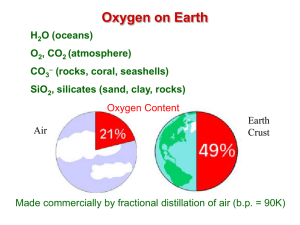
Chemistry Standard Course of Study -- Detailed - UNCG GK-12
... Periodic Table (nonmetals combined with nonmetals) or when EN < 1.7. Know that the diatomic elements have single, double, or triple bonds (For example: F2, O2, N2). Describe carbon bonds as either single, double ...
... Periodic Table (nonmetals combined with nonmetals) or when EN < 1.7. Know that the diatomic elements have single, double, or triple bonds (For example: F2, O2, N2). Describe carbon bonds as either single, double ...
Chapter 11 Chemical Reactions
... (aq) after the formula = dissolved in water, an aqueous solution: NaCl(aq) is a salt water solution used after a product indicates a gas has been produced: H2↑ used after a product indicates a solid has been produced: PbI2↓ ...
... (aq) after the formula = dissolved in water, an aqueous solution: NaCl(aq) is a salt water solution used after a product indicates a gas has been produced: H2↑ used after a product indicates a solid has been produced: PbI2↓ ...
Chapter 11 Chemical Reactions
... (aq) after the formula = dissolved in water, an aqueous solution: NaCl(aq) is a salt water solution used after a product indicates a gas has been produced: H2↑ used after a product indicates a solid has been produced: PbI2↓ ...
... (aq) after the formula = dissolved in water, an aqueous solution: NaCl(aq) is a salt water solution used after a product indicates a gas has been produced: H2↑ used after a product indicates a solid has been produced: PbI2↓ ...
Alcohols Oxidation by oxygen O2 in presence of
... examination of chemical properties and reactivity of cluster compounds of metal -oxygen named polyoxometalates. The reasons of this consideration are factors such as physical and chemical variation of these compounds, simple preparation, the ability of adjustment of acid power with opposite ion chan ...
... examination of chemical properties and reactivity of cluster compounds of metal -oxygen named polyoxometalates. The reasons of this consideration are factors such as physical and chemical variation of these compounds, simple preparation, the ability of adjustment of acid power with opposite ion chan ...
Chapter 2
... 1. When two elements form more than one compound with each other, the masses of one element in these compounds for a fixed mass of the other element are in ratios of small whole numbers. 2. Example. H and O combine to form two compounds: H2O and H2O2 Amount of Oxygen per gram of H in 1st compound Am ...
... 1. When two elements form more than one compound with each other, the masses of one element in these compounds for a fixed mass of the other element are in ratios of small whole numbers. 2. Example. H and O combine to form two compounds: H2O and H2O2 Amount of Oxygen per gram of H in 1st compound Am ...
Final Review Answers
... a) ammonia pyr./107°/P b) water bent/105°/P c) carbon dioxide linear/180°/NP d) carbon tetraiodide tetra/109.5°/NP 14)Differentiate between the three main types of intermolecular forces described in your text. Dipole - attraction between P molec.; Hydrogen - attraction between P molec. (H must be bo ...
... a) ammonia pyr./107°/P b) water bent/105°/P c) carbon dioxide linear/180°/NP d) carbon tetraiodide tetra/109.5°/NP 14)Differentiate between the three main types of intermolecular forces described in your text. Dipole - attraction between P molec.; Hydrogen - attraction between P molec. (H must be bo ...
pblock - Chemistry Courses
... 2nd period: Only s and p orbitals are possible with n = 2 Therefore, the maximum number of bonds is 4 (single and/or double bonds) Examples: CH4, NF4+, BH43rd (and higher periods): can use d-orbitals to make bonds E.g. ...
... 2nd period: Only s and p orbitals are possible with n = 2 Therefore, the maximum number of bonds is 4 (single and/or double bonds) Examples: CH4, NF4+, BH43rd (and higher periods): can use d-orbitals to make bonds E.g. ...
Chemistry of Cars unit_7_chemistry_of_cars
... rhodium to help reduce the NOx emissions. When an NO or NO2 molecule contacts the catalyst, the catalyst rips the nitrogen atom out of the molecule and holds on to it, freeing the oxygen in the form of O2. The nitrogen atoms bond with other nitrogen atoms that are also stuck to the catalyst, forming ...
... rhodium to help reduce the NOx emissions. When an NO or NO2 molecule contacts the catalyst, the catalyst rips the nitrogen atom out of the molecule and holds on to it, freeing the oxygen in the form of O2. The nitrogen atoms bond with other nitrogen atoms that are also stuck to the catalyst, forming ...
ch6 - ChemistryVCE
... In a metallic lattice, the positive ions are surrounded by delocalised electrons; in an ionic lattice, negative ions alternate with the positive ions. Agree. In a metallic lattice, each positive ion attracts the delocalised electrons in its region, and each delocalised electron is attracted to all n ...
