see link
... Pilot experiments are performed at the moment; this project depends on the outcome. MHV infects mouse cells in cell culture by using mCeacam1a as receptor. It remains unclear how the receptor mediates virus uptake by endocytosis and virus-cell fusion. Intracellular signaling of the receptor does not ...
... Pilot experiments are performed at the moment; this project depends on the outcome. MHV infects mouse cells in cell culture by using mCeacam1a as receptor. It remains unclear how the receptor mediates virus uptake by endocytosis and virus-cell fusion. Intracellular signaling of the receptor does not ...
licensed under a . Your use of this Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike License
... Number of reported mumps cases linked to multi-state outbreak, January 1 to May 2, 2006 N = 2,597 † 3 cases related to the outbreak § 12 cases related to the outbreak ...
... Number of reported mumps cases linked to multi-state outbreak, January 1 to May 2, 2006 N = 2,597 † 3 cases related to the outbreak § 12 cases related to the outbreak ...
donor selection
... • Autologous • Apheresis DONOR SELECTION This is the first and most important step in the safety of the blood supply! GUIDELINES Protect the health of the donor No harm to the donor Protect the health of the recipient Minimizing risk of transfusion transmitted infections and other adverse risk f ...
... • Autologous • Apheresis DONOR SELECTION This is the first and most important step in the safety of the blood supply! GUIDELINES Protect the health of the donor No harm to the donor Protect the health of the recipient Minimizing risk of transfusion transmitted infections and other adverse risk f ...
Infectious Diseases in Aging Populations: Unifying Statistical and Dynamical Approaches
... Demography has considerable implications for infectious disease transmission and risk across populations. For example, it is well known that high birth rates lead to annual patterns of incidence due to the numbers of individuals who are susceptible to disease being constantly replenished (e.g., meas ...
... Demography has considerable implications for infectious disease transmission and risk across populations. For example, it is well known that high birth rates lead to annual patterns of incidence due to the numbers of individuals who are susceptible to disease being constantly replenished (e.g., meas ...
19th-Century Medicine
... remains the cornerstone of modern medical science. In France, physiologist Claude Bernard performed important research on the pancreas, liver, and nervous system. His scientific studies, which emphasized that an experiment should be objective and prove or disprove a hypothesis, were the basis for th ...
... remains the cornerstone of modern medical science. In France, physiologist Claude Bernard performed important research on the pancreas, liver, and nervous system. His scientific studies, which emphasized that an experiment should be objective and prove or disprove a hypothesis, were the basis for th ...
07.08 Health Protection
... 7.8 Health Protection Infections continue to be a significant cause of ill health. In 2010 in England, infectious diseases accounted for 7% of all deaths, 4% of all potential life years lost (to age 75) and were also the primary cause of admission for 8% of all hospital bed days. They are responsibl ...
... 7.8 Health Protection Infections continue to be a significant cause of ill health. In 2010 in England, infectious diseases accounted for 7% of all deaths, 4% of all potential life years lost (to age 75) and were also the primary cause of admission for 8% of all hospital bed days. They are responsibl ...
Viruses
... • Lytic pathway – a type of viral reproduction where the virus lyses, or breaks open the host cell membrane in order to release the newly replicated viruses • New viruses leave host cell to infect other nearby cells • Lysis – viruses burst the cell membrane as they leave • Results in death of host c ...
... • Lytic pathway – a type of viral reproduction where the virus lyses, or breaks open the host cell membrane in order to release the newly replicated viruses • New viruses leave host cell to infect other nearby cells • Lysis – viruses burst the cell membrane as they leave • Results in death of host c ...
What is Barmah Forest Virus?
... and pain, dizziness and light-headedness—any of these may be present, with or without a prominent rash. Joint pain and fatigue may last up to 6 months. The condition is very similar to Ross River Virus, although generally of shorter duration. Who can get Barmah Forest Virus? The infection is unique ...
... and pain, dizziness and light-headedness—any of these may be present, with or without a prominent rash. Joint pain and fatigue may last up to 6 months. The condition is very similar to Ross River Virus, although generally of shorter duration. Who can get Barmah Forest Virus? The infection is unique ...
1 The Role of Factory Farming in the Cause and Spread of Swine
... The Role of Factory Farming in the Cause and Spread of Swine Influenza ...
