sympathomimetic toxidrome
... Sometimes confused with the anticholinergic syndrome, but the later is associated with dry skin and diminished bowel sounds. ...
... Sometimes confused with the anticholinergic syndrome, but the later is associated with dry skin and diminished bowel sounds. ...
GENERAL PHARMACOLOGY Distribution-1
... 1.Cardiac output and blood flow. 2. Physiochemical properties of the drug. ◦ Molecular weight ◦ Pka. ◦ Lipid solubility. 3. Capillary Permeability 4. Plasma protein binding 5. Tissue binding. ...
... 1.Cardiac output and blood flow. 2. Physiochemical properties of the drug. ◦ Molecular weight ◦ Pka. ◦ Lipid solubility. 3. Capillary Permeability 4. Plasma protein binding 5. Tissue binding. ...
general toxicology
... chemical interaction—the concentration of the drug at the site of action controls the effect. However, response to concentration may be complex and is often nonlinear. The relationship between the drug dose, regardless of route used, and the drug concentration at the cellular level is even more comp ...
... chemical interaction—the concentration of the drug at the site of action controls the effect. However, response to concentration may be complex and is often nonlinear. The relationship between the drug dose, regardless of route used, and the drug concentration at the cellular level is even more comp ...
Chemistry 910 Practical Medicinal Chemistry
... compound to progress in their pipeline to lead compound designation Each company must rationalise their selection process to a Medicinal Chemistry ...
... compound to progress in their pipeline to lead compound designation Each company must rationalise their selection process to a Medicinal Chemistry ...
Chapter 1
... • 1906 - Pure Food and Drug Act • 1938 - Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act and Amendments of 1951 and 1965 • 1970 Controlled Substances Act ...
... • 1906 - Pure Food and Drug Act • 1938 - Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act and Amendments of 1951 and 1965 • 1970 Controlled Substances Act ...
Topic 1 Chemical Reactions What is a chemical
... What is a chemical reaction? • A chemical reaction can be defined as the process in which changes occur in matter to produce new substances. • These chemical changes happen all around us. ...
... What is a chemical reaction? • A chemical reaction can be defined as the process in which changes occur in matter to produce new substances. • These chemical changes happen all around us. ...
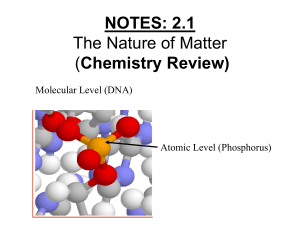
NOTES: 2.1 - Intro to Chemistry
... Isotopes: atoms of an element that have different # of neutrons ● in nature, elements occur as mixtures of isotopes ● some are radioactive: unstable isotope where nucleus decays emitting subatomic particles and/or energy as radioactivity causing one element to transform into another element ...
... Isotopes: atoms of an element that have different # of neutrons ● in nature, elements occur as mixtures of isotopes ● some are radioactive: unstable isotope where nucleus decays emitting subatomic particles and/or energy as radioactivity causing one element to transform into another element ...
Document
... genital sensitivity, insomnia, vomiting, diareaha, cramps, fever • Many symptoms occur because of hyperactive sympathetic nervous system ...
... genital sensitivity, insomnia, vomiting, diareaha, cramps, fever • Many symptoms occur because of hyperactive sympathetic nervous system ...
Drug metabolism2
... and liver blood flow are decreased .Metabolic inactivation of drugs is slowed Drugs persist for longer time and in higher concentration the must be lowered e.g. tricyclic ...
... and liver blood flow are decreased .Metabolic inactivation of drugs is slowed Drugs persist for longer time and in higher concentration the must be lowered e.g. tricyclic ...
IND/IDE Power Point Presentation
... • The packaging of some drugs is very important to preserve its chemical composition. Some drugs are in blister packs, because they decompose when they come in contact with air, dark brown glass bottle if photosensitive • The IUD was produced and marketed in an insertion kit which was removed and be ...
... • The packaging of some drugs is very important to preserve its chemical composition. Some drugs are in blister packs, because they decompose when they come in contact with air, dark brown glass bottle if photosensitive • The IUD was produced and marketed in an insertion kit which was removed and be ...