... In a metallic lattice, the positive ions are surrounded by delocalised electrons; in an ionic lattice, negative ions alternate with the positive ions. Agree. In a metallic lattice, each positive ion attracts the delocalised electrons in its region, and each delocalised electron is attracted to all n ...
AP Chemistry Summer Assignment 2016
... fuels are carbon dioxide and water. 2C3H7OH + 9O2 6CO2 + 8H2O ...
... fuels are carbon dioxide and water. 2C3H7OH + 9O2 6CO2 + 8H2O ...
Camp 1 - Quynh Nguyen Official Website
... Energy is the capacity to do work or supply heat. A system can exchange its energy with its surrounding in two forms: heat and work. Heat is the transfer of energy as a result of a difference in temperature. Work is done when an object is moved against an opposing force. Heat and work are equivalent ...
... Energy is the capacity to do work or supply heat. A system can exchange its energy with its surrounding in two forms: heat and work. Heat is the transfer of energy as a result of a difference in temperature. Work is done when an object is moved against an opposing force. Heat and work are equivalent ...
AP Chemistry Unit 1 Essential Questions Screencast 1
... Screencast 1-1 Introduction to the Periodic Table 1. What is an element? 2. How are the symbols for the elements determined? 3. How is the order of the elements determined on the modern periodic table? 4. What are the main regions of the periodic table? 5. What are the special named groups and where ...
... Screencast 1-1 Introduction to the Periodic Table 1. What is an element? 2. How are the symbols for the elements determined? 3. How is the order of the elements determined on the modern periodic table? 4. What are the main regions of the periodic table? 5. What are the special named groups and where ...
5073 Chemistry (SPA)
... 440 BC, the Greek Leucippus and his pupil Democritus coined the term atomos to describe the smallest particle of matter. It translates to mean something that is indivisible. In the eighteenth century, chemist, John Dalton, revived the term when he suggested that each element was made up of unique at ...
... 440 BC, the Greek Leucippus and his pupil Democritus coined the term atomos to describe the smallest particle of matter. It translates to mean something that is indivisible. In the eighteenth century, chemist, John Dalton, revived the term when he suggested that each element was made up of unique at ...
Chapter #2-Newest CPub
... • Law of Mass Conservation: The total mass of substances does not change during a chemical reaction (Lavoisier). • Law of Definite (or Constant) Composition: No matter what its source, a particular chemical compound is composed of the same elements in the same parts (fractions) by mass (Proust). • T ...
... • Law of Mass Conservation: The total mass of substances does not change during a chemical reaction (Lavoisier). • Law of Definite (or Constant) Composition: No matter what its source, a particular chemical compound is composed of the same elements in the same parts (fractions) by mass (Proust). • T ...
Chemistry - College Catalog
... courses in this sequence meet the general education requirement in the physical sciences. Not recommended for students majoring in Chemistry or Biological Chemistry. This three-quarter sequence is a systematic introduction to chemistry for beginning students in chemistry or for those whose exposure ...
... courses in this sequence meet the general education requirement in the physical sciences. Not recommended for students majoring in Chemistry or Biological Chemistry. This three-quarter sequence is a systematic introduction to chemistry for beginning students in chemistry or for those whose exposure ...
Test - Chemical Bonding- Practice Test
... ____ 37. type of compound composed only of non-metals that are covalently bonded together ____ 38. atoms react so as to acquire the stable electron structure of a noble gas with a full valence shell ____ 39. this type of bond is found in a molecule of water (H2O) ____ 40. a depiction (drawing) of va ...
... ____ 37. type of compound composed only of non-metals that are covalently bonded together ____ 38. atoms react so as to acquire the stable electron structure of a noble gas with a full valence shell ____ 39. this type of bond is found in a molecule of water (H2O) ____ 40. a depiction (drawing) of va ...
quiz questions chapters 1
... In which of the following species does the central atom violate the octet rule? A) CH4 B) SF4 C) PCl4+ D) CCl3+ E) NH3 Which statement is false concerning ionic bonds and compounds? A) Ionic bonds are a result of electrostatic forces. B) Ionic bonds usually occur between elements with high and low e ...
... In which of the following species does the central atom violate the octet rule? A) CH4 B) SF4 C) PCl4+ D) CCl3+ E) NH3 Which statement is false concerning ionic bonds and compounds? A) Ionic bonds are a result of electrostatic forces. B) Ionic bonds usually occur between elements with high and low e ...
Inorganic chemistry

Inorganic chemistry deals with the synthesis and behavior of inorganic and organometallic compounds. This field covers all chemical compounds except the myriad organic compounds (carbon based compounds, usually containing C-H bonds), which are the subjects of organic chemistry. The distinction between the two disciplines is far from absolute, and there is much overlap, most importantly in the sub-discipline of organometallic chemistry. It has applications in every aspect of the chemical industry–including catalysis, materials science, pigments, surfactants, coatings, medicine, fuel, and agriculture.