title - JustAnswer
... Consider colloids for pets with low levels of protein in the blood (known as “hypoproteinemia”) that need fluid therapy; “colloids” are fluids that contain larger molecules that stay within the circulating blood to help maintain circulating blood volume, examples are dextran and hetastarch ...
... Consider colloids for pets with low levels of protein in the blood (known as “hypoproteinemia”) that need fluid therapy; “colloids” are fluids that contain larger molecules that stay within the circulating blood to help maintain circulating blood volume, examples are dextran and hetastarch ...
1: Minimal change nephropathy.
... 1. Good control of blood pressure 2. Treatment of urinary tract infection 3. If chronic renal failure developed we start treatment of it Screening and genetic counseling ...
... 1. Good control of blood pressure 2. Treatment of urinary tract infection 3. If chronic renal failure developed we start treatment of it Screening and genetic counseling ...
Our Patient`s, their care and wellbeing are our first consideration
... wash their hands thoroughly both before and after visiting you. The nursing staff will advise if anything further is necessary. Friends or relatives who are unwell should NOT visit. If you have any concerns at all about someone visiting, please discuss this with a doctor or nurse. If your visitors g ...
... wash their hands thoroughly both before and after visiting you. The nursing staff will advise if anything further is necessary. Friends or relatives who are unwell should NOT visit. If you have any concerns at all about someone visiting, please discuss this with a doctor or nurse. If your visitors g ...
Document
... practitioners for acute illness in young children and a third of consultations in older children Respiratory illness leads to 20-35 % of acute paediatric admissions to hospital, some of which are lifethreatening Asthma is the most common chronic illness of childhood in the world ...
... practitioners for acute illness in young children and a third of consultations in older children Respiratory illness leads to 20-35 % of acute paediatric admissions to hospital, some of which are lifethreatening Asthma is the most common chronic illness of childhood in the world ...
Miscellaneous bacterial pathogens
... – Halotolerant to halophilic, grow in estuarine and marine environments – V. cholerae: cause of cholera • Toxin-mediated severe diarrhea • Salt, fluid leave intestinal cells, patient dies of dehydration. • Oral rehydration therapy (ORT): water, salts, and glucose, now saving lives. • Causes pandemic ...
... – Halotolerant to halophilic, grow in estuarine and marine environments – V. cholerae: cause of cholera • Toxin-mediated severe diarrhea • Salt, fluid leave intestinal cells, patient dies of dehydration. • Oral rehydration therapy (ORT): water, salts, and glucose, now saving lives. • Causes pandemic ...
Digestion Disorders
... body temperature or the pH of blood) in higher animals under fluctuating environmental conditions. How can homeostasis be disrupted in the human digestive system? ...
... body temperature or the pH of blood) in higher animals under fluctuating environmental conditions. How can homeostasis be disrupted in the human digestive system? ...
Bi 11 -` Most wanted` virus poster
... Hide out of the culprit (where it is most likely to be found) Most common injury done to victim Is it considered armed and dangerous? Rate the degree of damage caused. (The higher the degree of damage, the higher the reward) Most effective weapons against the germ any other identifying characteristi ...
... Hide out of the culprit (where it is most likely to be found) Most common injury done to victim Is it considered armed and dangerous? Rate the degree of damage caused. (The higher the degree of damage, the higher the reward) Most effective weapons against the germ any other identifying characteristi ...
Chapter Outline
... i. Enterotoxin ii. Heat-labile exotoxin called shiga toxin c. Transmission and epidemiology i. Oral route ii. Person-to-person contact d. Prevention and treatment 3. E. coli O157:H7 (EHEC) a. Enterohemorrhagic E. coli, or EHEC b. Signs and symptoms i.Mild gastroenteritis with fever ii. Hemolytic ure ...
... i. Enterotoxin ii. Heat-labile exotoxin called shiga toxin c. Transmission and epidemiology i. Oral route ii. Person-to-person contact d. Prevention and treatment 3. E. coli O157:H7 (EHEC) a. Enterohemorrhagic E. coli, or EHEC b. Signs and symptoms i.Mild gastroenteritis with fever ii. Hemolytic ure ...
Health Protection in Merton
... • All those aged 6 months and over in clinical risk group •All immuno-compromised individuals •Those living amongst a residential care homes or other long stay care facilities • Those in receipt of carers allowance and those who are the main carer of the elderly or disabled person SWL Health Protect ...
... • All those aged 6 months and over in clinical risk group •All immuno-compromised individuals •Those living amongst a residential care homes or other long stay care facilities • Those in receipt of carers allowance and those who are the main carer of the elderly or disabled person SWL Health Protect ...
Vaccinations
... and eyes, loss of appetite and diarrhoea, may experience fits. An airborne virus that puts younger dogs at greatest risk. Infectious Canine Hepatitis: Vomiting, pale gums, very high temperature, loss of appetite, abdominal pain, diarrhoea. Later on jaundice. An airborne virus that affects the live ...
... and eyes, loss of appetite and diarrhoea, may experience fits. An airborne virus that puts younger dogs at greatest risk. Infectious Canine Hepatitis: Vomiting, pale gums, very high temperature, loss of appetite, abdominal pain, diarrhoea. Later on jaundice. An airborne virus that affects the live ...
Criteria for Parents to Determine Whether to Keep a Child Home
... WHEN TO KEEP A CHILD HOME WITH ILLNESS DURING COLD AND FLU SEASON Sometimes it can be difficult for a parent to decide whether to send children to school when they wake up with early symptoms of an illness or complaints that they do not feel well. In general, during cold and flu season, unless your ...