Lec.7-311-1
... • Strategies designed to target drugs to particular cells or tissues are likely to lead to safer drugs with fewer side effects. • Drugs can be linked to amino acids or nucleic acid bases to target them against fast-growing and rapidly divided cells. • Drugs can be targeted to the GIT by making them ...
... • Strategies designed to target drugs to particular cells or tissues are likely to lead to safer drugs with fewer side effects. • Drugs can be linked to amino acids or nucleic acid bases to target them against fast-growing and rapidly divided cells. • Drugs can be targeted to the GIT by making them ...
Unit 13 - Drug Abuse
... a) Define a drug as any externally administered substance that modifies or affects chemical reactions in the body; b) describe the medicinal use of antibiotics for the treatment of bacterial infection; c) describe the effects of the abuse of heroin: a powerful depressant, problems of addition, sever ...
... a) Define a drug as any externally administered substance that modifies or affects chemical reactions in the body; b) describe the medicinal use of antibiotics for the treatment of bacterial infection; c) describe the effects of the abuse of heroin: a powerful depressant, problems of addition, sever ...
HOW TO DISPOSE
... 2. Mix drugs with an undesirable substance, such as cat litter or used coffee grounds. 3. Put the mixture into a disposable container with a lid, such as an empty margarine tub, or into a sealable bag. 4. Conceal or remove any personal information, including Rx number, on the empty containers by cov ...
... 2. Mix drugs with an undesirable substance, such as cat litter or used coffee grounds. 3. Put the mixture into a disposable container with a lid, such as an empty margarine tub, or into a sealable bag. 4. Conceal or remove any personal information, including Rx number, on the empty containers by cov ...
B.C. PharmaCare Drug Information Sheet for drug generic name
... • advice from a national group called the Common Drug Review (CDR) • what the drug costs and whether it is a good value for the people of B.C. • ethical considerations involved with covering or not covering the drug • input from physicians, patients, caregivers, patient groups and drug submission sp ...
... • advice from a national group called the Common Drug Review (CDR) • what the drug costs and whether it is a good value for the people of B.C. • ethical considerations involved with covering or not covering the drug • input from physicians, patients, caregivers, patient groups and drug submission sp ...
Building a better drug
... Her aggressive tone serves a noble goal, however. The compounds she focuses on have the potential to destroy cancer or infectious bacteria or parasites—if only they could cross the cell membrane. To breach that obstacle, Meyers has designed something called a prodrug. In prodrug design, scientists s ...
... Her aggressive tone serves a noble goal, however. The compounds she focuses on have the potential to destroy cancer or infectious bacteria or parasites—if only they could cross the cell membrane. To breach that obstacle, Meyers has designed something called a prodrug. In prodrug design, scientists s ...
3-Chemical evaluation
... It involves detailed examination of the drug and it can be used to identify the organized drugs by their known histological characters. It is mostly used for qualitative evaluation of organized crude drugs in entire and powder forms with help of microscope. ...
... It involves detailed examination of the drug and it can be used to identify the organized drugs by their known histological characters. It is mostly used for qualitative evaluation of organized crude drugs in entire and powder forms with help of microscope. ...
3-Chemical evaluation
... It involves detailed examination of the drug and it can be used to identify the organized drugs by their known histological characters. It is mostly used for qualitative evaluation of organized crude drugs in entire and powder forms with help of microscope. ...
... It involves detailed examination of the drug and it can be used to identify the organized drugs by their known histological characters. It is mostly used for qualitative evaluation of organized crude drugs in entire and powder forms with help of microscope. ...
Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics
... ⑤Usually drug in combination is the best way to prevent from side effects. ...
... ⑤Usually drug in combination is the best way to prevent from side effects. ...
A public perspective on disinvestment in cancer drug funding
... DONNA: I wouldn’t switch. [---] I can't agree with Drug A because the quality of life has gone down. JODY: If we can get it for say half the price, [---] then we have $750,000 to spend on another drug or to spend on more drugs to help more people. That's the trade-off I see. FRED: Three points out o ...
... DONNA: I wouldn’t switch. [---] I can't agree with Drug A because the quality of life has gone down. JODY: If we can get it for say half the price, [---] then we have $750,000 to spend on another drug or to spend on more drugs to help more people. That's the trade-off I see. FRED: Three points out o ...
