)


![drug master file: [18f]fdg](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/005674940_1-7a8834b1965c0c17ce552f91dd656783-300x300.png)