... The Role of Factory Farming in the Cause and Spread of Swine Influenza ...
THE GLOBAL STRATEGY ON DIET, PHYSICAL ACTIVITY AND HEALTH FACTS:
... diseases, account for 59% of the 56.5 million deaths annually and 45.9% of the global burden of disease. Half of these (17 million annually) are CVD, the majority heart disease and stroke. Five of the top 10 selected global disease burden risk factors identified by World Health Report 2002: reducing ...
... diseases, account for 59% of the 56.5 million deaths annually and 45.9% of the global burden of disease. Half of these (17 million annually) are CVD, the majority heart disease and stroke. Five of the top 10 selected global disease burden risk factors identified by World Health Report 2002: reducing ...
DISEASE IN HUMAN EVOLUTION: THE RE
... source of a serious epidemic (affecting a large number of people at the same time) disease in another group. Cross-continental trade and travel resulted in intense epidemics (McNeill 1976). The Black Death, resulting from a new pathogen, took its toll in Europe in the 1300s; this epidemic eliminated ...
... source of a serious epidemic (affecting a large number of people at the same time) disease in another group. Cross-continental trade and travel resulted in intense epidemics (McNeill 1976). The Black Death, resulting from a new pathogen, took its toll in Europe in the 1300s; this epidemic eliminated ...
Adenovirus Type 21–Associated Acute Flaccid Paralysis during an
... and sensory nerves, with denervation. These findings suggest that Ad21 might cause AFP by anterior horn cell damage or neuropathy of the brachial or lumbosacral plexus. The occurrence of these unusual adenovirus infections during an outbreak of EV71-associated HFMD suggests that an interaction betwe ...
... and sensory nerves, with denervation. These findings suggest that Ad21 might cause AFP by anterior horn cell damage or neuropathy of the brachial or lumbosacral plexus. The occurrence of these unusual adenovirus infections during an outbreak of EV71-associated HFMD suggests that an interaction betwe ...
Ebola virus: the biology, epidemiology, and sociology
... chances of survival if done EARLY • Immunity: antibodies post-survival last ~10 years at least • Unknown if re-infection can occur with same or different strain ...
... chances of survival if done EARLY • Immunity: antibodies post-survival last ~10 years at least • Unknown if re-infection can occur with same or different strain ...
Chapter 12 - Cloudfront.net
... such as bacteria, fungi, protozoans, and viruses…even some larger creatures like parasitic worms… ...
... such as bacteria, fungi, protozoans, and viruses…even some larger creatures like parasitic worms… ...
Sexually Transmitted Diseases (STDs), formerly known as venereal
... age of 12 is infected with HSV type 2, and the vast majority of those infected—about 90 percent—do not know they have the disease. Blood tests can detect HSV infection, even if a person has no symptoms. The symptoms of HSV can be treated with antiviral drugs, such as acyclovir, but HSV cannot be era ...
... age of 12 is infected with HSV type 2, and the vast majority of those infected—about 90 percent—do not know they have the disease. Blood tests can detect HSV infection, even if a person has no symptoms. The symptoms of HSV can be treated with antiviral drugs, such as acyclovir, but HSV cannot be era ...
Health Care Healthcare in Africa How can African countries
... In 2000, AIDS took the lives of three million people worldwide. Of these, 2.4 million lived in sub-Saharan Africa. In Swaziland, three of every four deaths were attributed to AIDS. The AIDS epidemic in Swaziland has caused life expectancy there to drop from 58 years to 39 years. In 2000, nearly 26 m ...
... In 2000, AIDS took the lives of three million people worldwide. Of these, 2.4 million lived in sub-Saharan Africa. In Swaziland, three of every four deaths were attributed to AIDS. The AIDS epidemic in Swaziland has caused life expectancy there to drop from 58 years to 39 years. In 2000, nearly 26 m ...
The classical definition of Greek origin Epi –upon Domos – the
... Number of existing cases of disease or other condition o Proportion of individuals in a population with disease or condition at a specific point of time Diabetes prevalence, smoking prevalence o Provides estimate of the probability or risk that one will be affected at a point in time o Provides an ...