Use of melanotan I and II in the general population
... of developing the metabolite bremelanotide (formerly known as PT-141).11 During clinical trials of bremelanotide, the drug was found to induce hypertension in some people, which led to this work being discontinued. It is now being developed as a treatment for haemorrhagic shock.11 Most users inject ...
... of developing the metabolite bremelanotide (formerly known as PT-141).11 During clinical trials of bremelanotide, the drug was found to induce hypertension in some people, which led to this work being discontinued. It is now being developed as a treatment for haemorrhagic shock.11 Most users inject ...
a) - WordPress.com
... Tour the pharmacy department and all other areas in the hospital where pharmacists are located Tour the main areas of the hospital, noting where any drug distribution system areas are located If possible, tour other regional hospitals to observe different drug distribution systems Complete the gener ...
... Tour the pharmacy department and all other areas in the hospital where pharmacists are located Tour the main areas of the hospital, noting where any drug distribution system areas are located If possible, tour other regional hospitals to observe different drug distribution systems Complete the gener ...
BIOM 255: Molecular basis of drug action and disease therapy
... • Patients and health providers (e.g., physicians and pharmacists) are partners that seek to optimize drug prescription/dispensing/administration and thereby maximize efficacy and minimize toxicity, thus increasing the “therapeutic window” (between beneficial and toxic effects). • Adherence (complia ...
... • Patients and health providers (e.g., physicians and pharmacists) are partners that seek to optimize drug prescription/dispensing/administration and thereby maximize efficacy and minimize toxicity, thus increasing the “therapeutic window” (between beneficial and toxic effects). • Adherence (complia ...
PHYSICo chemicaL PROPERTIES
... STERIC FEATURES OF DRUGS The drug most possess a high degree of structural specificity or stereo selectivity. Many drugs show stereo selectivity because mostly reeptor binds are optically active biological macromolecules such as protein, polynuclootide or glycolipds. For e.g. Diethyl stilbosterol ...
... STERIC FEATURES OF DRUGS The drug most possess a high degree of structural specificity or stereo selectivity. Many drugs show stereo selectivity because mostly reeptor binds are optically active biological macromolecules such as protein, polynuclootide or glycolipds. For e.g. Diethyl stilbosterol ...
Drug discovery
In the fields of medicine, biotechnology and pharmacology, drug discovery is the process by which new candidate medications are discovered. Historically, drugs were discovered through identifying the active ingredient from traditional remedies or by serendipitous discovery. Later chemical libraries of synthetic small molecules, natural products or extracts were screened in intact cells or whole organisms to identify substances that have a desirable therapeutic effect in a process known as classical pharmacology. Since sequencing of the human genome which allowed rapid cloning and synthesis of large quantities of purified proteins, it has become common practice to use high throughput screening of large compounds libraries against isolated biological targets which are hypothesized to be disease modifying in a process known as reverse pharmacology. Hits from these screens are then tested in cells and then in animals for efficacy.Modern drug discovery involves the identification of screening hits, medicinal chemistry and optimization of those hits to increase the affinity, selectivity (to reduce the potential of side effects), efficacy/potency, metabolic stability (to increase the half-life), and oral bioavailability. Once a compound that fulfills all of these requirements has been identified, it will begin the process of drug development prior to clinical trials. One or more of these steps may, but not necessarily, involve computer-aided drug design. Modern drug discovery is thus usually a capital-intensive process that involves large investments by pharmaceutical industry corporations as well as national governments (who provide grants and loan guarantees). Despite advances in technology and understanding of biological systems, drug discovery is still a lengthy, ""expensive, difficult, and inefficient process"" with low rate of new therapeutic discovery. In 2010, the research and development cost of each new molecular entity (NME) was approximately US$1.8 billion. Drug discovery is done by pharmaceutical companies, with research assistance from universities. The ""final product"" of drug discovery is a patent on the potential drug. The drug requires very expensive Phase I, II and III clinical trials, and most of them fail. Small companies have a critical role, often then selling the rights to larger companies that have the resources to run the clinical trials.Discovering drugs that may be a commercial success, or a public health success, involves a complex interaction between investors, industry, academia, patent laws, regulatory exclusivity, marketing and the need to balance secrecy with communication. Meanwhile, for disorders whose rarity means that no large commercial success or public health effect can be expected, the orphan drug funding process ensures that people who experience those disorders can have some hope of pharmacotherapeutic advances.