... WHEN TO KEEP A CHILD HOME WITH ILLNESS DURING COLD AND FLU SEASON Sometimes it can be difficult for a parent to decide whether to send children to school when they wake up with early symptoms of an illness or complaints that they do not feel well. In general, during cold and flu season, unless your ...
Travel and Tropical Medicine
... • children with severe anemia usually have acidosis (deep Kussmaul breathing); • malarial anemia kills as many children as cerebral malaria (mortality = 5-15%; mortality from acidosis = 24%; mortality from severe anemia + acidosis = 35%) • also common in pregnant women ...
... • children with severe anemia usually have acidosis (deep Kussmaul breathing); • malarial anemia kills as many children as cerebral malaria (mortality = 5-15%; mortality from acidosis = 24%; mortality from severe anemia + acidosis = 35%) • also common in pregnant women ...
3. non invasive bacterial enteritis
... - Fluid and electrolyte replacement in early stage (life saving). - Antibiotics: Tetracycline or co-trimoxazole. ...
... - Fluid and electrolyte replacement in early stage (life saving). - Antibiotics: Tetracycline or co-trimoxazole. ...
Covenant Children`s Center Health Policies
... COLDS: Children should stay home as long as they have sneezing, coughing, eye watering, profuse nasal dripping and irritability. FEVER: Following any infection associated with fever over 100 F oral and 100.5 F rectal, a child must remain at home until s/he has been without fever for at least 24 ho ...
... COLDS: Children should stay home as long as they have sneezing, coughing, eye watering, profuse nasal dripping and irritability. FEVER: Following any infection associated with fever over 100 F oral and 100.5 F rectal, a child must remain at home until s/he has been without fever for at least 24 ho ...
Vibrio cholerae
... water and electrolytes causing the diarrhea, loss of electrolytes, and dehydration that are characteristic of cholera. ...
... water and electrolytes causing the diarrhea, loss of electrolytes, and dehydration that are characteristic of cholera. ...
03 Vibrio_Cholerae
... water and electrolytes causing the diarrhea, loss of electrolytes, and dehydration that are characteristic of cholera. ...
... water and electrolytes causing the diarrhea, loss of electrolytes, and dehydration that are characteristic of cholera. ...
U-Microbiology-Safety
... – chemical causes can include ciguatoxin and scombrotoxin, both from fish as well as any environmental toxins – onset time may be dose related ...
... – chemical causes can include ciguatoxin and scombrotoxin, both from fish as well as any environmental toxins – onset time may be dose related ...
Pneumonia or Bronchitis? - Rockcastle Regional Hospital
... Not very sick; children are more likely to wheeze and are often “happy wheezers” who have no difficulty breathing ...
... Not very sick; children are more likely to wheeze and are often “happy wheezers” who have no difficulty breathing ...
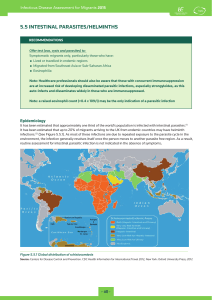
5.5 INTESTINAL PARASITES/HELMINTHS
... = Migrated from Southeast Asia or Sub-Saharan Africa = Eosinophilia ...
... = Migrated from Southeast Asia or Sub-Saharan Africa = Eosinophilia ...
Bovine Respiratory Disease Complex
... disease due to interactions between viruses, bacteria and physical, psychologic, physiologic, and environmental stress factors. In uncomplicated viral infections, the signs are subclinical, and in severe cases, a bacterial bronchopneumonia and/or fibrinous pneumonia are always present. Clinical Symp ...
... disease due to interactions between viruses, bacteria and physical, psychologic, physiologic, and environmental stress factors. In uncomplicated viral infections, the signs are subclinical, and in severe cases, a bacterial bronchopneumonia and/or fibrinous pneumonia are always present. Clinical Symp ...
Bacterial Diseases
... Tularemia/Rabbit Fever is a zoonotic disease caused by the bacterium Francisella tularensis. What are the characteristics of this parasite? How can it enter the body? What are the signs associated with this disease? Proliferation can lead to sepsis. Streptomycin is the antibiotic of choice. ...
... Tularemia/Rabbit Fever is a zoonotic disease caused by the bacterium Francisella tularensis. What are the characteristics of this parasite? How can it enter the body? What are the signs associated with this disease? Proliferation can lead to sepsis. Streptomycin is the antibiotic of choice. ...
Gastroenteritis

Gastroenteritis or infectious diarrhea is a medical condition from inflammation (""-itis"") of the gastrointestinal tract that involves both the stomach (""gastro""-) and the small intestine (""entero""-). It causes some combination of diarrhea, vomiting, and abdominal pain and cramping. Dehydration may occur as a result. Gastroenteritis has been referred to as gastro, stomach bug, and stomach virus. Although unrelated to influenza, it has also been called stomach flu and gastric flu.Globally, most cases in children are caused by rotavirus. In adults, norovirus and Campylobacter are more common. Less common causes include other bacteria (or their toxins) and parasites. Transmission may occur due to consumption of improperly prepared foods or contaminated water or via close contact with individuals who are infectious. Prevention includes drinking clean water, hand washing with soap, and breast feeding babies instead of using formula. This applies particularly where sanitation and hygiene are lacking. The rotavirus vaccine is recommended for all children.The key treatment is enough fluids. For mild or moderate cases, this can typically be achieved via oral rehydration solution (a combination of water, salts, and sugar). In those who are breast fed, continued breast feeding is recommended. For more severe cases, intravenous fluids from a healthcare centre may be needed. Antibiotics are generally not recommended. Gastroenteritis primarily affects children and those in the developing world. It results in about three to five billion cases and causes 1.4 million deaths a year.