... Number of existing cases of disease or other condition o Proportion of individuals in a population with disease or condition at a specific point of time Diabetes prevalence, smoking prevalence o Provides estimate of the probability or risk that one will be affected at a point in time o Provides an ...
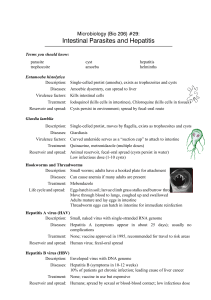
Terms you should know: parasite trophozoite cyst amoeba hepatitis
... Description: Small, naked virus with single-stranded RNA genome Diseases: Hepatitis A (symptoms appear in about 25 days); usually no complications Treatment: None; vaccine approved in 1995, recommended for travel to risk areas Reservoir and spread: Human virus; fecal-oral spread Hepatitis B virus (H ...
... Description: Small, naked virus with single-stranded RNA genome Diseases: Hepatitis A (symptoms appear in about 25 days); usually no complications Treatment: None; vaccine approved in 1995, recommended for travel to risk areas Reservoir and spread: Human virus; fecal-oral spread Hepatitis B virus (H ...
Bovine zoonoses
... ▫ Avoid consuming unpasteurized milk or untreated water ▫ When working with animals, particularly animals with diarrheal or reproductive illness, wear gloves and wash hands frequently ...
... ▫ Avoid consuming unpasteurized milk or untreated water ▫ When working with animals, particularly animals with diarrheal or reproductive illness, wear gloves and wash hands frequently ...
Exam 3 Study Guide PUBHLTH 350 Fall 2015 Logistics: The exam
... Define incubation period, latent period What are the differences among infectivity, pathogenicity, and virulence? What are the category A bioterrorism agents? Distinguish between endemic, epidemic, and pandemic diseases. What are the different infectious disease transmission modalities? What are som ...
... Define incubation period, latent period What are the differences among infectivity, pathogenicity, and virulence? What are the category A bioterrorism agents? Distinguish between endemic, epidemic, and pandemic diseases. What are the different infectious disease transmission modalities? What are som ...
Communicable disease control in The Netherlands
... 3. Epidemiological measures (counter transmission between groups of human hosts): staying at home, closing schools, cancelling large gatherings of humans, evacuation, cohort nursing 4. Source and contact tracing among hosts, followed by isolation of infectious hosts and quarantining of contacts of i ...
... 3. Epidemiological measures (counter transmission between groups of human hosts): staying at home, closing schools, cancelling large gatherings of humans, evacuation, cohort nursing 4. Source and contact tracing among hosts, followed by isolation of infectious hosts and quarantining of contacts of i ...
MAFF CLASSIFICATION OF ANIMAL PATHOGENS (Viruses only)
... stomatitis virus are being handled as part of a plaque assay system for human ...
... stomatitis virus are being handled as part of a plaque assay system for human ...
Disease - Health Science
... Notifiable Diseases in the United States Notifiable diseases are those of considerable public health importance because of their seriousness Such diseases Cause serious morbidity or death Have the potential to spread Can be controlled with appropriate intervention ...
... Notifiable Diseases in the United States Notifiable diseases are those of considerable public health importance because of their seriousness Such diseases Cause serious morbidity or death Have the potential to spread Can be controlled with appropriate intervention ...
Chapter 13 - eacfaculty.org
... frequency in a particular location over time • Sporadic – occasional cases at irregular intervals • Epidemic – increase beyond what might be expected in a given population • Pandemic – spread of epidemics across continents ...
... frequency in a particular location over time • Sporadic – occasional cases at irregular intervals • Epidemic – increase beyond what might be expected in a given population • Pandemic – spread of epidemics across continents ...
Pandemic

A pandemic (from Greek πᾶν pan ""all"" and δῆμος demos ""people"") is an epidemic of infectious disease that has spread through human populations across a large region; for instance multiple continents, or even worldwide. A widespread endemic disease that is stable in terms of how many people are getting sick from it is not a pandemic. Further, flu pandemics generally exclude recurrences of seasonal flu. Throughout history there have been a number of pandemics, such as smallpox and tuberculosis. More recent pandemics include the HIV pandemic as well as the 1918 and 2009 H1N1 pandemics. The Black Death was a devastating pandemic, killing over 75 million people.